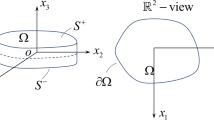
Abstract
Electric fields can be focused by micropipette-based electrodes to induce stresses on cell membranes leading to tension and poration. To date, however, these membrane stress distributions have not been quantified. In this study, we determine membrane tension, stress, and strain distributions in the vicinity of a microelectrode using finite element analysis of a multiscale electro-mechanical model of pipette, media, membrane, actin cortex, and cytoplasm. Electric field forces are coupled to membranes using the Maxwell stress tensor and membrane electrocompression theory. Results suggest that micropipette electrodes provide a new non-contact method to deliver physiological stresses directly to membranes in a focused and controlled manner, thus providing the quantitative foundation for micreoelectrotension, a new technique for membrane mechanobiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinlaja J, Sachs F (1998) The breakdown of cell membranes by electrical and mechanical stress. Biophys J 75:247–254
Ashkin A, Dziedzic JM, Yamane T (1987) Optical trapping and manipulation of single cells using infrared laser beams. Nature 330:769–771
Bae C, Butler PJ (2006) Automated single-cell electroporation. Biotechniques 41:399–400, 402
Bausch AR, Ziemann F, Boulbitch AA, Jacobson K, Sackmann E (1998) Local measurements of viscoelastic parameters of adherent cell surfaces by magnetic bead microrheometry. Biophys J 75:2038–2049
Charras GT, Williams BA, Sims SM, Horton MA (2004) Estimating the sensitivity of mechanosensitive ion channels to membrane strain and tension. Biophys J 87:2870–2884
Crowley JM (1973) Electrical breakdown of biomolecular lipid-membranes as an electromechanical instability. Biophysical J 13:711–724
Dai J, Sheetz MP (1999) Membrane tether formation from blebbing cells. Biophys J 77:3363–3370
Ermolina I, Polevaya Y, Feldman Y (2000) Analysis of dielectric spectra of eukaryotic cells by computer modeling. Eur Biophys J 29:141–145
Evans EA, Waugh R, Melnik L (1976) Elastic area compressibility modulus of red cell membrane. Biophys J 16:585–595
Fung YC, Liu SQ (1993) Elementary mechanics of the endothelium of blood vessels. J Biomech Eng 115:1–12
Gosse C, Croquette V (2002) Magnetic tweezers: micromanipulation and force measurement at the molecular level. Biophys J 82:3314–3329
Helfrich W (1974) Deformation of lipid bilayer spheres by electric fields. Z Naturforsch [C] 29:182–183
Isambert H (1998) Understanding the electroporation of cells and artificial bilayer membranes. Phy Rev Lett 80:3404–3407
Khine M, Lau A, Ionescu-Zanetti C, Seo J, Lee LP (2005) A single cell electroporation chip. Lab Chip 5:38–43
Kinosita K Jr, Ashikawa I, Saita N, Yoshimura H, Itoh H, Nagayama K, Ikegami A (1988) Electroporation of cell membrane visualized under a pulsed-laser fluorescence microscope. Biophys J 53:1015–1019
Kinosita K Jr, Tsong TY (1979) Voltage-induced conductance in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 554:479–497
Ko YTC, Huang JP, Yu KW (2004) The dielectric behaviour of single-shell spherical cells with a dielectric anisotropy in the shell. J Phys Condensed Matter 16:499–509
Kummrow M, Helfrich W (1991) Deformation of giant lipid vesicles by electric fields. Phys Rev A 44:8356–8360
Lundqvist JA, Sahlin F, Aberg MA, Stromberg A, Eriksson PS, Orwar O (1998) Altering the biochemical state of individual cultured cells and organelles with ultramicroelectrodes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10356–10360
Needham D, Hochmuth RM (1989) Electro-mechanical permeabilization of lipid vesicles. Role of membrane tension and compressibility. Biophys J 55:1001–1009
Nolkrantz K, Farre C, Brederlau A, Karlsson RI, Brennan C, Eriksson PS, Weber SG, Sandberg M, Orwar O (2001) Electroporation of single cells and tissues with an electrolyte-filled capillary. Anal Chem 73:4469–4477
Rae JL, Levis RA (2002) Single-cell electroporation. Pflugers Arch 443:664–670
Rand RP, Burton AC (1964) Mechanical properties of red cell membrane. I. Membrane stiffness + intracellular pressure. Biophys J 4:115
Riske KA, Dimova R (2005) Electro-deformation and poration of giant vesicles viewed with high temporal resolution. Biophys J 88:1143–1155
Riske KA, Dimova R (2006) Electric pulses induce cylindrical deformations on giant vesicles in salt solutions. Biophys J 91:1778–1786
Satcher R, Dewey CF Jr, Hartwig JH (1997) Mechanical remodeling of the endothelial surface and actin cytoskeleton induced by fluid flow. Microcirculation 4:439–453
Sato M, Levesque MJ, Nerem RM (1987) Micropipette aspiration of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells exposed to shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 7:276–286
Sens P, Isambert H (2002) Undulation instability of lipid membranes under an electric field. Phys Rev Lett 88:128102
Simon SA, McIntosh TJ (1986) Depth of water penetration into lipid bilayers. Methods Enzymol 127:511–521
Svoboda K, Block SM (1994) Biological applications of optical forces. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23:247–285
Tang Y, Cao G, Chen X, Yoo J, Yethiraj A, Cui Q (2006) A finite element framework for studying the mechanical response of macromolecules: application to the gating of the mechanosensitive channel MscL. Biophys J 91:1248–1263
Teissie J, Golzio M, Rols MP (2005) Mechanisms of cell membrane electropermeabilization: a minireview of our present (lack of ?) knowledge. Biochim Biophys Acta 1724:270–280
Tracqui P, Ohayon J (2004) Transmission of mechanical stresses within the cytoskeleton of adherent cells: a theoretical analysis based on a multi-component cell model. Acta Biotheor 52:323–341
Weaver JC (1993) Electroporation: a general phenomenon for manipulating cells and tissues. J Cell Biochem 51:426–435
Weaver JC (1995) Electroporation theory. Concepts and mechanisms. Methods Mol Biol 55:3–28
Zhang PC, Keleshian AM, Sachs F (2001) Voltage-induced membrane movement. Nature 413:428–432
Zhelev DV, Needham D (1993) Tension-stabilized pores in giant vesicles: determination of pore size and pore line tension. Biochim Biophys Acta 1147:89–104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, C., Butler, P.J. Finite element analysis of microelectrotension of cell membranes. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 7, 379–386 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-007-0093-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-007-0093-y