Abstract
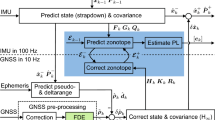
In the complex urban environments, land vehicle navigation purely relying on GNSS cannot satisfy user needs due to the loss of satellite signals caused by obstructions such as buildings, tunnels, and trees. To solve this problem, we introduce a GPS-/MSINS-/magnetometer-integrated urban navigation system based on context awareness. In this system, the data from the Micro Strapdown Inertial Navigation System (MSINS) are used to analyze and detect the context knowledge of vehicles, whose sensor errors can be compensated by the heuristic drift reduction algorithm for different motion situations. When GPS is available, the vehicle position can be estimated by unscented Kalman Filter, whereas in the case of GPS outages, the vehicle attitude is provided by an attitude and heading reference system and the motion constraints-aided algorithm is used to complete the positioning. In the experiment validation, the integrated navigation system is set up by low-cost inertial sensors. The result shows that the proposed system can achieve high accuracy when GPS is available. For most of the time without GPS, the system can guarantee the positioning precision of 10 m and compensate the errors of MSINS effectively, which fully satisfies positioning needs in complex urban environments.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adusumilli S, Bhatt D, Wang H, Bhattacharya P, Devabhaktuni V (2013) A low-cost INS/GPS integration methodology based on random forest regression. Expert Syst Appl 40(11):4653–4659
Angrisano A, Petovello M, Pugliano G (2012) Benefits of combined GPS/GLONASS with low-cost MEMS IMUs for vehicular urban navigation. Sensors 12(4):5134–5158
Bhatt D, Aggarwal P, Devabhaktuni V, Bhattacharya P (2014) A novel hybrid fusion algorithm to bridge the period of GPS outages using low-cost INS. Expert Syst Appl 41(5):2166–2173
Borenstein J, Ojeda L, Kwanmuang S (2009) Heuristic reduction of gyro drift for personnel tracking system. J Navig 62:41–58
Ding YR, Hsiao FB (2013) Application of a single-antenna GPS-based attitude estimation on the stability control of a small unmanned aerial vehicle. J Aerosp Eng 26(4):768–785
Faouzi NE, Leung H, Kurian A (2012) Data fusion in intelligent transportation systems: progress and challenges—a survey. Inf Fusion 12:4–10
Godha S, Cannon ME (2005) Integration of DGPS with a low cost MEMS—based Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) for land vehicle navigation application. Proceedings of International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation
Hwang CL, Shih CY (2009) A distributed active-vision network-space approach for the navigation of a car-like wheeled robot. Ind Electron IEEE Trans 56(3):846–855
Kang L, Ye L et al (2014) Attitude heading reference system using MEMS inertial sensors with dual-axis rotation. Sensors 14(10):18075–18095
Lei X, Li J (2013) An adaptive navigation method for a small unmanned aerial rotorcraft under complex environment. Measurement 46(10):4166–4171
Li W, Teunissen P, Zhang B (2013) Precise point positioning using GPS and compass observations. In: CSNC 2013 Proceedings. Springer, Berlin 244:367–378
Martí ED, García J (2012) Context-aided sensor fusion for enhanced urban navigation. Sensors 12(12):16802–16837
Martí ED, García J, Molina JM (2011) Context-awareness at the service of sensor fusion systems: inverting the usual scheme. In: Proceedings of the ISCIF Conference Torremolinos-Málaga, Spain, pp 653–660
Park M, Gao Y (2008) Error and performance analysis of MEMS-based inertial sensors with a low-cost GPS receiver. Sensors 8(4):2240–2261
Shaheen SA, Finson R (2013) intelligent transportation systems. Reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Skog I, Händel P (2009) In-car positioning and navigation technologies—a survey. Intell Transp Syst IEEE Trans 10(1):4–21
Titterton D, Weston J (2004) Strapdown inertial navigation technology, 2nd edn. AIAA, Washington, DC
Zhang T, Xu X (2012) A new method of seamless land navigation for GPS/INS integrated system. Measurement 45(4):691–701
Zhang GW, Zhang XY, Song CL (2013) Research and design of MEMS SINS/GPS integrated navigation system based on adaptive filter applied. Mech Mater 341:1048–1052
Zhao L, Wang QY (2013). Design of an attitude and heading reference system based on distributed filtering for small UAV. Math Probl Eng 1–9
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the key program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61039003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41274038), the Aeronautical Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2013ZC51027), the Aerospace Innovation Foundation of China(CASC201102), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, N., Zhao, L. An integrated land vehicle navigation system based on context awareness. GPS Solut 20, 509–524 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-015-0460-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-015-0460-6