Abstract
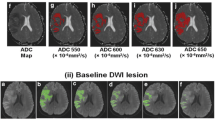
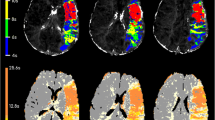
Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has emerged as a promising tool for diagnosing ischemic stroke and for determining treatment strategies in the acute phase. The detection and quantification of the penumbra and the infarct core regions aid the assessment of the potential risks and benefits of thrombolysis by providing information on salvageable tissue or ischemic lesion age. In this study, we proposed a fully automated and real-time algorithm to compute parameter maps of perfusion-weighted images (PWIs) and to identify an infarct core from diffusion-weighted images (DWIs). DWI and PWI were obtained using a 1.5 Tesla MRI scanner for 15 patients with acute ischemic stroke. Parameter maps of PWI were computed using restricted gamma-variate curve fitting and Fourier-based deconvolution. The ischemic penumbra was identified using time-to-maximum (Tmax) > 6 s as the mutual optimal threshold, while the infarct core was segmented using an adaptive thresholding on DWI. When the penumbra on PWI was compared with that generated using commercial software Pearson’s linear correlation coefficient between penumbra volumes was 0.601 (p = 0.030), and the Dice coefficient was 0.51 ± 0.15. The infarct core on DWI was compared with the manually segmented gold standard. Dice coefficient between the manually drawn and automated segmented infarct cores was 0.62 ± 0.18. The processing times for PWI and DWI were 222.9 ± 16.4 and 53.4 ± 4.8 s, respectively. In conclusion, we demonstrate a fully automated and real-time algorithm to segment the penumbra and the infarct core regions based on PWI and DWI.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin EJ et al.: Heart disease and stroke statistics—2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 135:e146–e603, 2017
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, Khatri P, McMullan PW Jr, Qureshi AI, Rosenfield K, Scott PA, Summers DR, Wang DZ, Wintermark M, Yonas H, American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, Council on Clinical Cardiology: Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 44:870–947, 2013
Committee TESOEECatEW: Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc Dis 25:457–507, 2008
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Dávalos A, Guidetti D, Larrue V, Lees KR, Medeghri Z, Machnig T, Schneider D, von Kummer R, Wahlgren N, Toni D, ECASS Investigators: Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 359:1317–1329, 2008
Bluhmki E, Chamorro Á, Dávalos A, Machnig T, Sauce C, Wahlgren N, Wardlaw J, Hacke W: Stroke treatment with alteplase given 3.0-4.5 h after onset of acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS III): additional outcomes and subgroup analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 8:1095–1102, 2009
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg L, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, Schonewille WJ, Vos JA, Nederkoorn PJ, Wermer MJ, van Walderveen M, Staals J, Hofmeijer J, van Oostayen J, Lycklama à Nijeholt GJ, Boiten J, Brouwer PA, Emmer BJ, de Bruijn SF, van Dijk L, Kappelle LJ, Lo RH, van Dijk E, de Vries J, de Kort PL, van Rooij W, van den Berg J, van Hasselt B, Aerden LA, Dallinga RJ, Visser MC, Bot JC, Vroomen PC, Eshghi O, Schreuder TH, Heijboer RJ, Keizer K, Tielbeek AV, den Hertog H, Gerrits DG, van den Berg-Vos R, Karas GB, Steyerberg EW, Flach HZ, Marquering HA, Sprengers ME, Jenniskens SF, Beenen LF, van den Berg R, Koudstaal PJ, van Zwam W, Roos YB, van der Lugt A, van Oostenbrugge R, Majoie CB, Dippel DW, MR CLEAN Investigators: A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:11–20, 2015
