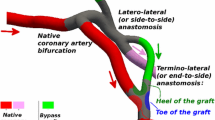
Abstract
Recent development of computational technology allows a level of knowledge of biomechanical factors in the healthy or pathological cardiovascular system that was unthinkable a few years ago. In particular, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and computational structural (CS) analyses have been used to evaluate specific quantities, such as fluid and wall stresses and strains, which are very difficult to measure in vivo. Indeed, CFD and CS offer much more variability and resolution than in vitro and in vivo methods, yet computations must be validated by careful comparison with experimental and clinical data. The enormous parallel development of clinical imaging such as magnetic resonance or computed tomography opens a new way toward a detailed patient-specific description of the actual hemodynamics and structural behavior of living tissues. Coupling of CFD/CS and clinical images is becoming a standard evaluation that is expected to become part of the clinical practice in the diagnosis and in the surgical planning in advanced medical centers. This review focuses on computational studies of fluid and structural dynamics of a number of vascular anastomoses: the coronary bypass graft anastomoses, the arterial peripheral anastomoses, the arterio-venous graft anastomoses and the vascular anastomoses performed in the correction of congenital heart diseases.













Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ballyk PD, Steinman DA, Ethier CR (1994) Simulation of non-Newtonian blood flow in an end-to-side anastomosis. Biorheology 31:565–586
Ballyk PD, Walsh C, Butany J, Ojha M (1998) Compliance mismatch may promote graft-artery intimal hyperplasia by altering suture-line stresses. J Biomech 31:229–237
Barnea O, Santamore WP, Rossi A, Salloum E, Chien S, Austin EH (1998) Estimation of oxygen delivery in newborns with a univentricular circulation. Circulation 98:1407–1413
Bassiouny HS, White S, Glagov S, Choi E, Giddens DP, Zarins CK (1992) Anastomotic intimal hyperplasia: mechanical injury or flow induced. J Vasc Surg 15:708–716
Bathe M, Kamm RD (1999) A fluid-structure interaction finite element analysis of pulsatile blood flow through a compliant stenotic artery. J Biomech Eng 121:361–369
Berthier B, Bouzerar R, Legallais C (2002) Blood flow patterns in an anatomically realistic coronary vessel: influence of three different reconstruction methods. J Biomech 35:1347–1356
Bertolotti C, Deplano V (2000) Three-dimensional numerical simulations of flow through a stenosed coronary bypass. J Biomech 33:1011–1122
Bertolotti C, Deplano V, Fuseri J, Dupouy P (2001) Numerical and experimental models of post-operative realistic flows in stenosed coronary bypasses. J Biomech 34:1049–1064
Bolzon G, Pedrizzetti G, Grigioni M, Zovatto L, Daniele C, D’Avenio G (2002) Flow on the symmetry plane of a total cavo-pulmonary connection. J Biomech 35:595–608
Bonert M, Myers JG, Fremes S, Williams J, Ethier CR (2002) A numerical study of blood flow in coronary artery bypass graft side-to-side anastomoses. Ann Biomed Eng 30:599–611
Boutsianis E, Dave H, Frauenfelder T, Poulikakos D, Wildermuth S, Turina M, Ventikos Y, Zund G (2004) Computational simulation of intracoronary flow based on real coronary geometry. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 26:248–256
Bove EL, de Leval MR, Migliavacca F, Guadagni G, Dubini G (2003) Computational fluid dynamics in the evaluation of hemodynamic performance of cavopulmonary connections after the Norwood procedure for hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 126:1040–1047
Bryant SR, Bjercke RJ, Erichsen DA, Rege A, Lindner V (1999) Vascular remodeling in response to altered blood flow is mediated by fibroblast growth factor-2. Circ Res 84:323–328
Cavalcanti S, Tura A (1999) Hemodynamic and mechanical performance of arterial grafts assessed by numerical simulation: a design oriented study. Artif Organs 23:175–185
Cole JS, Watterson JK, O’Reilly MJ (2002a) Is there a haemodynamic advantage associated with cuffed arterial anastomoses? J Biomech 35:1337–1346
Cole JS, Wijesinghe LD, Watterson JK, Scott DJ (2002b) Computational and experimental simulations of the haemodynamics at cuffed arterial bypass graft anastomoses. Proc Inst Mech Eng [H] 216:135–143
Cole JS, Watterson JK, O’Reilly MJ (2002c) Numerical investigation of the haemodynamics at a patched arterial bypass anastomosis. Med Eng Phys 24:393–401
Crawshaw H M, Quist W C, Serrallach E, Valeri R, Logerfo FW (1980) Flow disturbance at the distal end-to-side anastomosis. Arch Surg 115:1280–1284
