Abstract
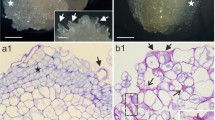
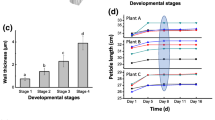
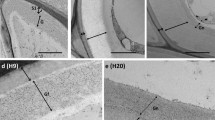
The Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume) ‘Huaihuang’ was chosen as the experimental material to observe embryogenesis and the dynamic changes of cell wall components during this process. Various developmental stages of embryos, including globular embryos, heart embryos, torpedo embryos and cotyledon embryos, were observed. The results showed that during embryogenesis, cellulose increased, and callose rapidly degraded. In the cell walls of developing embryos, pectic homogalacturonan (HG), especially low-esterified HG, was abundant, suggesting rapid synthesis and de-methyl-esterification of HG. Extensin and galactan increased with the development of the embryos. In contrast, the arabinan epitopes decreased in developing embryos but were more abundant than galactan epitopes at all stages. Xylan epitopes showed explicit boundaries between the outer epidermal wall and the rest of the inner tissues, and the fluorescence intensity of the outer epidermal wall was significantly higher than that of the inner tissues. Furthermore, the results indicated that the outer epidermal wall contained high amounts of cellulose, HG pectin and hemicellulose, especially arabinan and xylan. These results suggested the presence of rapid pectin metabolism, cellulose synthesis, rapid degradation of callose, different distributive patterns and dynamic changes of hemicellulose (galactan, arabinan and xylan) and extensin during embryogenesis. Various cell wall components exist in different tissues of the embryo, and dynamic changes in cell wall components are involved in the embryonic development process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albersheim P, Jh AN, Freshour G, Fuller MS, Darvill A, Huang J, Whitcombe A (1994) Structure and function studies of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Biochem Soc Trans 22:374. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0220374
Barany I, Fadon B, Risueno MC, Testillano PS (2010) Cell wall components and pectin esterifification levels as markers of proliferation and differentiation events during pollen development and pollen embryogenesis in Capsicum annuum. J Exp Bot 61:1159–1175. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp392
Baronepel O, Gharyal PK, Schindler M (1988) Pectins as mediators of wall porosity in soybean cells. Planta 175:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396345
Beeckman T, Przemeck GK (2002) Genetic complexity of cellulose synthase a gene function in arabidopsis embryogenesis. Plant Physiol 130:1883–1893. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.010603
Bertin N, Lecomte A, Brunel B, Fishman S, Genard M (2007) A model describing cell polyploidization in tissues of growing fruit as related to cessation of cell proliferation. J Exp Bot 58:1903–1913. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erm0
Bethke G, Thao A, Xiong G, Li B, Soltis NE, Hatsugai N (2016) Pectin biosynthesis is critical for cell wall integrity and immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 28:537–556. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00404
Bidhendi AJ, Geitmann A (2015) Relating the mechanics of the primary plant cell wall to morphogenesis. J Exp Bot 67:449–461. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv535
Bowling AJ, Vaughn KC, Turley RB (2011) Polysaccharide and glycoprotein distribution in the epidermis of cotton ovules during early fiber initiation and growth. Protoplasma 248:579–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-010-0212-y
Carpita N, Gibeaut DM (1993) Structural models of primary cell walls in flowering plants: consistency of molecylar structure with the physical properties of the walls during growth. Plant J 3:1–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.1993.tb00007.x
Chapman A, Slomianny C, Vasseur J, Blervacq AS, Théo H, Hilbert JL (2000) Cell wall differentiation during early somatic embryogenesis in plants. II. Ultrastructural study and pectin immunolocalization on chicory embryos. Can J Bot 78:816–823. https://doi.org/10.1139/b00-059
Chen HW, Persson S, Grebe M, Mcfarlane HE (2018) Cellulose synthesis during cell plate assembly. Physiol Plant 164:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12703
Chen D, Melton LD, Zujovic Z, Harris PJ (2019) Developmental changes in collenchyma cell-wall polysaccharides in celery (Apium graveolens) petioles. BMC Plant Biol 19:81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.1993.tb00007.x
Cosgrove DJ, Jarvis MC (2012) Comparative structure and biomechanics of plant primary and secondary cell walls. Front Plant Sci 3:204. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00204
de Vries SC, Weijers D (2017) Plant embryogenesis. Curr Biol 27:R870–R873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.05.026
