Abstract
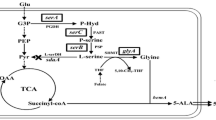
Metabolic engineering is a powerful tool which has been widely used for producing valuable products. For improving l-phenylalanine (l-Phe) accumulation in Corynebacterium glutamicum, we have investigated the target genes involved in the biosynthetic pathways. The genes involved in the biosynthesis of l-Phe were found to be strictly regulated genes by feedback inhibition. As a result, overexpression of the native wild-type genes aroF, aroG or pheA resulted in a slight increase of l-Phe. In contrast, overexpression of aroF wt or pheA fbr from E. coli significantly increased l-Phe production. Co-overexpression of aroF wt and pheA fbr improved the titer of l-Phe to 4.46 ± 0.06 g l−1. To further analyze the target enzymes in the aromatic amino acid synthesis pathway between C. glutamicum and E. coli, the wild-type gene aroH from E. coli was overexpressed and evaluated in C. glutamicum. As predicted, upregulation of the wild-type gene aroH resulted in a remarkable increase of l-Phe production. Co-overexpression of the mutated pheA fbr and the wild-type gene aroH resulted in the production of l-Phe up to 4.64 ± 0.09 g l−1. Based on these results we conclude that the wild-type gene aroH from E. coli is an appropriate target gene for pathway engineering in C. glutamicum for the production of aromatic amino acids.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baez-Viveros JL, Osuna J, Hernandez Chavez G, Soberon X, Bolivar F, Gosset G (2004) Metabolic engineering and protein directed evolution increase the yield of l-phenylalanine synthesized from glucose in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 87:516–524
Becker J, Wittmann C (2012) Bio-based production of chemicals, materials and fuels–Corynebacterium glutamicum as versatile cell factory. Curr Opin Microbiol 23:631–640
Date M, Itaya H, Matsui H, Kikuchi Y (2006) Secretion of human epidermal growth factor by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Lett Appl Microbiol 42:66–70
Date M, Yokoyama K, Umezawa Y, Matsui H, Kikuchi Y (2003) Production of native-type Streptoverticillium mobaraense transglutaminase in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3011–3014
Dueber JE, Wu GC, Malmirchegini GR, Moon TS, Petzold CJ, Ullal AV, Prather KL, Keasling JD (2009) Synthetic protein scaffolds provide modular control over metabolic flux. Nat Biotechnol 27:753–759
Eggeling L, Bott M (2005) Handbook of Corynebacterium glutamicum. CRC Press, Baton Rouge
Gelfand DH, Steinberg RA (1977) Escherichia coli mutants deficient in the aspartate and aromatic amino acid aminotransferases. J Bacteriol 130:429–440
Gerigk MR, Maass D, Kreutzer A, Sprenger G, Bongaerts J, Wubbolts M, Takors R (2002) Enhanced pilot-scale fed-batch l-phenylalanine production with recombinant Escherichia coli by fully integrated reactive extraction. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 25:43–52
Gopinath V, Murali A, Dhar KS, Nampoothiri KM (2012) Corynebacterium glutamicum as a potent biocatalyst for the bioconversion of pentose sugars to value-added products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:95–106
Gu P, Yang F, Kang J, Wang Q, Qi Q (2012) One-step of tryptophan attenuator inactivation and promoter swapping to improve the production of l-tryptophan in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 11:30–38
Henderson JW, Ricker RD, Bidlingmeyer BA et al (2000) Rapid, accurate, sensitive, and reproducible HPLC analysis of amino acids. USA (Agilent App Note 5980–1193E). Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara
Hsu SK, Lin LL, Lo HH, Hsu WH (2004) Mutational analysis of feedback inhibition and catalytic sites of prephenate dehydratase from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Arch Microbiol 181:237–244
Hu C, Jiang P, Xu J, Wu J, Huang W (2003) Mutation analysis of the feedback inhibition site of phenylalanine-sensitive 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase of Escherichia coli. J Basic Microbiol 43:399–406
Hudson GS, Davidson BE (1984) Nucleotide sequence and transcription of the phenylalanine and tyrosine operons of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol 180:1023–1051
Ikeda M (2006) Towards bacterial strains overproducing l-tryptophan and other aromatics by metabolic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:615–626
