Abstract.
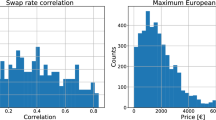
In economic decision problems such as credit loan approval or risk analysis, models are required to be monotone with respect to the decision variables involved. Also in hedonic price models it is natural to impose monotonicity constraints on the price rule or function. If a model is obtained by a “unbiased” search through the data, it mostly does not have this property even if the underlying database is monotone. In this paper, we present methods to enforce monotonicity of decision trees for price prediction. Measures for the degree of monotonicity of data are defined and an algorithm is constructed to make non-monotone data sets monotone. It is shown that monotone data truncated with noise can be restored almost to the original data by applying this algorithm. Furthermore, we demonstrate in a case study on house prices that monotone decision trees derived from cleaned data have significantly smaller prediction errors than trees generated using raw data.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
MSC code:
90-08 (Computational methods)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velikova, M., Daniels, H. Decision trees for monotone price models. Computational Management Science 1, 231–244 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10287-004-0014-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10287-004-0014-9