Abstract
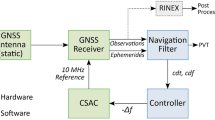
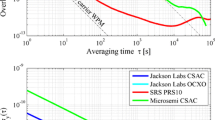
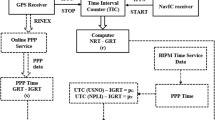
GNSS receivers are often integrated with other sensors such as inertial navigation system (INS) and camera. The pulse per second (PPS) signal from GNSS receiver is commonly used as the benchmark for time synchronization with other sensors, which is crucial for the accuracy of the sensor integration. Therefore, the timing quality of the PPS signal is important and worthy to be evaluated comprehensively. We use a chip scale cesium atomic clock to evaluate the PPS quality of three popular commercial GNSS receivers. A practical evaluation method is proposed, which can mitigate the systematic error of the reference clock effectively. The PPS interval stabilities are evaluated by Allan variance to reflect the PPS time offset, and the clock divergences during GNSS signal loss are measured to reflect the capability to maintain the clock accuracy. The test results show that with nominal GNSS satellite signal condition, the standard deviations of the PPS intervals are in the order of 10E−8 s, and the maximum clock offset after 10 min of losing lock is at microsecond level. The qualities of the PPS signal from the tested receivers are sufficient for the time synchronization of the integrated navigation systems.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Itzhack IY, Vitek Y (1985) The enigma of false bias detection in a strapdown system during transfer alignment. J Guid Control Dyn 8(2):175–180
Lewandowski W, Azoubib J, Klepczynski WJ (1999) GPS: primary tool for time transfer. Proc IEEE 87(1):163–172
Mannermaa J, Kalliomaki K, Mansten T, Turunen S (1999) Timing performance of various GPS receivers. In proceedings of the 1999 joint meeting of the European frequency and time forum and the IEEE international frequency control symposium, p 287–290, April 1999
Misra P, Enge P (2004) Global positioning system: signals, measurements, and performance. Ganga-Jamuna Press, Lincoln, pp 220–223
NetR9 (2010) User guide: trimble NetR9 GNSS reference receiver, version 4.15, revision A. Trimble Navigation Limited, Ohio, USA
OEMV (2010) OEMV family firmware reference manual, OM-20000094, revision 8. NovAtel Inc, Calgary
Seco-Granados G, Lopez-Salcedo JA, Jimenez-Banos D, Lopez-Risueno G (2012) Challenges in indoor global navigation satellite systems: unveiling its core features in signal processing. Signal Process Mag IEEE 29(2):108–131
Symmetricom (2011) SA.45 s Chip-scale atomic clock user’s guide, No. 098-00055-000, revision A, Symmetricom, Inc, Beverly, USA
Symmetricom (2013) Quantum SA.45 s CSAC: Chip Scale Atomic Clock, Symmetricom, Inc, Beverly, USA
Waegli A, Skaloud J (2009) Optimization of two GPS/MEMS-IMU integration strategies with application to sports. GPS Solut 13(4):315–326
Wang JL, Garratt M, Lambert A, Wang JJ, Han S, Sinclair D (2008) Integration of GPS/INS/vision sensors to navigate unmanned aerial vehicles. IAPRSSIS 37(B1):963–969
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41174028), the National High Technology Research and Develop Program of China (2012AA12A206), and the Open Research Fund of the Academy of Satellite Application. Symmetricom is acknowledged for providing the CSAC atomic clock evaluation board with relevant technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, X., Yan, K., Zhang, T. et al. Quality evaluation of the pulse per second (PPS) signals from commercial GNSS receivers. GPS Solut 19, 141–150 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0375-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0375-7