Ikeda M, Katsumata R (1992) Metabolic engineering to produce tyrosine or phenylalanine in a tryptophan-producing Corynebacterium glutamicum Strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:781–785
Ikeda M, Ozaki A, Katsumata R (1993) Phenylalanine production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum with the pheA gene of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:318–323
Jakoby M, Ngouoto-Nkili CE, Burkovski A (1999) Construction and application of new Corynebacterium glutamicum vectors. Biotechnol Technol 13:437–441
Juminaga D, Baidoo EEK, Redding-Johanson AM, Batth TS, Burd H, Mukhopadhyay A, Petzold CJ, Keasling JD (2011) Modular Engineering of l-Tyrosine Production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:89–98
Kikuchi Y, Date M, Yokoyama K, Umezawa Y, Matsui H (2003) Secretion of active-form Streptoverticillium mobaraense transglutaminase by Corynebacterium glutamicum: processing of the pro-transglutaminase by a cosecreted subtilisin-like protease from Streptomyces albogriseolus. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:358–366
Li PP, Liu YJ, Liu SHJ (2009) Genetic and biochemical identification of the chorismate mutase from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microbiology 155:3382–3391
Liu DX, Fan CS, Tao JH, Liang GX, Gao SE, Wang HJ, Li X, Song DX (2004) Integration of E. coli aroG-pheA tandem genes into Corynebacterium glutamicum tyrA locus and its effect on l-phenylalanine biosynthesis. World J Gastroenterol 10:3683–3687
Nešvera J, Pátek M (2011) Tools for genetic manipulations in Corynebacterium glutamicum and their applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1641–1654
Shu CH, Liao CC (2002) Optimization of l-phenylalanine production of Corynebacterium glutamicum under product feedback inhibition by elevated oxygen transfer rate. Biotechnol Bioeng 77:131–141
Sprenger G (2007) Aromatic amino acids. In: Wendisch VF (ed) Amino acid biosynthesis pathways regulation and metabolic engineering. Springer, Berlin, pp 93–127
Takors R, Bathe B, Rieping M, Hans S, Kelle R, Huthmacher K (2007) Systems biology for industrial strains and fermentation processes-example: amino acids. J Biotechnol 129:181–190
Tribe D, Camakaris H, Pittard J (1976) Constitutive and repressivle enzymes of the common pathway of aromatic biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K-12: regulation of enzyme synthesis at different growth rates. J Bacteriol 127:1085
Tyo KE, Kocharin K, Nielsen J (2010) Toward design-based engineering of industrial microbes. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:255–262
Wu YQ, Jiang PH, Fan CS, Wang JG, Shang L, Huang WD (2003) Co-expression of five genes in E. coli or l-phenylalanine in Brevibacterium flavum. World J Gastroentero 9:342–346
Xu DQ, Tan YZ, Huan XJ, Hu XQ, Wang XY (2010) Construction of a novel shuttle vector for use in Brevibacterium flavum, an industrial amino acid producer. J Microbiol Method 80:86–92
Yakandawala N, Romeo T, Friesen AD, Madhyastha S (2008) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to enhance phenylalanine production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:283–291
Yin L, Hu X, Xu D, Ning J, Chen J, Wang X (2012) Co-expression of feedback-resistant threonine dehydratase and acetohydroxy acid synthase increase l-isoleucine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Metab Eng 14:542–550
Zhou H, Liao X, Wang T, Du G, Chen J (2010) Enhanced l-phenylalanine biosynthesis by co-expression of pheA fbr and aroF wt. Bioresour Technol 101:4151–4156
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Byong Lee at Jiangnan University for his discussion and revision. This work was financially supported by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31130043), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31200020, 31000054, 31171638), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, the Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (1101053C) and the Independent Innovation Program of Jiangnan University (JUSRP111A23).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Zhang, J., Kang, Z. et al. Enhanced production of l-phenylalanine in Corynebacterium glutamicum due to the introduction of Escherichia coli wild-type gene aroH . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 643–651 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1262-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1262-x