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, Roy D, Jovin TG, Willinsky RA, Sapkota BL, Dowlatshahi D, Frei DF, Kamal NR, Montanera WJ, Poppe AY, Ryckborst KJ, Silver FL, Shuaib A, Tampieri D, Williams D, Bang OY, Baxter BW, Burns PA, Choe H, Heo JH, Holmstedt CA, Jankowitz B, Kelly M, Linares G, Mandzia JL, Shankar J, Sohn SI, Swartz RH, Barber PA, Coutts SB, Smith EE, Morrish WF, Weill A, Subramaniam S, Mitha AP, Wong JH, Lowerison MW, Sajobi TT, Hill MD: Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:1019–1030, 2015
Campbell BCV, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, Yan B, Dowling RJ, Parsons MW, Oxley TJ, Wu TY, Brooks M, Simpson MA, Miteff F, Levi CR, Krause M, Harrington TJ, Faulder KC, Steinfort BS, Priglinger M, Ang T, Scroop R, Barber PA, McGuinness B, Wijeratne T, Phan TG, Chong W, Chandra RV, Bladin CF, Badve M, Rice H, de Villiers L, Ma H, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM: Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 372:1009–1018, 2015
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Albers GW, Cognard C, Cohen DJ, Hacke W, Jansen O, Jovin TG, Mattle HP, Nogueira RG, Siddiqui AH, Yavagal DR, Baxter BW, Devlin TG, Lopes DK, Reddy VK, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Singer OC, Jahan R: Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 372:2285–2295, 2015
Campbell BCV, Mitchell PJ, Yan B, Parsons MW, Christensen S, Churilov L, Dowling RJ, Dewey H, Brooks M, Miteff F, Levi C, Krause M, Harrington TJ, Faulder KC, Steinfort BS, Kleinig T, Scroop R, Chryssidis S, Barber A, Hope A, Moriarty M, McGuinness B, Wong AA, Coulthard A, Wijeratne T, Lee A, Jannes J, Leyden J, Phan TG, Chong W, Holt ME, Chandra RV, Bladin CF, Badve M, Rice H, de Villiers L, Ma H, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM, EXTEND-IA investigators: A multicenter, randomized, controlled study to investigate extending the time for thrombolysis in emergency neurological deficits with intra-arterial therapy (EXTEND-IA). Int J Stroke 9:126–132, 2014
Endovascular treatment for small core and anterior circulation proximal occlusion with emphasis on minimizing CT to recanalization times (ESCAPE). Available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01778335. Accessed Apr 2019
Solitaire™ FR with the intention for thrombectomy as primary endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke (SWIFT PRIME) clinical trial. Available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01657461. Accessed Apr 2019
Fransen PSS et al.: MR CLEAN, a multicenter randomized clinical trial of endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke in the Netherlands: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 15:343, 2014
Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC, Bonafe A, Budzik RF, Bhuva P, Yavagal DR, Ribo M, Cognard C, Hanel RA, Sila CA, Hassan AE, Millan M, Levy EI, Mitchell P, Chen M, English JD, Shah QA, Silver FL, Pereira VM, Mehta BP, Baxter BW, Abraham MG, Cardona P, Veznedaroglu E, Hellinger FR, Feng L, Kirmani JF, Lopes DK, Jankowitz BT, Frankel MR, Costalat V, Vora NA, Yoo AJ, Malik AM, Furlan AJ, Rubiera M, Aghaebrahim A, Olivot JM, Tekle WG, Shields R, Graves T, Lewis RJ, Smith WS, Liebeskind DS, Saver JL, Jovin TG, DAWN Trial Investigators: Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med 378:11–21, 2018
Albers GW, Marks MP, Kemp S, Christensen S, Tsai JP, Ortega-Gutierrez S, McTaggart R, Torbey MT, Kim-Tenser M, Leslie-Mazwi T, Sarraj A, Kasner SE, Ansari SA, Yeatts SD, Hamilton S, Mlynash M, Heit JJ, Zaharchuk G, Kim S, Carrozzella J, Palesch YY, Demchuk AM, Bammer R, Lavori PW, Broderick JP, Lansberg MG, DEFUSE 3 Investigators: Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med 378:708–718, 2018
Lo EH: A new penumbra: transitioning from injury into repair after stroke. Nat Med 14:497–500, 2008
Paciaroni M, Caso V, Agnelli G: The concept of ischemic penumbra in acute stroke and therapeutic opportunities. Eur Neurol 61:321–330, 2009
Schlaug G, Benfield A, Baird AE, Siewert B, Lovblad KO, Parker RA, Edelman RR, Warach S: The ischemic penumbra: Operationally defined by diffusion and perfusion MRI. Neurology 53:1528–1537, 1999