Dheilly E, Gall SL, Guillou MC, Renou JP, Bonnin E, Orsel M (2016) Cell wall dynamics during apple development and storage involves hemicellulose modifications and related expressed genes. BMC Plant Biol 16:201. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0887-016-0887-0
Dobrowolska I, Majchrzak O, Baldwin TC, Kurczynska EU (2012) Differences in protodermal cell wall structure in zygotic and somatic embryos of Daucus carota cultured on solid and in liquid media. Protoplasma 249:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-011-0268-3
Fang KF, Zhang WW, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Yang L, Cao QQ, Qin L (2016) Boron toxicity causes multiple effects on Malus domestica pollen tube growth. Front Plant Sci 7:208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00208
Fang KF, Du BS, Zhang Q, Xing Y, Cao QQ, Qin L (2019) Boron deficiency alters cytosolic Ca2+ concentration affects the cell wall components of pollen tubes in Malus domestica. Plant Biol 21:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.1
Francin-Allami M, Alvarado C, Guillon F (2019) Spatial and temporal distribution of cell wall polysaccharides during grain development of Brachypodium distachyon. Plant Sci 280:367–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.12.0
Francisca M, Castillo J, Daniel F (2018) Expansin genes expression in growing ovaries and grains of sunflower are tissue-specific and associate with final grain weight. BMC Plant Biol 18:327. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-15357
Fujita M, Wasteneys GO (2013) A survey of cellulose microfibril patterns in dividing, expanding, and differentiating cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. Protoplasma 251:687–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-013-0571-2
Gillaspy G, Ben-David H, Gruissem W (1993) Fruits: a developmental perspective. Plant Cell 5:1439–1451. https://doi.org/10.2307/3869794
Gomez LD, Steele-King CG, Jones L, Foster JM, Mcqueen-Mason SJ (2009) Arabinan metabolism during seed development and germination in arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2:966–976. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssp050
Goulao LF, Oliveira CM (2008) Cell wall modifications during fruit ripening: when a fruit is not the fruit. Trends Food Sci Tech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2007.07.002
Goulao LF, Santos J, Sousa ID, Oliveira CM (2007) Patterns of enzymatic activity of cell wall-modifying enzymes during growth and ripening of apples. Postharvest Biol Technol 43:307–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.10
Grantham NJ, Wurman-Rodrich J, Terrett OM, Lyczakowski JJ, Stott K, Iuga D (2017) An even pattern of xylan substitution is critical for interaction with cellulose in plant cell walls. Nat Plants 3:859–865. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-017-0030-8
Ingram G, Nawrath C (2017) The roles of the cuticle in plant development: organ adhesions and beyond. J Exp Bot 68:5307–5321. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx313
Javelle M, Vernoud V, Ingram RGC (2011) Epidermis: the formation and functions of a fundamental plant tissue. New Phytol 189:17–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03514.x
Jones L, Milne JL, Ashford D, McQueen-Mason SJ (2003) Cell wall arabinan is essential for guard cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:11783–11788. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1832434100
Lee YK, Ayeh KO, Ambrose M, Hvoslef-Eide AK (2016) Immunolocalization of pectic Polysaccharides during abscission in pea seeds (Pisum sativum) and in abscission less def pea mutant seeds. BMC Res Notes 9:427. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-016-2231-z
Levesque-Tremblay G, Pelloux J, Braybrook SA, Müller K (2015a) Tuning of pectin methylesterification: consequences for cell wall biomechanics and development. Planta 242:791–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2358-5
Levesque-Tremblay G, Müller K, Mansfield SD, Haughn GW (2015b) Highly methylesterified seeds, is a pectin methylesterase involved in embryo development. Plant Physiol 167:725–737. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.255604
Lionetti V, Cervone F, Bellincampi D (2012) Methyl esterification of pectin plays a role during plant-pathogen interactions and affects plant resistance to diseases. J Plant Physiol 169:1623–1630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2
Liu HZ, Zhang GS, Zhu WW, Ba QS, Niu N, Wang JW (2015) Relationship between male sterility and Î2-1,3-glucanase activity and callose deposition-related gene expression in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Genet Mol Res 14:574. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.January.26.12
Lockhart JA, Bretz C, Kenner R (2006) An analysis of cell wall extension. Ann NY Acad Sci 144:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb33998.x
