Abstract
Objectives
To apply both autoregressive (AR) and fast Fourier transform (FFT) spectral analysis at rest, during two different dynamic exercise intensities and in recovery from maximal exercise and to compare raw and normalized powers obtained with both methods.
Methods
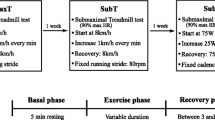
Sixteen participants (age 22.3 ± 4.3 year) performed resting, submaximal and maximal protocols. The submaximal protocol consisted of two 5-min walks at 4 km h−1 at treadmill grades of 0 and 7.5%. Beat-to-beat R-R series were recorded. FFT and AR analyses were preformed on the same R-R series.
Results
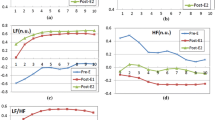
Compared to AR, FFT provided higher total power (TP) and raw high-frequency (HF) power at rest and exercise. Furthermore, FFT LF/HF ratio was lower than with the AR, except under resting conditions. Both methods showed reductions in TP, raw HF and LF powers during exercise and recovery. Only the AR revealed a significant reduction for normalized HF power and increase for normalized LF power in transition from rest to exercise conditions.
Interpretation
AR and FFT methods are not interchangeable at rest or during dynamic exercise conditions. The AR method is more sensitive to the effects of exercise on the normalized power spectra of heart rate variability (HRV) than FFT. Finally, as both approaches are equally insensitive to the increase of exercise relative intensity, there is no practical advantage of performing HRV spectral analyses by the AR or FFT at higher workloads.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai Y, Saul J, Albrecht P, Hartley L, Lilly L, Cohen R (1989) Modulation of cardiac autonomic activity during and immediately after exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ O Physiol 256:H132–H141
Badilini F, Maison-Blanche P, Champomier P, Provost J, Coumel P, Milon H (2000) Frequency-domain heart rate variability in 24-hour holter recordings: role of spectral method to assess circadian patterns and pharmacological autonomic modulation. J Electrocardiol 33:147–157
Badilini F, Maison-Blanche P, Coumel P (1998) Heart rate variability in passive tilt test: comparative evaluation of autoregressive and FFT spectral analyses. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 21:1122–1132
Bernardi L, Salvucci F, Suardi R, Solda P, Calciati A, Perlini S, Falcone C, Ricciardi L (1990) Evidence for an intrinsic mechanism regulating heart rate variability in the transplanted and the intact heart during submaximal exercise? Cardiovasc Res 24:969–981
Boardman A, Chlindwein F, Rocha A, Leite A (2002) A study on the optimum order of autoregressive models for heart rate variability. Physiol Meas 23:325–336
Breuer H, Skyschally A, Schulz R, Martin C, Wehr M, Heusch G (1993) Heart rate variability and circulating catecholamine concentrations in healthy volunteers. Br Heart J 70:144–149
Camm A, Malik M, Bigger J, Günter B, Cerutti S, Choen R, Coumel P, Fallen E, Kennedy H, Kleiger R, Lombardi F, Malliani A, Moss A, Rotmann J, Schwartz P, Singer D (1996) Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 93:1043–1065
Casadei B, Cochrane S, Johnston J, Conway J, Sleight P (1995) Pitfalls in the interpretation of spectral analysis of the heart rate variability during exercise in humans. Cardiovasc Res 24:969–981
Casadei B, Moon J, Johnston J, Caiazza A, Sleight P (1996) Is respiratory sinus arrhythmia a good index of cardiac vagal tone in exercise? J Appl Physiol 81:556–564
Chemla D, Young J, Badilini F, Maison-Blanche P, Affres H, Lecarpentier Y, Chanson P (2005) Comparison of fast Fourier transform and autoregressive spectral analysis for the study of heart rate variability in diabetic patients. Int J Cardiol 104:307–313
Dixon E, Kamath M, McCartney N, Fallen E (1992) Neural regulation of heart rate variability in endurance athletes and sedentary controls. Cardiovasc Res 26:713–719
Ewing D, Campbell W, Murray A, Neilson J, Clarke B (1978) Immediate heart-rate response to standing: simple test for autonomic neuropathy in diabetes. BMJ 1:145–147
Fagard R, Pardaens K, Staessen J, Thijs L (1998) Power spectral analysis of heart rate variability by autoregressive modelling and fast Fourier transform: a comparative study. Acta Cardiol 53:211–218
Furlan R, Guzzetti S, Crivellaro W, Dassi S, Tinelli M, Baselli G, Cerutti S, Lombardi F, Pagani M, Malliani A (1990) Continuous 24-hour assessment of the neural regulation of systemic arterial pressure and RR variabilities in ambulant subjects. Circulation 81:537–547
Gregoire J, Tuck S, Yamamoto Y, Hughson RL (1996) Heart rate variability at rest and exercise: influence of age, gender, and physical training. Can J Appl Physiol 21:455–470
Imai K, Sato H, Hori M, Kusuoka H, Ozaki H, Ykoyama H, Takeda H, Inoue M, Kamada T (1994) Vagally mediated heart rate recovery after exercise in accelerated athletes but blunted in patients with chronic heart failure. Am J Coll Cardiol 24:1529–1535
Kaikkonen P, Nummela A, Rusko H (2007) Heart rate variability dynamics during early recovery after different endurance exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:79–86