Neumann-Haefelin T, Wittsack HJ̈, Wenserski F, Siebler M, Seitz R̈J, Mödder U, Freund HJ: Diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MRI. The DWI/PWI mismatch region in acute stroke. Stroke 30:1591–1597, 1999
Heiss W-D: The ischemic penumbra: correlates in imaging and implications for treatment of ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 32:307–320, 2011
Forkert ND, Kaesemann P, Treszl A, Siemonsen S, Cheng B, Handels H, Fiehler J, Thomalla G: Comparison of 10 TTP and Tmax estimation techniques for MR perfusion-diffusion mismatch quantification in acute stroke. Am J Neuroradiol 34:1697–1703, 2013
Straka M, Albers GW, Bammer R: Real-time diffusion-perfusion mismatch analysis in acute stroke. J Magn Reson Imaging 32:1024–1037, 2010
Jacobs MA, Knight RA, Soltanian-Zadeh H, Zheng ZG, Goussev AV, Peck DJ, Windham JP, Chopp M: Unsupervised segmentation of multiparameter MRI in experimental cerebral ischemia with comparison to T2, diffusion, and ADC MRI parameters and histopathological validation. J Magn Reson Imaging 11:425–437, 2000
Maier O, Menze BH, von der Gablentz J, Ḧani L, Heinrich MP, Liebrand M, Winzeck S, Basit A, Bentley P, Chen L, Christiaens D, Dutil F, Egger K, Feng C, Glocker B, Götz M, Haeck T, Halme HL, Havaei M, Iftekharuddin KM, Jodoin PM, Kamnitsas K, Kellner E, Korvenoja A, Larochelle H, Ledig C, Lee JH, Maes F, Mahmood Q, Maier-Hein KH, McKinley R, Muschelli J, Pal C, Pei L, Rangarajan JR, Reza SMS, Robben D, Rueckert D, Salli E, Suetens P, Wang CW, Wilms M, Kirschke JS, Kr Amer UM, Münte TF, Schramm P, Wiest R, Handels H, Reyes M: ISLES 2015 - a public evaluation benchmark for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation from multispectral MRI. Med Image Anal 35:250–269, 2017
Mah Y-H, Jager R, Kennard C, Husain M, Nachev P: A new method for automated high-dimensional lesion segmentation evaluated in vascular injury and applied to the human occipital lobe. Cortex 56:51–63, 2014
Charoensuk W, Covavisaruch N, Lerdlum S, Likitjaroen Y: Acute stroke brain infarct segmentation in DWI images. Int J Pharma Med Biol Sci 4:115–122, 2015
Rosen BR, Belliveau JW, Vevea JM, Brady TJ: Perfusion imaging with NMR contrast agents. Magn Reson Med 14:249–265, 1990
Østergaard L, Weisskoff RM, Chesler DA, Gyldensted C, Rosen BR: High resolution measurement of cerebral blood flow using intravascular tracer bolus passages. Part I: mathematical approach and statistical analysis. Magn Reson Med 36:715–725, 1996
Calamante F, Christensen S, Desmond PM, Østergaard L, Davis SM, Connelly A: The physiological significance of the time-to-maximum (Tmax) parameter in perfusion MRI. Stroke 41:1169–1174, 2010
Fieselmann A, Kowarschik M, Ganguly A, Hornegger J, Fahrig R: Deconvolution-based CT and MR brain perfusion measurement: theoretical model revisited and practical implementation details. J Biomed Imaging 2011:1–20, 2011
Calamante F: Arterial input function in perfusion MRI: a comprehensive review. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 74:1–32, 2013
Shih LC et al.: Perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging thresholds identifying core, irreversibly infarcted tissue. Stroke 34:125–1430, 2003
Funding
This research was financially supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI12C1847).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the local institutional review board. Due to the retrospective nature of the study, written informed consent was waived.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H., Jung, K., Kang, DW. et al. Fully Automated and Real-Time Volumetric Measurement of Infarct Core and Penumbra in Diffusion- and Perfusion-Weighted MRI of Patients with Hyper-Acute Stroke. J Digit Imaging 33, 262–272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-019-00222-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-019-00222-2