Abstract
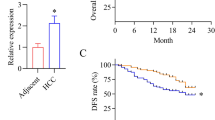
Recently, many studies show that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play important roles in cancer biology. Although its expression was reported dysregulated during tumorigenesis, the contributions of lncRNAs to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are still largely unknown. In particular, the lncRNA CARLo-5 has a functional role in cell-cycle regulation in colon cancer, while the clinical significance and biological function of CARLo-5 in HCC remain unelucidated. In order to fill those study blanks, the expression level of CARLo-5 in human HCC specimens was tested, and its correlation with clinicopathologic features as well as the prognosis for patients with HCC was analyzed. Additionally, MTT, wound healing and transwell assays were employed to investigate the biological function of CARLo-5. The results showed that CARLo-5 levels were significantly overexpressed in HCC tissues compared to ANLT. Besides, high expression of CARLo-5 was associated with liver cirrhosis (P = 0.001), tumor number (P < 0.001), vascular invasion (P = 0.001), capsular formation (P = 0.014) and Edmondson–Steiner grade (P < 0.001), which proved that CARLo-5 was an independent risk factor for overall survival and disease-free survival. In addition, in highly metastatic HCC cell lines (HCCLM3 and MHCC97-L), CARLo-5 was up-regulated, but in lowly metastatic HCC cell lines (HepG2, SNU387), it showed down-regulated. Besides, by using gain and loss of function experiments in HCC cell lines (HCCLM3 and HepG2), the results showed that CARLo-5 overexpression significantly enhanced cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. Our study also revealed that CARLo-5 was prominently up-regulated in HCC specimens and its high expression was associated with poor prognosis of HCC patients. Totally, those findings together indicate that CARLo-5 promotes proliferation and metastasis of HCC and potentially emerged as a novel therapeutic target.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Feng GS. Conflicting roles of molecules in hepatocarcinogenesis: paradigm or paradox. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:150–4.
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–55.
El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–27.
Cheng W, Zhang Z, Wang J. Long noncoding RNAs: new players in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013;339:8–14.
Huang JL, Zheng L, Hu YW, Wang Q. Characteristics of long non-coding RNA and its relation to hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:507–14.
Maass PG, Luft FC, Bahring S. Long non-coding RNA in health and disease. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014;92:337–46.
Panzitt K, Tschernatsch MM, Guelly C, et al. Characterization of HULC, a novel gene with striking up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma, as noncoding RNA. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:330–42.
Lai MC, Yang Z, Zhou L, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT-1 overexpression predicts tumor recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Med Oncol. 2012;29:1810–6.
Wang F, Yuan JH, Wang SB, et al. Oncofetal long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and stem cell-like property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilizing NOP2. Hepatology. 2014;60:1278–90.
Quagliata L, Matter MS, Piscuoglio S, et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTTIP/HOXA13 expression is associated with disease progression and predicts outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Hepatology. 2014;59:911–23.
Yuan SX, Tao QF, Wang J, et al. Antisense long non-coding RNA PCNA-AS1 promotes tumor growth by regulating proliferating cell nuclear antigen in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2014;349:87–94.
Kim T, Cui R, Jeon YJ, et al. Long–range interaction and correlation between MYC enhancer and oncogenic long noncoding RNA CARLo-5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:4173–8.
Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:674–87.
Bruix J, Gores GJ, Mazzaferro V. Hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut. 2014;63:844–55.
Yuan JH, Yang F, Wang F, et al. A long noncoding RNA activated by TGF-beta promotes the invasion-metastasis cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:666–81.
Malz M, Bovet M, Samarin J, et al. Overexpression of far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein (FBP)-interacting repressor (FIR) supports growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2014;60:1241–50.
Pedica F, Ruzzenente A, Bagante F, et al. A re-emerging marker for prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: the add-value of fishing c-myc gene for early relapse. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e68203.
Ding J, Huang S, Wu S, et al. Gain of miR-151 on chromosome 8q24.3 facilitates tumour cell migration and spreading through downregulating RhoGDIA. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:390–9.
Pomerantz MM, Ahmadiyeh N, Jia L, et al. The 8q24 cancer risk variant rs6983267 shows long–range interaction with MYC in colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2009;41:882–4.
Ahmadiyeh N, Pomerantz MM, Grisanzio C, et al. 8q24 prostate, breast, and colon cancer risk loci show tissue-specific long–range interaction with MYC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:9742–6.
Sur IK, Hallikas O, Vaharautio A, et al. Mice lacking a Myc enhancer that includes human SNP rs6983267 are resistant to intestinal tumors. Science. 2012;338:1360–3.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by medical innovation subject of Fujian Province (2009-CXB-58).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There were no financial disclosures from any authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Xie, C., Zhao, W. et al. Long non-coding RNA CARLo-5 expression is associated with disease progression and predicts outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin Exp Med 17, 33–43 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-015-0395-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-015-0395-9