Abstract
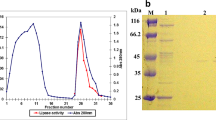
A lipase-producing bacterium was isolated and identified as Pseudomonas monteilii TKU009. A lipase (F2) and lipase-like materials (F1) were purified from the culture supernatant of P. monteilii TKU009 with soybean powder as the sole carbon/nitrogen source. The molecular mass of F1 and F2 was estimated to be 44 kDa by SDS-PAGE and gel filtration. The optimum pH, optimum temperature, and pH and thermal stabilities of F2 were 7, 40°C, 8–11, and 50°C; and of F1 were 6, 40°C, 6–7, and 50°C, respectively. F2 was completely inhibited by EDTA and slightly by Mg2+, Fe2+, Mn2+, and SDS. F1 was completely inhibited by EDTA and Fe2+ and strongly by Zn2+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and SDS. The activities of both the enzymes were enhanced by the addition of non-ionic surfactants Triton X–100 and Tween 40, especially for F1. F2 preferably acted on substrates with a long chain (C10–C18) of fatty acids, while F1 showed a broad spectrum on those with chain length of C4–C18. The marked activity of F2 in organic solvents makes it an ideal choice for application in a water-restricted medium including organic synthesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Annibale A, Sermanni GG, Federici F, Petruccioli M (2006) Olive-mill wastewaters: a promising substrate for microbial lipase production. Bioresour Technol 97:1823–1833
Jaeger KE, Ransac S, Dijkstra BW, Colson C, Mv Heuvel, Misset O (1994) Bacterial lipases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:29–63. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00121.x
Jaeger KE, Reetz MT (1998) Microbial lipases form versatile tools for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 16:396–403. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(98)01195-0
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:235–251. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.016
Aloulou A, Rodriguez JA, Puccinelli D, Mouz N, Leclaire J, Leblond Y et al (2007) Purification and biochemical characterization of the LIP2 lipase from Yarrowia lipolytica. Biochim Biophys Acta 1771:228–237
Noureddini H, Gao X, Philkana RS (2005) Immobilized Pseudomonas cepacia lipase for biodiesel fuel production from soybean oil. Bioresour Technol 96:769–777. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2004.05.029
Burkert JFM, Maugeri F, Rodrigues MI (2004) Optimization of extracellular lipase production by Geotrichum sp. using factorial design. Bioresour Technol 91:77–84. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00152-4
Bornscheuer UT, Kazlauskas RJ (2006) Hydrolases in organic synthesis—regio- and stereoselective biotransformations, 2nd edn. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Karadzic I, Masui A, Zivkovic LI, Fujiwara N (2006) Purification and characterization of an alkaline lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from putrid mineral cutting oil as component of metalworking fluid. J Biosci Bioeng 102:82–89. doi:10.1263/jbb.102.82
Singh S, Banerjee UC (2007) Purification and characterization of trans-3-(4-methoxyphenyl) glycidic acid methyl ester hydrolyzing lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Process Biochem 42:1063–1068. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2007.04.006
Kim KR, Kwon DY, Yoon SH, Kim WY, Kim KH (2005) Purification, refolding, and characterization of recombinant Pseudomonas fluorescens lipase. Protein Expr Purif 39:124–129. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2004.09.014
Jinwal UK, Roy U, Chowdhury A, Bhaduri A, Roy PK (2003) Purification and characterization of an alkaline lipase from a newly isolated Pseudomonas mendoncina PK-12Cs and chemoselective hydolysis of fatty acid ester. Bioorg Med Chem 11:1041–1046. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(02)00516-3
Reetz MT, Jaeger KE (1998) Overexpression, immobilization and biotechnological application of Pseudomonas lipases. Chem Phys Lipids 93:3–14. doi:10.1016/S0009-3084(98)00033-4
Krieg NR, Holt JG (1984) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
Wang SL, Hsu WT, Liang TW, Yen YH, Wang CL (2008) Purification and characterization of three keratinolytic metalloproteases produced by Chryseobacterium indologenes TKU014 in a shrimp shell powder medium. Bioresour Technol 99(13):5679–5686
Kumar S, Kikon K, Upadhyay A, Kanwar SS, Gupta R (2005) Production, purifcation, and characterization of lipase from thermophilic and alkaliphilic Bacillus coagulans BTS-3. Protein Expr Purif 41:38–44. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2004.12.010
Castro-Ochoa LD, Rodríguez-Gómez C, Valerio-Alfaro G, Oliart Ros R (2005) Screening, purification and characterization of the thermoalkalophilic lipase produced by Bacillus thermoleovorans CCR11. Enzyme Microb Technol 37:648–654. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.06.003
Saxena RK, Sheoran A, Giri B, Davidson WS (2003) Purification strategies for microbial lipases. J Microbiol Methods 52:1–18. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(02)00161-6
Tan T, Zhang M, Xu J, Zhang J (2004) Optimization of culture conditions and properties of lipase from Penicillium camembertii Thom PG-3. Process Biochem 39:1495–1502. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00296-6
Rahman RNZRA, Baharum SN, Basri M, Salleh AB (2005) High-yield purification of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Pseudomonas sp. strain S5. Anal Biochem 341:267–274. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.03.006
Lee KW, Bae HA, Shin GS, Lee YH (2006) Purification and catalytic properties of novel enantioselective lipase from Acinetobacter sp. ES-1 for hydrolysis of (S)-ketoprofen ethyl ester. Enzyme Microb Technol 38:443–448. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.06.017
Chen S, Qian L, Shi B (2007) Purification and properties of enantioselective lipase from a newly isolated Bacillus cereus C71. Process Biochem 42:988–994. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2007.03.010
Lima VMG, Krieger N, Mitchell DA, Fontana JD (2004) Activity and stability of a crude lipase from Penicillium aurantiogriseum in aqueous media and organic solvents. Biochem Eng J 18:65–71. doi:10.1016/S1369-703X(03)00165-7
Yu M, Qin S, Tan T (2007) Purification and characterization of the extracellular lipase Lip2 from Yarrowia lipolytica. Process Biochem 42:384–391. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.09.019
Sharma R, Soni SK, Vohra RM, Gupta LK, Gupta JK (2002) Purification and characterisation of a thermostable alkaline lipase from a new thermophilic Bacillus sp. RSJ-1. Process Biochem 37:1075–1084. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(01)00316-8
Sinchaikul S, Sookkheo B, Phutrakul S, Pan FM, Chen ST (2001) Optimization of a thermostable lipase from Bacillus stearothermophilus P1: overexpression, purification, and characterization. Protein Expr Purif 22:388–398. doi:10.1006/prep.2001.1456
Amada K, Kwon HJ, Haruki M (2001) Ca2+-induced folding of a family I.3 lipase with repetitive Ca2+ binding motifs at the C-terminus. FEBS Lett 509:17–21. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)03108-8
Ogino H, Ishikawa H (2001) Enzymes which are stable in the presence of organic solvents. J Biosci Bioeng 91:109–116. doi:10.1263/jbb.91.109
Torres S, Castro G (2004) Non-aqueous biocatalysis in homogenous systems. Food Technol Biotechnol 42:271–277
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by a grant from the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC94-2313-B-212-003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Li-June Ming is a visiting Professor at the National Cheng Kung University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, SL., Lin, YT., Liang, TW. et al. Purification and characterization of extracellular lipases from Pseudomonas monteilii TKU009 by the use of soybeans as the substrate. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 65–73 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0473-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0473-z