Abstract
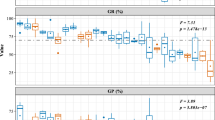
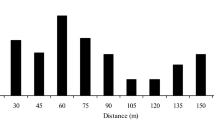
We evaluated the degree of selfing and inbreeding depression at the seed and seedling stages of a threatened tropical canopy tree, Neobalanocarpus heimii, using microsatellite markers. Selection resulted in an overall decrease in the level of surviving selfed progeny from seeds to established seedlings, indicating inbreeding depression during seedling establishment. Mean seed mass of selfed progeny was lower than that of outcrossed progeny. Since the smaller seeds suffered a fitness disadvantage at germination in N. heimii, the reduced seed mass of selfed progeny would be one of the determinants of the observed inbreeding depression during seedling establishment. High selfing rates in some mother trees could be attributed to low local densities of reproductive individuals, thus maintenance of a sufficiently high density of mature N. heimii should facilitate regeneration and conservation of the species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appanah S (1979) The ecology of insect pollination of some Malaysian rain forest trees. PhD Thesis, University of Malaya
Appanah S, Weinland G (1993) Planting quality timber trees in peninsular Malaysia—a review. Forest Research Institute of Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur
Ashton PS (1982) Dipterocarpaceae. Flora Malesiana Ser I Spermatophyta 9:237–552
Bawa KS (1998) Conservation of gengetic resources in the Dipterocarpaceae. In: Appanah S, Turnbull JM (eds) A review of dipterocarps: taxonomy, ecology and silviculture. Center for International Forestry Research, Bogor, pp 45–55
Bonfil C (1998) The effects of seed size, cotyledon reserves, and herbivory on seedling survival and growth in Quercus rugosa and Q. laurina (Fagaceae). Am J Bot 85:79–87
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B (1987) Inbreeding depression and its evolutionary consequences. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:237–268
Frankham R, Ballou JD, Briscoe DA (2002) Introduction to conservation genetics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hall P, Walker S, Bawa KS (1996) Effect of forest fragmentation on genetic diversity and mating system in a tropical tree, Pithecellobium elegans. Conserv Biol 10:757–768
Hufford KM, Hamrick JL (2003) Viability selection at three early life stages of the tropical tree, Platypodium elegans (Fabaceae , Papilionoideae). Evolution 57:518–526
Husband BC, Schemske DW (1996) Evolution of the magnitude and timing of inbreeding depression in plants. Evolution 50:54–70
IUCN (2003) IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. http://www.redlist.org. Downloaded on 3 March 2004
Iwata H, Konuma A, Tsumura Y (2000) Development of microsatellite markers in the tropical tree Neobalanocarpus heimii (Dipterocarpaceae). Mol Ecol 9:1684–1685
Khan ML (2004) Effects of seed mass on seedling success in Artocarpus heterophyllus L., a tropical tree species of north-east India. Acta Oecologica 25:103–110
Kitamura K, Rahman MYBA, Ochiai Y, Yoshimaru H (1994) Estimation of the outcrossing rate on Dryobalanops aromatica Gaertn. f. in primary and secondary forests in Brunei, Borneo, Southeast Asia. Plant Species Biol 9:37–41
Konuma A, Tsumura Y, Lee CT, Lee SL, Okuda T (2000) Estimation of gene flow in the tropical-rainforest tree Neobalanocarpus heimii (Dipterocarpaceae), inferred from paternity analysis. Mol Ecol 9:1843–1852
Lee SL (2000) Mating system parameters of Dryobalanopus aromatica Gaertn. f. (Dipterocarpaceae) in three different forest types and a seed orchard. Heredity 85:338–345
Lee SL, Wickneswar R, Mahani MC, Zakari AH (2000) Mating system parameters in a tropical tree species, Shorea leprosula Miq. (Dipterocarpaceae) from Malaysian lowland dipterocarp forest. Biotrop 32:693–702
Marshall TC (2001) CERVUS ver. 2.0 Available at http://helios.bto.ed.ac.uk/evolgen
