Abstract
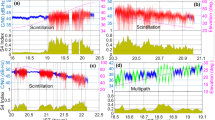
With advances in Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver hardware, increased sampling rates have become available, allowing for more robust spectral analysis in the field of ionospheric scintillation research. However, with previous work having access to GPS observables sampled at 50 Hz in the Canadian auroral region, the higher-frequency results have been dismissed, typically denoted as noise with the assumption that no scintillation characteristics can be obtained therein. The introduction of the Septentrio PolaRxS Pro GPS receiver, which can sample at a maximum rate of 100 Hz, allows for a robust analysis of these higher frequencies. Spectral characteristics of both signal intensity and carrier phase on the L1 carrier, obtained within the Canadian auroral region, are presented in this paper. These spectra are shown to deviate from the expected power-law behavior in the higher-frequency region. This region is shown to be free of observable scintillation characteristics in the signal intensity spectra and is likely a contamination due to white noise, confirming the results of previous work. The carrier phase spectrum, on the other hand, displays characteristics less likely to be noise. The expected power-law behavior is observed in these spectra, with a shallowing of the slope seen in the higher frequencies.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akala AO, Awoyele A, Doherty PH (2016) Statistics of GNSS amplitude scintillation occurrences over Dakar, Senegal at varying elevation angles during the maximum phase of solar cycle 24. Space Weather 14:233–246
Briggs BH, Parkin IA (1963) On the variation of radio star and satellite scintillations with zenith angle. J Atmos Terr Phys 25(6):339–366
Choi K, Bilich A, Larson K, Axelrad P (2004) Modified sidereal filtering: implications for high-rate GPS positioning. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2004gl021621
Cronyn WM (1970) The analysis of radio scattering and space-probe observations of small-scale structure in the interplanetary medium. Astrophys J 161:755
Elkins TJ, Papagiannis MD (1969) Measurement and interpretation of power spectrums of ionospheric scintillation at a sub-auroral location. J Geophys Res 74(16):4105–4115
Getmantsev GG, Eroukhimov LM (1969) Radio star and satellite scintillations. Ann IQSY 5:229–259
Gruber S (1961) Statistical analysis of radio star scintillation. J Atmos Terr Phys 20(1):59–71
Jayachandran PT, Langley RB, MacDougall JW, Mushini SC, Pokhotelov D, Hamza AM, Mann IR, Milling DK, Kale ZC, Chadwick R, Kelly T, Danskin DW, Carrano CS (2009) The Canadian high arctic ionospheric network (CHAIN). Radio Sci 44:RS0A03. doi:10.1029/2008RS004046
Jespersen JL, Kamas G (1964) Satellite scintillation observations at Boulder, Colorado. J Atmos Terr Phys 26(4):457–473
Jones IL (1960) Further observations of radio stellar scintillation. J Atmos Terr Phys 19(1):26–36
Leick A (2004) GPS satellite surveying. Wiley, Hoboken
Li G, Ning B, Yuan H (2007) Analysis of ionospheric scintillation spectra and TEC in the Chinese low latitude region. Earth Planets Space 59(4):279–285
Mann IR, Milling DK, Rae IJ, Ozeke LG, Kale A, Kale ZC, Murphy KR, Parent A, Usanova M, Pahud DM, Lee EA (2008) The upgraded CARISMA magnetometer array in the THEMIS era. Space Sci Rev 141(1):413–451
McCaffrey AM, Jayachandran PT (2014) Auroral scintillation characteristics using 100 Hz sampling of global positioning satellite systems. In: International Union of Radio Science General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS) conference, Beijing, China, August 16–23, 2014
McCaffrey AM, Jayachandran PT (2017) Observation of sub‐second variations in auroral region total electron content using 100 Hz sampling of GPS observables. J Geophys Res Space Phys 122(6):6892–6900
