Abstract
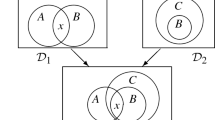
In this paper we will present a graph-transformation based method for the verification of heterogeneous first order logic (FOL) and Euler/Venn proofs. In previous work, it has been shown that a special collection of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) can be used interchangeably with Euler/Venn diagrams in reasoning processes. Thus, proofs which include Euler/Venn diagrams can be thought of as proofs with DAGs where steps involving only Euler/Venn diagrams can be treated as particular DAG transformations. Here we will show how the characterization of these manipulations can be used to verify Euler/Venn proofs. Also, a method for verifying the use of heterogeneous Euler/Venn and FOL reasoning rules will be presented that is also based upon DAG transformations .
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barwise J, Etchemendy J (1994) Hyperproof. CSLI Publications, Stanford
Dretske FI (1969) Seeing and Knowing. Chicago University Press, Chicago
Flower J, Howse J (2002) Generating euler diagrams. In: Hegarty et al. [7], pp 61–75
Gil JY, Howse J, Kent S (1999) Constraint diagrams: a step beyond uml. In: Proceedings TOOLS USA. IEEE Computer Society Press, pp 453–463
Gil JY, Howse J, Kent S (1999) Formalising spider diagrams. In: Proceedings IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages (VL99). IEEE Computer Society Press, pp 130–137
Hammer EM (1995) Logic and Visual Information. CSLI and FOLLI, Stanford
Hegarty M, Meyer B, Narayanan NH (eds) (2002) Diagrammatic Representation and Inference. Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, vol 2317. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Howse J, Molina F, Taylor J, Kent S, Gil JY (2001) Spider diagrams: A diagrammatic reasoning system. Journal of Visual Languages and Computing 12(3):299–324, June
Howse J, Stapleton G, Flower J, Taylor J (2002) Corresponding regions in euler diagrams. In: Hegarty et al. [7], pp 76–90
Kent S (1997) Constraint diagrams: visualizing invariants in object-oriented models. In: Proceedings of the 1997 ACM SIGPLAN conference on Object-oriented programming systems, languages and applications. ACM Press, pp 327–341
Rumbaugh J, Jacobson I, Booch G (1999) Unified Modeling Language Reference Manual. Addison Wesley Professional
Sawamura H, Kiyozuka K (2000) Jvenn: A visual reasoning system with diagrams and sentences. In: Anderson M, Cheng P, Haarslev V (eds) Theory and Application of Diagrams, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, vol 1889. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 271–285
Shin S-J (1995) The Logical Status of Diagrams. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Swoboda N (2002) Implementing Euler/Venn reasoning systems. In: Anderson M, Meyer B, Olivier P (eds) Diagrammatic Representation and Reasoning. Springer-Verlag, London, pp 371–386
Swoboda N, Allwein G (2002) A case study of the design and implementation of heterogeneous reasoning systems. In: Magnani L, Nersessian NJ, Pizzi C (eds) Logical and Computational Aspects of Model-Based Reasoning. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 3–20
Swoboda N, Allwein G (2002) Modeling heterogeneous systems. In: Hegarty et al. [7], pp 131–145
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swoboda, N., Allwein, G. Using DAG transformations to verify Euler/Venn homogeneous and Euler/Venn FOL heterogeneous rules of inference. Softw Syst Model 3, 136–149 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-003-0044-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-003-0044-8