Lu P, Porat R, Nadeau JA, O’Neill SD (1996) Identification of a meristem L1 layer-specific gene in Arabidopsis that is expressed during embryonic pattern formation and defines a new class of homeobox genes. Plant Cell 8:2155–2168. https://doi.org/10.2307/3870458
Luna E, Pastor V, Robert J, Flors V, Mauch-Mani B, Ton J (2011) Callose deposition: a multifaceted plant defense response. Mol Plant Microbe In 24:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-07-10-0149
Malinowski R, Filipecki M (2002) The role of cell wall in plant embryogenesis. Cell Mol Biol Lett 7:1137–1151. https://doi.org/10.0000/PMID12511981
Mansfield SG, Gordonweeks PR (1991) Dynamic post-translational modification of tubulin in rat cerebral cortical neurons extending neurites in culture: effects of taxol. J Neurocytol 20:654–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01187067
Moussu S, San-Bento R, Galletti R, Creff A, Farcot E, Ingram G (2013) Embryonic cuticle establishment: the great (apoplastic) divide. Plant Signal Behav 8:e27491. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.27491
Nguemaona E, Vicrégibouin M, Gotté M, Plancot B, Lerouge P, Bardor M (2014) Cell wall o-glycoproteins and n-glycoproteins: aspects of biosynthesis and function. Front Plant Sci 5:499. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00499
Palmer R, Cornuault Marcus SE, Knox JP, Shewry PR, Tosi P (2015) Comparative in situ analyses of cell wall matrix polysaccharide dynamics in developing rice and wheat grain. Planta 241:669–685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2201-4
Palovaara J, de Zeeuw T, Weijers D (2016) Tissue and organ initiation in the plant embryo: a first time for everything. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 32:47–756. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-111315-124929
Parra-Vega V, Corral-Martínez P, Alba RS, Seguí-Simarro JM (2015) Induction of embryogenesis in Brassica napus microspores produces a callosic subintinal layer and abnormal cell walls with altered levels of callose and cellulose. Front Plant Sci 6:1018. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01018
Peralta AG, Venkatachalam S, Stone SC, Pattathil S (2017) Xylan epitope profiling: an enhanced approach to study organ development-dependent changes in xylan structure, biosynthesis, and deposition in plant cell walls. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:245. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0935-5
Pérez-Pérez Y, Carneros E, Berenguer E, Solís MT, Bárány I, Pintos B, Gómez-Garay A, Risueño MC, Testillano PS (2019) Pectin de-methylesterification and AGP increase promote cell wall remodeling and are required during somatic embryogenesis of Quercus Suber. Front Plant Sci. 9:1915. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01915
Prasanna V, Prabha TN, Tharanathan RN (2007) Fruit ripening phenomena–an overview. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 47:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390600976841
Rivas-Sendra A, Corral-Martínez P, Seguí-Simarro JM (2019) Embryogenic competence of microspores is associated with their ability to form a callosic, osmoprotective subintinal layer. J Exp Bot 70:1267–1281. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery458
Rodríguez-Sanz H, Manzanera JA, Solís MT (2014) Early markers are present in both embryogenesis pathways from microspores and immature zygotic embryos in cork oak (Quercus suber L). BMC Plant Biol 14:224. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0224-4
Sakai K, Taconnat L, Borrega N (2018) Combining laser-assisted microdissection (lam) and rna-seq allows to perform a comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of epidermal cells of arabidopsis embryo. Plant Methods 14:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-018-0275-x
Segado P, Domínguez E, Heredia A (2016) Ultrastructure of the epidermal cell wall and cuticle of tomato fruit (Solanum lycopersicum) during development. Plant Physiol 170:935–946. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01725
Sene C, Mccann MC, Wilson RH, Grinter R (1994) Fourier-transform raman and fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (an investigation of five higher plant cell walls and their components). Plant Physiol 106:1623–1631. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.4.1623
Shi Z, Stösser R (2005) Reproductive biology of Chinese Chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume). Eur J Hortic Sci 70:96–103
Solís MT, Berenguer E, Risueno MC, Testillano PS (2016) Bnpme is progressively induced after microspore reprogramming to embryogenesis, correlating with pectin de-esterification and cell differentiation in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol 16:176. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0863-8
Somerville C, Bauer S, Youngs H (2004) Toward a systems approach to understanding plant cell walls. Science 306:2206–2211. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102765
Soriano M, Li H, Boutilier K (2013) Microspore embryogenesis: establishment of embryo identity and pattern in culture. Plant Reprod 26:181–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-013-0226-7