Kesselbrener L, Akselrod S (1996) Selective discrete Fourier transform algorithm for time-frequency analysis: method and application on simulated cardiovascular signals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 43:789
Leicht A, Sinclair W, Spinks W (2008) Effect of exercise mode on heart rate variability during steady state exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:195–204
Malliani A, Pagani M, Lombardi F, Cerutti S (1991) Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain. Circulation 84:482–492
Malik M (1998) Heart rate variability. Curr Opin Cardiol 13:36–44
Martinmäki K, Rusko H (2008) Time-frequency analysis of heart rate variability during immediate recovery from low and high intensity exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:353–360
McArdle W, Katch F, Katch V (2001) Individual differences and measurement of energy capacities. In: Exercise physiology: energy, nutrition and human performance. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 222–248
Niskanen J, Tarvainen M, Ranta-aho P, Karjalainen P (2004) Software for advanced HRV analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 76:73–81
Orizio C, Perini R, Comandè A, Castellano M, Beschi M, Veicsteinas A (1998) Plasma catecholamines and heart rate at the beginning of muscular exercise in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:644–651
Perini R, Milesi S, Biancardi L, Pendergast D, Veicsteinas A (1998) Heart rate variability in exercising humans: effect of water immersion. Eur J Appl Physiol 77:326–332
Perini R, Milesi S, Fisher N, Pendergast D, Veicsteinas A (2000) Heart rate variability during dynamic exercise in elderly males and females. Eur J Appl Physiol 82:8–15
Perini R, Orizio C, Comandè A, Castellano M, Beschi M, Veicsteinas A (1989) Plasma norepinephrine and heart rate dynamics during recovery from submaximal exercise in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 58:879–883
Perini R, Orizio C, Baselli G, Gerutti S, Veicsteinas A (1990) The influence of exercise intensity on the power spectrum of heart rate variability. Eur J Appl Physiol 61:143–148
Pichon A, de Bisschop C, Roulaud A, Papellier Y (2004) Spectral analysis of heart rate variability during exercise in trained subjects. Med Sci Sport Exerc 36:1702–1708
Pichon A, Roulaud M, Antoine-Jonville S, Bisschop C, Denjean A (2006) Spectral analysis of heart rate variability: inter-changeability between autoregressive analysis and fast Fourier transform. J Electrocardiol 39:31–37
Rimoldi O, Furlan R, Pagani M, Piazza S, Guazzi M, Pagani M, Malliani A (1992) Analysis of neural mechanisms accompanying different intensities of dynamic exercise. Chest 101:226–230
Robinson B, Epstein S, Beise G, Braunwald E (1966) Control of heart rate by autonomic nervous system. Studies in man on the interrelation between baroreceptor mechanisms and exercise. Circ Res 19:400–411
Sandercock R, Brodie D (2006) The use of heart rate variability measures to assess autonomic control during exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 16:302–313
Tarvainen M, Ranta-aho P, Karjalainen P (2001) An advanced detrending method with application to HRV analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 49:172–175
Terziotti P, Schen F, Gulli G (2001) Post-exercise recovery of autonomic cardiovascular control: a study by spectrum and cross-spectrum analysis in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:187–194
Tulppo M, Hughson R, Mäkikallio T, Juhani Airaksinen K, Seppänen T, Huikuri H (2001) Effects of exercise and passive head-up tilt on fractal and complexity properties of heart rate dynamics. Am J Physiol Heart Circ O Physiol 280:H1081–H1087
Tulppo M, Mäkikallio T, Seppänen T, Laukkanen R, Huikuri H (1998) Vagal modulation of heart rate during exercise: effects of age and physical fitness. Am J Physiol 274:H424–H429
Vilhena de Mendonça G, Pereira F (2008) Between-day variability of net and gross oxygen uptake during grade treadmill walking: effects of different walking intensities on the reliability of walking economy. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 33:1199–1206
Warren J, Jaffe R, Wraa C, Stebbins C (1997) Effect of autonomic blockade on power spectrum of heart rate variability during exercise. Am J Physiol 273:R495–R502
Whipp B (1971) Rate constant for the kinetics of oxygen uptake during light exercise. J Appl Physiol 30(2):261–263
Winsley R, Armstrong N, Bywater K, Fawkner S (2003) Reliability of heart rate variability measures at rest and during light exercise in children. Br J Sports Med 37:550–552
Yamamoto Y, Hughson R, Peterson J (1991) Autonomic control of heart rate during exercise studied by heart rate variability spectral analysis. J Appl Physiol 71:1136–1142
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Center of Human Performance (CIPER), Faculty of Human Kinetics, Lisbon, Portugal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendonca, G.V., Fernhall, B., Heffernan, K.S. et al. Spectral methods of heart rate variability analysis during dynamic exercise. Clin Auton Res 19, 237–245 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-009-0018-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-009-0018-1