Mezaoui H, Hamza AM, Jayachandran PT (2014) Investigating high-latitude ionospheric turbulence using global positioning system data. Geophys Res Lett 41(19):6570–6576
Mushini SC (2013) Characteristics of scintillating GPS signal at high latitudes during solar minima. Doctoral Dissertation, University of New Brunswick, Department of Physics
Mushini SC, Jayachandran PT, Langley RB, MacDougall JW, Pokhotelov D (2012) Improved amplitude-and phase-scintillation indices derived from wavelet detrended high-latitude GPS data. GPS Sol 16(3):363–373
Phelps ADR, Sagalyn RC (1976) Plasma density irregularities in the high-latitude top side ionosphere. J Geophys Res 81(4):515–523
Prikryl P, Jayachandran PT, Mushini SC, Chadwick R (2011) Climatology of GPS phase scintillation and HF radar backscatter for the high-latitude ionosphere under solar minimum conditions. Ann Geophys 29(2):377–392
Prikryl P, Ghoddousi-Fard R, Kunduri BSR, Thomas EG, Coster AJ, Jayachandran PT, Danskin DW (2013) GPS phase scintillation and proxy index at high latitudes during a moderate geomagnetic storm. Ann Geophys 31(5):805–816. doi:10.5194/angeo-31-805-2013
Rufenach CL (1971) A radio scintillation method of estimating the small-scale structure in the ionosphere. J Atmos Terr Phys 33(12):1941–1951
Rufenach CL (1972) Power-law wavenumber spectrum deduced from ionospheric scintillation observations. J Geophys Res 77(25):4761–4772
Rumsey VH (1975) Scintillations due to a concentrated layer with a power-law turbulence spectrum. Radio Sci 10(1):107–114
Serrano L, Kim D, Langley RB (2005) A new carrier-phase multipath observable for GPS real-time kinematics based on between receiver dynamics. In: Proceedings of Annual Meeting of Institute of Navigation, pp 1105–1115
Skone S, Knudsen K, de Jong M (2001) Limitations in GPS receiver tracking performance under ionospheric scintillation conditions. Phys Chem Earth A 26(6–8):613–621. doi:10.1016/s1464-1895(01)00110-7
Spiker J, Parkinson BW (1996) The global positioning system: theory and application. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Washington DC, pp 717–763
Tsunoda RT (1988) High-latitude F region irregularities: a review and synthesis. Rev Geophys 26(4):719–760
Urneki R, Liu CH, Yeh KC (1977) Multifrequency studies of ionospheric scintillations. Radio Sci 12(2):311–317
Van Dierendonck AJ, Klobuchar J, Hua Q (1993) Ionospheric scintillation monitoring using commercial single frequency C/A code receivers. In: Proceedings of ION GPS 1993, Salt Palace Convention Center, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, September 22–24, pp 1333–1342
Watson C, Jayachandran PT, Spanswick E, Donovon EF, Danskin DW (2011) GPS TEC technique for observation of the evolution of substorm particle injection. Geophys Res 116:A00I90. doi:10.1029/2010JA015732
Wernik AW (1997) Wavelet transform of nonstationary ionospheric scintillation. Acta Geophys Pol 45:237–253
Wernik AW, Liu CH (1974) Ionospheric irregularities causing scintillation of GHz frequency radio signals. J Atmos Terr Phys 36(5):871–879
Yeh KC, Liu CH (1982) Radio wave scintillations in the ionosphere. Proc IEEE 70(4):324–360
Acknowledgements
Infrastructure funding for CHAIN was provided by the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) and the New Brunswick Innovation Foundation (NBIF). CHAIN is conducted in collaboration with the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). Additional funding is provided by the David M. Armstrong fellowship, established by Dr. Richard Armstrong. The authors thank I.R. Mann, D.K. Milling, and the rest of the CARISMA team for data. CARISMA is operated by the University of Alberta, funded by the Canadian Space Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCaffrey, A.M., Jayachandran, P.T. Spectral characteristics of auroral region scintillation using 100 Hz sampling. GPS Solut 21, 1883–1894 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0664-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0664-z