Abstract
A pectate lyase gene (pl-str) was cloned from Streptomyces sp. S27 and expressed in Escherichia coli Rosetta. The full-length pl-str consists of 972 bp and encodes for a protein of 323 amino acids without signal peptide that belongs to family PF00544. The recombinant enzyme (r-PL-STR) was purified to electrophoretic homogeneity using Ni2+–NTA chromatography and showed apparent molecular mass of ~35 kDa. The pH optimum of r-PL-STR was found to be 10.0, and it exhibited >70% of the maximal activity at pH 12.0. After incubation at 37°C for 1 h without substrate, the enzyme retained more than 55% activity at pH 7.0–12.0. Compared with the commercial complex enzyme Scourzyme@301L from Novozymes, purified r-PL-STR showed similar efficacy in reducing the intrinsic viscosity of polygalacturonic acid (49.0 vs. 49.7%). When combined with cellulase and α-amylase, r-PL-STR had comparable performance in bioscouring of jute fabric (22.39 vs. 22.99%). Thus, r-PL-STR might represent a good candidate for use in alkaline industries such as textile.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barras F, van Gijsegem F, Chatterjee A (1994) Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu Rev Phytopathol 32:201–234
Berensmeier S, Singh S, Meens J, Buchholz K (2004) Cloning of the pelA gene from Bacillus licheniformis 14A and biochemical characterization of recombinant, thermostable, high-alkaline pectate lyase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:560–567
Chotigeat W, Duangchu S, Wititsuwannakun R, Phongdara A (2009) Cloning and characterization of pectate lyase from Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:243–247
Collmer A, Ried J, Mount M (1988) Assay methods for pectic enzymes. Methods Enzymol 161:329–335
Hoondal G, Tiwari R, Tewari R, Dahiya N, Beg Q (2002) Microbial alkaline pectinases and their industrial applications: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:409–418
Huang H, Shao N, Wang Y, Luo H, Yang P, Zhou Z, Zhan Z, Yao B (2009) A novel beta-propeller phytase from Pedobacter nyackensis MJ11 CGMCC 2503 with potential as an aquatic feed additive. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:249–259
Jayani R, Saxena S, Gupta R (2005) Microbial pectinolytic enzymes: a review. Process Biochem 40:2931–2944
Klugsantner B, Schnitzhofer W, Vrsanska M, Weber J, Agrawal P, Nierstrasz V, Guebitz G (2006) Purification and characterization of a new bioscouring pectate lyase from Bacillus pumilus BK2. J Biotechnol 121:390–401
Kobayashi T, Koike K, Yoshimatsu T, Higaki N, Suzumatsu A, Ozawa T, Hatada Y, Ito S (1999) Purification and properties of a low-molecular-weight, high-alkaline pectate lyase from an alkaliphilic strain of Bacillus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63:65–72
Kuhad R, Kapoor M, Rustagi R (2004) Enhanced production of an alkaline pectinase from Streptomyces sp. RCK-SC by whole-cell immobilization and solid-state cultivation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:257–263
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Li N, Shi P, Yang P, Wang Y, Luo H, Bai Y, Zhou Z, Yao B (2008) A xylanase with high pH stability from Streptomyces sp. S27 and its carbohydrate-binding module with/without linker-region-truncated versions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:99–107
Liao C, Sasaki K, Nagahashi G, Hicks K (1992) Cloning and characterization of a pectate lyase gene from the soft-rotting bacterium Pseudomonas viridiflava. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 5:301–308
Margesin R, Fauster V, Fonteyne PA (2005) Characterization of cold active pectate lyases from psychrophilic Mrakia frigida. Lett Appl Microbiol 40:453–459
Muccilli V, Licciardello C, Fontanini D, Russo MP, Cunsolo V, Saletti R, Giuseppe RR, Salvatore F (2009) Proteome analysis of Citrus sinensis L. (Osbeck) flesh at ripening time. J Proteomics 73:134–152