Takada S, Jurgens G (2007) Transcriptional regulation of epidermal cell fate in the arabidopsis embryo. Development 134:1141–1150. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02803
Tan L, Pu Y, Pattathil S, Avci U, Qian J, Arter A (2014) Changes in cell wall properties coincide with overexpression of extensin fusion proteins in suspension cultured tobacco cells. PLoS One 9:e115906. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115906
Tao L, Yang Y, Wang Q, You X (2012) Callose deposition is required for somatic embryogenesis in plasmolyzed Eleutherococcus senticosus zygotic embryos. Int J Mol Sci 13:14115–14126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114115
Taylor NG, Gardiner JC, Whiteman R, Turner SR (2004) Cellulose synthesis in the arabidopsis secondary cell wall. Cellulose 11:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:cell.0000046405.11326.a8
Terao A, Hyodo H, Satoh S, Iwai H (2013) Changes in the distribution of cell wall polysaccharides in early fruit pericarp and ovule, from fruit set to early fruit development, in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). J Plant Res 126:719–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-013-0555-5
Turbant A, Fournet F, Lequart M, Zabijak L, Pageau K, Bouton S (2016) Pme58 plays a role in pectin distribution during seed coat mucilage extrusion through homogalacturonan modification. J Exp Bot 67:2177–2190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-013-0555-5
Ulvskov P, Wium H, Bruce D, Sørensen SO (2005) Biophysical consequences of remodeling the neutral side chains of rhamnogalacturonan I in tubers of transgenic potatoes. Planta 220:609–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1373-8
Velasquez SM, Ricardi MM, Dorosz JG, Fernandez PV, Nadra AD, Pol-Fachin L (2011) O-glycosylated cell wall proteins are essential in root hair growth. Science 332:1401–1403. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1206657
Vincken JP, Schols HA, Visser RG (2003) If homogalacturonan were a side chain of rhamnogalacturonan I implications for cell wall architecture. Plant Physiol 132:1781–1789. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.022350
Willats WG, Steele-King CG, Marcus SE, Knox JP (1999) Side chains of pectic polysaccharides are regulated in relation to cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Plant J 20:619–628
Willats WG, Orfila C, Knox JP (2001) Modulation of the degree and pattern of methyl-esterification of pectic homogalacturonan in plant cell walls. Implications for pectin methyl esterase action, matrix properties, and cell adhesion. J Biol Chem 276:19404–19413. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M011242200
Woodenberg WR, Pammenter NW, Farrant JM, Driouich A, Berjak P (2015) Embryo cell wall properties in relation to development and desiccation in the recalcitrant-seeded Encephalartos natalensis (zamiaceae) dyer and verdoorn. Protoplasma 252:245–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0672-6
Yoshida S, Barbier RP, Lane B, Prusinkiewicz P, Smith RS, Weijers D (2014) Genetic control of plant development by overriding a geometric division rule. Dev Cell 29:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.02.002
Zablackis E, Huang J, Darvill AG, Albersheim P (1995) Characterization of the cell-wall polysaccharides of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant Physiol 107:1129–1138. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.4.1129
Zykwinska AW, Ralet MCJ, Thibault GJFJ (2005) Evidence for in vitro binding of pectin side chains to cellulose. Plant Physiol 139:397–407. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.065912
Zykwinska A, Thibault JF, Ralet MC (2007) Organization of pectic arabinan and galactan side chains in association with cellulose microfibrils in primary cell walls and related models envisaged. J Exp Bot 58:1795–1802. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erm037
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270719), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD1000605), the Project of Construction of Innovative Teams and Teacher Career Development for Universities and Colleges Under Beijing Municipality (IDHT20180509), Beijing Nature Science Foundation (KZ201710020012) and the Supporting Plan for Cultivating High Level Teachers in Colleges and Universities in Beijing (CIT&TCD20180317).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KF and LQ designed the research and edited the paper; BD performed the main experiments and drafted the paper; QZ, QC and YX revised the paper. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, B., Zhang, Q., Cao, Q. et al. Changes of cell wall components during embryogenesis of Castanea mollissima. J Plant Res 133, 257–270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-020-01170-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-020-01170-7