Abstract.
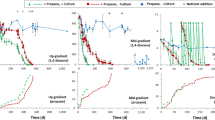
Sphingomonas cloacae S-3T, a nonylphenol (NP)-degrading bacterium, was evaluated for its utility in the remediation of NP-contaminated wastewater. In flask-scale experiments, S-3T cells immobilized on porous polypropylene carriers (beads) efficiently degraded NP to concentrations routinely measured in aquatic environments [a few parts per billion (ppb), or micrograms per liter). Therefore, we constructed and evaluated a laboratory-scale wastewater treatment system with a 3-l carrier-filled column. The system worked properly and consistently removed several hundred ppb of NP to ecologically safe concentrations of less than 10 ppb in industrial wastewater without the addition of nutrients. The effect of wastewater pH on the system performance was also evaluated; and wastewater samples with pH values of 6 or 8 were treated efficiently without pH adjustment. These results suggest that a biotreatment system using NP-degrading bacteria can efficiently remediate industrial wastewater and contribute to the preservation of aquatic environments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahel M, Giger W (1985) Determination of alkylphenols and alkylphenol mono- and di-ethoxylates in environmental samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chem 57:1577–1583
Becton Dickinson (1998) Yeast media. In: Difco (ed) Difco Manual, 11th edn. Difco, New York, pp 576–580
Brunner PH, Capli S, Marcomini A, Giger W (1988) Occurrence and behaviour of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates, nonylphenol, nonylphenol mono- and nonylphenol diethoxylates in sewage and sewage sludge treatment. Water Res 22:1465–1472
Fujii K, Urano N, Ushio H, Satomi M, Iida H, Ushio-Sata N, Kimura S (2000) Profile of a nonylphenol-degrading microflora and its potential for bioremedial applications. J Biochem 128:909–916
Fujii K, Urano N, Ushio H, Satomi M, Kimura S (2001) Sphingomonas cloacae sp. nov., a nonylphenol-degrading bacterium isolated from wastewater of a sewage-treatment plant in Tokyo. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:603–610
Giger W, Stephanou E, Schaffner C (1981) Persistent organic chemicals in sewage effluents: I. Identifications of nonylphenols and nonylphenol ethoxylates by glass capillary gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 10:1253–1263
Harries JE, Sheahan DA, Jobling S, Matthiessen P, Neall P, Routledge EJ, Rycroft R, Sumpter JP, Tylor T (1996) A survey of estrogenic activity in United Kingdom island waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1993–2002
Harries JE, Sheahan DA, Jobling S, Matthiessen P., Neall P, Sumpter JP, Tylor T, Zaman N (1997) Estrogenic activity in five United Kingdom rivers detected by measurement of vitellogenesis in caged male trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:534–542
Isobe T, Takada H (1998) Behaviour and effect of nonylphenol in aquatic environment (in Japanese). Mizukankyou Gakkaishi 21:203–208
Jobling S, Noran M, Tyler CR, Brighty G, Sumpter JP (1998) Widespread sexual disruption in wild fish. Environ Sci Technol 32:2498–2506
Kojima S, Watanabe S (1998) Distribution of alkylphenol polyethoxylate (APE) and their metabolites in the aquatic environment in Nagoya city (in Japanese). Mizukankyou Gakkaishi 21:302–309
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 93:265–275
Rudel RA, Melly SJ, Geno PW, Sun G, Brody JG (1998) Identification of alkylphenols and other estrogenic phenolic compounds in wastewater, septage, and groundwater on Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Environ Sci Technol 32:861–869
Sole M, Lopez de Alda MJ, Castillo M, Porte C, Ladegaard-Pedersen K, Barcelo, D (2000) Estrogenicity determination in sewage treatment plans and surface waters from the Catalonian area (NE Spain). Environ Sci Technol 34:5076–5083
Tsuda T, Takino A, Kojima M, Harada H, Muraki K, Tsuji M (2000) 4-nonylphenol and 4-tert-octylphenol in water and fish from rivers flowing into Lake Biwa. Chemosphere 41:757–762
Acknowledgment.
We thank Mr. Tsuyoshi Sasai for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujii, K., Yamamoto, R., Tanaka, T. et al. Potential of a new biotreatment: Sphingomonas cloacae S-3T degrades nonylphenol in industrial wastewater. J IND MICROBIOL BIOTECHNOL 30, 531–535 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-003-0072-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-003-0072-y