Ogawa A, Sawada K, Saito K, Hakamada Y, Sumitomo N, Hatada Y, Kobayashi T, Ito S (2000) A new high-alkaline and high-molecular-weight pectate lyase from a Bacillus isolate: enzymatic properties and cloning of the gene for the enzyme. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1133–1141
Pissavin C, Robert-Baudouy J, Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N (1998) Biochemical characterization of the pectate lyase PelZ of Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937. Biochim Biophys Acta 1383:188–196
Ricard M, Reid I (2004) Purified pectinase lowers cationic demand in peroxide-bleached mechanical pulp. Enzyme Microb Tech 34:499–504
Ridley BL, O’Neill MA, Mohnen D (2001) Pectins: structure, biosynthesis, and oligogalacturonide-related signaling. Phytochemistry 57:929–967
Roeder D, Collmer A (1985) Marker-exchange mutagenesis of a pectate lyase isozyme gene in Erwinia chrysanthemi. J Bacteriol 164:51–56
Shi P, Yao G, Yang P, Li N, Luo H, Bai Y, Wang Y, Yao B (2009) Cloning, characterization, and antifungal activity of an endo-1,3-β-d-glucanase from Streptomyces sp. S27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1483–1490
Solbak AI (2004) Discovery of pectin-degrading enzymes and directed evolution of a novel pectate lyase for processing cotton fabric. J Biol Chem 280:9431–9438
Starr MP, Moran F (1962) Eliminative split of pectic substances by phytopathogenic soft-rot bacteria. Science 135:920–921
Tanabe H, Yoshihara K, Tamura K, Kobayashi Y, Akamatsu I, Niyomwan N, Footrakul P (1987) Pretreatment of pectic wastewater from orange canning process by an alkalophilic Bacillus sp. J Ferment Technol 65:243–246
Tonouchi A, Hara Y, Umehara R, Sanuki T, Fukusawa T, Miyairi K (2010) Cloning of the gene encoding an endo-acting pectate lyase from Streptomyces thermocarboxydus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:433–436
Trigui-Lahiani H, Gargouri A (2007) Cloning, genomic organisation and mRNA expression of a pectin lyase gene from a mutant strain of Penicillium occitanis. Gene 388:54–60
Wynne EC, Pemberton JM (1986) Cloning of a gene cluster from Cellvibrio mixtus which codes for cellulase, chitinase, amylase, and pectinase. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:1362–1367
Yuan P, Meng K, Huang H, Shi P, Luo H, Yang P, Yao B (2011) A novel acidic and low-temperature-active endo-polygalacturonase from Penicillium sp. CGMCC 1669 with potential for application in apple juice clarification. Food Chem 129:1369–1375
Yuan P, Meng K, Luo H, Shi P, Huang H, Bai Y, Yang P, Yao B (2011) A novel low-temperature active alkaline pectate lyase from Klebsiella sp. Y1 with potential in textile industry. Process Biochem 46:1921–1926
Zhai C (2003) Cloning and expression of a pectate lyase gene from Bacillus alcalophilus NTT33. Enzyme Microb Tech 33:173–178
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the China Modern Agriculture Research System (CARS-42), the National Science and Technology Support Program (2011BADB02), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Conversion Funds (2009GB23260444).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Peng Yuan and Kun Meng contributed equally to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10295_2012_1085_MOESM1_ESM.tif
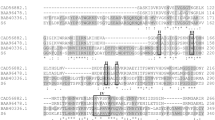
Supplementary Fig. S1. Multiple alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence of pl-str from Streptomyces sp. S27 and two pectate lyases from A. mirum DSM 43827 (ACU35796) and Pseudonocardia sp. (AAC38059). Identical residues are shaded in black, and similar residues are shaded in gray. The putative catalytic residue is indicated by a dot. The internal peptide sequences of deduced PL-STR identified by LC–ESI–MS are underlined. Supplementary Material 1 (TIFF 156 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, P., Meng, K., Shi, P. et al. An alkaline-active and alkali-stable pectate lyase from Streptomyces sp. S27 with potential in textile industry. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 909–915 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1085-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1085-1