Marshall TC, Slate J, Kruuk LEB, Pemberton JM (1998) Statistical confidence for likelihood-based paternity inference in natural populations. Mol Ecol 7:639–655
Murawski DA, Bawa KS (1994) Genetic structure and mating system of Stemonoporus oblongifolius (Dipterocarpaceae) in Sri Lanka. Am J Bot 81:155–160
Murawski DA, Hamrick JL (1991) The effect of the density of flowering individuals on the mating systems of nine tropical tree species. Heredity 67:167–174
Murawski DA, Hamrick JL, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1990) Mating systems of two Bombacaceous trees of a neotropical moist forest. Oecologia 82:501–506
Murawski DA, Gunatilleke IAUN, Bawa KS (1994a) The effect of selective logging on inbreeding in Shorea megistophylla (Dipterocarpaceae) from Sri Lanka. Conserv Biol 8:997–1002
Murawski DA, Dayanandan B, Bawa KS (1994b) Outcrossing rates of two endemic Shorea species from Sri Lankan tropical rain forests. Biotrop 26:23–29
Nagamitsu T, Ichikawa S, Ozawa M, Shimamura R, Kachi N, Tsumura Y, Norwati M. (2001) Microsatellite analysis of the breeding system and seed dispersal in Shorea leprosula (Dipterocarpaceae). Int J Plant Sci 162:155–159
Nei M (1977) F-statics and analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Ann Hum Genet 41:225–233
Nei M, Syakudo K (1958) The estimation of outcrossing in natural populations. Jpn J Genet 33:46–51
Obayashi K, Tsumura Y, Ihara-Ujino T, Niiyama K, Tanouchi H, Suyama Y, Washitani I, Lee CT, Lee SL, Norwati M. (2002) Genetic diversity and outcrossing rate between undisturbed and selectively logged forests of Shorea curtisii (Dipterocarpaceae) using microsattellite DNA analysis. Int J Plant Sci 163:151–158
Seiwa K (2000) Effects of seed size and emergence time on tree seedling establishment: importance of developmental constraints. Oecologia 123:208–215
Stanton ML (1984) Seed variation in wild radish: effect of seed size on components of seedling and adult fitness. Ecology 65:1105–1112
Symington CF (2004) Forester’s manual of dipterocarps (2nd edn., revised by Ashton PS, Appanah S). Malayan Forest Records no. 16. pp. 519. Forest Research Institute Malaysia and Malaysian Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur
Tripathi RS, Khan ML (1990) Effects of seed weight and microsite characteristics on germination and seedling fitness in two species of Quercus in a subtropical wet hill forest. Oikos 57:289–296
Tsumura Y, Kawahara T, Wickneswari R, Yoshimura K (1996) Molecular phylogeny of Dipterocarpaceae in Southeast Asia using RFLP of PCR-amplified chloroplast genes. Theor Appl Genet 93:22–29
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. M. Yasuda for helpful discussions and permission to use his unpublished data; members of the Genetics Unit of FRIM for their assistance with laboratory work and nursery experiments; and Ms. Y. Kawamata, Ms. K. Obayashi, and Ms. Y. Takeuchi for their assistance during sample processing and collection. We also thank Mr. Quah and Ms. K Obayashi for their assistance in plot construction and field observations. Many thanks are also due to the members of the Genome Analysis Laboratory of the Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute and Tohoku University, and two anonymous reviewers for their invaluable comments and helpful discussions. This study was part of a joint research project undertaken by FRIM, Universiti Putera Malaysia, and Japan’s National Institute for Environmental Studies (Global Environment Research Program supported by the Ministry of Environment in Japan, grant no. E-4). The study was also partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 15405026) provided by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naito, Y., Konuma, A., Iwata, H. et al. Selfing and inbreeding depression in seeds and seedlings of Neobalanocarpus heimii (Dipterocarpaceae). J Plant Res 118, 423–430 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-005-0245-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-005-0245-z