Abstract
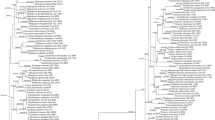
Polyporus longiporus, belonging to group Polyporellus, is newly reported from Japan in what also constitutes the second report of the species since its original description. This species is characterized by radially elongated pores, smooth and brown to dark brown pileus, and cylindrical and slightly curved basidiospores. Phylogenetic analysis based on the ITS region revealed that P. longiporus forms a terminal, strongly supported clade that is closely related to P. ciliatus. A description and illustrations of the present species and a key to the species of group Polyporellus are provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernicchia A (2005) Polyporaceae s.l. Edizioni Candusso, Alassio
Boulet B (2003) Les champignons des arbres de l’est de l’ Amérique du Nord. Les Publications du Québec, Québec
Dai Y-C (1996) Changbai wood-rotting fungi 5. Study on Polyporus mongolicus and P. tubaeformis. Ann Bot Fenn 33:153–163
Dai Y-C (2009) Type studies on polypores described by J.D. Zhao, either alone or with other mycologists. Ann Bot Fenn (in press)
Domański S, Orłaś H, Skirgiełło A (1967) Fungi. Polyporaceae II (pileatae) Mucronoporaceae II (pileatae) Ganodermataceae, Bondarzewiaceae, Boletopsidaceae, Fistulinaceae (Grzyby), revised edition. Translated from Polish. Foreign scientific publications department of the National Center for Scientific, Technical, and Economic Information, Warsaw, 1973
Gilbertson RL, Ryvarden L (1987) North American polypores, vol. 2. Fungiflora, Oslo
Hibbett DS, Donoghue MJ (1995) Progress toward a phylogenetic classification of the Polyporaceae through parsimony analyses of mitochondrial ribosomal DNA sequences. Can J Bot 73(suppl 1): S853–S861
Hibbett DS, Thorn RG (2001) Basidiomycota: Homobasidiomycetes. In: McLaughlin FJ, McLaughlin EG, Lemke PA (eds) Systematics and evolution. The Mycota, vol VII. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 121–168
Hoffmann P, Esser K (1978) Genetics of speciation in the basidiomycetous genus Polyporus. Theor Appl Genet 53:273–282
Holmgren PK, Holmgren NH, Barnett LC (1990) Index herbariorum. Part 1: The herbaria of the world, 8th edn. New York Botanical Garden, New York
Käärik A (1965) The identification of the mycelia of wood-decay fungi by their oxidation reactions with phenolic compounds. Bibl Mycol 81:1–151
Katoh T (2008) Recent developments in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Brief Bioinform 9:286–298 (preprint)
Kreisel H (1963) Über Polyporus brumalis und verwandte Arten. Feddes Repert 68:129–138
Krüger D, Gargas A (2004) The basidiomycete genus Polyporus: an emendation based on phylogeny and putative secondary structure of ribosomal RNA molecules. Feddes Repert 115:530–546
Krüger D, Hughes KW, Petersen RH (2004) The tropical Polyporus tricholoma (Polyporaceae): taxonomy, phylogeny, and the development of methods to detect cryptic species. Mycol Prog 3:65–80
Nobles MK (1965) Identification of cultures of wood-inhabiting Hymenomycetes. Can J Bot 43:1097–1139
Núñez M, Ryvarden L (1995a) Polyporus (Basidiomycotina) and related genera. Synopsis Fungorum 10:1–85
Núñez M, Ryvarden L (1995b) Polyporus new to Japan 1. Species of Polyporus, with a note on P. hartmanni. Mycoscience 36:61–65
Núñez M, Ryvarden L (2001) East Asian polypores 2. Polyporaceae s. lato. Synopsis Fungorum 14:170–522
Overholts LO (1953) Polyporaceae of the United States, Alaska and Canada. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Pegler DN (1983) The genus Lentinus: a world monograph. Kew Bull Addit Ser 10:1–281
Pilát A (1940) Basidiomycetes chinenses. Ann Mycol 38:61–82
Silveira RMB, Wright JE (2002) Polyporus s. str. in southern South America: mating tests. Mycol Res 106:1323–1330
Silveira RMB, Wright JE (2005) The taxonomy of Echinochaete and Polyporus s. str. in South America. Mycotaxon 93:1–59
Sotome K, Hattori T, Kakishima M (2007) Polyporus phyllostachydis sp. nov. with notes on other rhizophilic species of Polyporus (Basidiomycota, Polyporaceae). Mycoscience 48:42–46
Sotome K, Hattori T, Ota Y, To-anun C, Salleh B, Kakishima M (2008) Phylogenetic relationships of Polyporus and morphologically allied genera. Mycologia 100:603–615
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP 4.0b10: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Zhao J-D (1998) Flora fungorum sinicorum, vol. 3. Polyporaceae. Science Press, Beijing
Zhao J-D, Zhang X-Q (1992) The polypores of China. Bibl Mycol 145:1–524
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sotome, K., Hattori, T., Ota, Y. et al. Second report of Polyporus longiporus and its phylogenetic position. Mycoscience 50, 415–420 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10267-009-0506-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10267-009-0506-0