Abstract
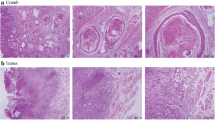
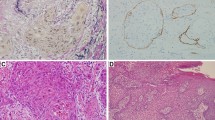
Cervical lymph node (CLN) metastasis from oral cancer correlates with poor prognosis. Therefore, accurate assessment of CLN status is crucial in treatment planning. However, there are few reports focusing on CLN metastasis from tongue cancer. Further, the growth and progress of the tumor are known to be profoundly related to histological malignancy, tumor angiogenesis, and lymphangiogenesis. Thus, this study aimed to identify predictive factors for CLN metastasis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Initial biopsy specimens obtained from 30 patients with tongue SCC were examined to evaluate histological malignancy according to Anneroth’s classification. In addition, blood vessel density, lymph vessel density, and lymphatic invasion in the tumor were evaluated immunohistochemically using CD31, CD34, D2-40, and AE1/AE3, and then the relationships of CLN metastasis to these parameters were investigated. Histological malignancy grade, blood vessel density, and lymphatic invasion were significantly related to CLN metastasis (P < 0.05), but there was no relationship between lymph vessel density and CLN metastasis. However, double immunostaining showed that lymphatic invasion by tumor cells was significantly related to CLN metastasis. The results indicate that Anneroth’s histological malignancy grade of 16 or more, tumor blood vessel density of more than 37, and the presence of lymphatic invasion by tumor cells can be predictive factors for CLN metastases in tongue SCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamamoto E, Miyakawa A, Kohama G-I. Mode of invasion and lymph node metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Head Neck Surg 1984;6:938–947.
Lim SC, Zhang S, Ishii G, Endoh Y, Kodama K, Miyamoto S, Hayashi R, Ebihara S, Cho JS, Ochiai A. Predictive markers for late cervical metastasis in stage I and II invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:166–172.
Woolgar JA. Histological distribution of cervical lymph node metastases from intraoral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1999;37:175–180.
Okada Y, Mataga I, Katagiri M, Ishii K. An analysis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma: relationship between grade of histological malignancy and lymph nodes metastasis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2003;32:284–288.
Warburton G, Nikitakis NG, Roberson P, Marinos NJ, Wu T, Sauk JJ Jr, Ord RA, Wahl SM. Histopathological and lymphangiogenic parameters in relation to lymph node metastasis in early stage oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007;65:475–484.
Avery JK, Strachan DS. Histology of the oral mucosa and tonsils. In: Avery JK, editor. Oral development and histology. 3rd ed. New York: Thieme; 2001. p. 243–262.
Kai Y. Radiological study of the vascularization of DMBA induced hamster tongue cancer. Odontology 1986;73:1525–1545.
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis — Correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1991;324:1–8.
Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1995;1:27–31.
Okada Y, Kato J, Katagiri M. A clinicopathologic study of autopsy cases with oral malignant tumors. Odontology 1996;84:255–274.
Smith BD, Smith GL. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor protein levels in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2000;18:2046–2052.
Beasley NJP, Prevo R, Banerji S, Leek RD, Moore J, van Trappen P, Cox G, Harris AL, Jackson DG. Intratumoral lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 2002;62:1315–1320.
Kishimoto K, Sasaki A, Yoshihama Y, Mese H, Tsukamoto G, Matsumura T. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C predicts regional lymph node metastasis in early oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 2003;39:391–396.
Anneroth G, Batsakis J, Luna M. Review of the literature and a recommended system of malignancy grading in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Scand J Dent Res 1987;95:229–249.
Robbins KT, Clayman G, Levine PA, Medina J, Sessions R, Shaha A, Som P, Wolf GT, and the Committee for Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology, American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. Neck dissection classification update, revisions proposed by the American Head and Neck Society and the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2002;128:751–758.
Robbins KT, Shaha AR, Medina JE, Califano JA, Wolf GT, Ferlito A, Som PM, Day TA, for the Committee for Neck Dissection Classification, American Head and Neck Society. Consensus statement on the classification and terminology of neck dissection. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2008;134:536–538.
Lindberg R. Distribution of cervical lymph node metastases from squamous cell carcinoma of the upper respiratory and digestive tracts. Cancer 1972;29:1446–1449.
Woolgar JA. Detailed topography of cervical lymph-node metastases from oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1997;26:3–9.
Segawa A. Clinical and pathological studies on metastasis to the cervical lymph node of head and neck carcinoma. Dent J Iwate Med Univ 2003;28:213–227.
Woolgar JA. The topography of cervical lymph node metastases revisited: the histological findings in 526 sides of neck dissection from 439 previously untreated patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007;36:219–225.
Broders AC. Squamous cell epithelioma of the lip. JAMA 1920;74:656–664.
Arthur JF, Fenner ML. The influence of histological grading of prognosis in carcinoma of the tongue (A computer analysis of 299 cases). Clin Radiol 1966;17:384–396.
Jakobsson PÅ, Eneroth C-M, Killander D, Moberger G, Mårtensson B. Histologic classification and grading of malignancy in carcinoma of the larynx. Acta Radiol Ther Phys Biol 1973;12:1–8.
Willen R, Nathanson A, Moberger G, Anneroth G. Squamous cell carcinoma of the gingiva. Histological classification and grading of malignancy. Acta Otolaryngol 1975;79:146–154.
Lund C, Sogaard H, Elbrond O, Jorgensen K, Andersen AP. Epidermoid carcinoma of the tongue: histologic grading in the clinical evaluation. Acta Radiol 1975;14:513–521.
Holm L-E, Lundquist P-G, Silfversward C, Sobin A. Histological grading of malignancy in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Acta Otolaryngol 1982;94:185–192.
Leu AJ, Berk DA, Lymboussaki A, Alitalo K, Jain RK. Absence of functional lymphatics within a murine sarcoma: A molecular and functional evaluation. Cancer Res 2000;60:4324–4327.
Kaipainen A, Korhonen J, Mustonen T, van Hinsbergh VW, Fang GH, Dumont D, Breitman M, Alitalo K. Expression of the fms-like tyrosine kinase 4 gene becomes restricted to lymphatic endothelium during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995;92:3566–3570.
Kahn HJ, Bailey D, Marks A. Monoclonal antibody D2-40, a new marker of lymphatic endothelium, reacts with Kaposi’s sarcoma and a subset of angiosarcoma. Mod Pathol 2002;15:434–440.
Niki T, Iba S, Tokunou M, Yamada T, Matsuno Y, Hirohashi S. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A, B, C, and D and their relationships to lymph node status in lung adenocarcinoma, Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:2431–24
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo R, Riccardi L, Alitalo K, Claffey K, Detmar M. Inducation of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat Med 2001;7:192–198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, Y. Relationships of cervical lymph node metastasis to histopathological malignancy grade, tumor angiogenesis, and lymphatic invasion in tongue cancer. Odontology 98, 153–159 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-010-0131-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-010-0131-6