De Hart J, Baaijens FP, Peters GW, Schreurs PJ (2003a) A computational fluid-structure interaction analysis of a fiber-reinforced stentless aortic valve. J Biomech 36:699–712
De Hart J, Peters GW, Schreurs PJ, Baaijens FP (2003b) A three-dimensional computational analysis of fluid-structure interaction in the aortic valve. J Biomech 36:103–112
De Hart J, Peters GW, Schreurs PJ, Baaijens FP (2004) Collagen fibers reduce stresses and stabilize motion of aortic valve leaflets during systole. J Biomech 37:303–311
DeGroff C, Shandas R (2002) Designing the optimal total cavopulmonary connection: pulsatile versus steady flow experiments. Med Sci Monit 8:MT41-MT45
DeGroff CG, Shandas R, Kwon J, Valdes-Cruz L (2000) Accuracy of the Bernoulli equation for estimation of pressure gradient across stenotic Blalock-Taussig shunts: an in vitro and numerical study. Pediatr Cardiol 21:439–447
Deplano V, Bertolotti C, Boiron O (2001) Numerical simulations of unsteady flows in a stenosed coronary bypass graft. Med Biol Eng Comput 39:488–499
Di Martino ES, Guadagni G, Fumero A, Ballerini G, Spirito R, Biglioli P, Redaelli A (2001) Fluid-structure interaction within realistic three-dimensional models of the aneurysmatic aorta as a guidance to assess the risk of rupture of the aneurysm. Med Eng Phys 23:647–655
Dobrin PB, Littooy FN, Endean ED (1989) Mechanical factors predisposing to intimal hyperplasia and medial thickening in autogenous vein grafts. Surgery 105:393–400
Douglas WI, Goldberg CS, Mosca RS, Law IH, Bove EL (1999) The hemi-Fontan procedure for hypoplastic left heart syndrome: Intermediate outcome and suitability for Fontan. Ann Thor Surg 68:1361–1368
Dubini G, de Leval MR, Pietrabissa R, Montevecchi FM, Fumero R (1996) A numerical fluid mechanical study of repaired congenital heart defects. Application to the total cavopulmonary connection. J Biomech 29:111–121
Ene-Iordache B, Mosconi L, Remuzzi G, Remuzzi A (2001) Computational fluid dynamics of a vascular access case for hemodialysis. J Biomech Eng 123:284–292
Ensley AE, Lynch P, Chatzimavroudis GP, Lucas C, Sharma S, Yoganathan AP (1999) Toward designing the optimal total cavopulmonary connection: an in vitro study. Ann Thorac Surg 68:1384–1390
Ethier CR, Steinman DA, Zhang X, Karpik SR, Ojha M (1998) Flow waveform effects on end-to-side anastomotic flow patterns. J Biomech 31:609–617
Fei DY, Thomas JD, Rittgers SE (1994) The effect of angle and flow rate upon hemodynamics in distal vascular graft anastomoses: a numerical model study. J Biomech Eng 116:331–336
Fisher RK, How TV, Bakran A, Brennan JA, Harris PL (2004) Outflow distribution at the distal anastomosis of infrainguinal bypass grafts. J Biomech 37:417–420
Gasser TC, Schulze-Bauer CA, Holzapfel GA (2002) A three-dimensional finite element model for arterial clamping. J Biomech Eng 124:355–363
Gerdes A, Kunze J, Pfister G, Sievers HH (1999) Addition of a small curvature reduces power losses across total cavopulmonary connections. Ann Thorac Surg 67:1760–1764
Glagov S, Zarins C, Giddens DP, Ku DN (1988) Hemodynamics and atherosclerosis: insights and perspectives gained from studies of human arteries. Arch Pathol Lab Med 112:1018–1031
Grigioni M, Daniele C, Del Gaudio C, Morbiducci U, Balducci A, D’Avenio G, Amodeo A, Barbaro V, Di Donato R (2003) Numerical simulation of a realistic total cavo-pulmonary connection: effect of unbalanced pulmonary resistances on hydrodynamic performance. Int J Artif Organs 26:1005–1014
Guo LR, Steinman DA, Moon BC, Wan WK, Millsap RJ (2001) Effect of distal graft anastomosis site on retrograde perfusion and flow patterns of native coronary vasculature. Ann Thorac Surg 72:782–787
Haller JA, Adkins JC, Worthington M, Ravenhorst J (1966) Experimental studies on permanent bypass of the right heart. Surgery 59:1128–1132
Haruguchi H, Teraoka S (2003) Intimal hyperplasia and hemodynamic factors in arterial bypass and arteriovenous grafts: a review. J Artif Organs 6:227–235
Healy TM, Lucas C, Yoganathan AP (2001) Noninvasive fluid dynamic power loss assessments for total cavopulmonary connections using the viscous dissipation function: a feasibility study. J Biomech Eng 123:317–324
Henry FS, Collins MW, Hughes PE, How TV (1996) Numerical investigation of steady flow in proximal and distal end-to-side anastomoses. J Biomech Eng 118:302–310
Henry FS, Kupper C, Lewington NP (2002) Simulation of flow through a Miller cuff bypass graft. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 5:207–217
Hodgson L, Tarbell JM (2002) Solute transport to the endothelial intercellular cleft: the effect of wall shear stress. Ann Biomed Eng 30:936–945
Hofer M, Rappitsch G, Perktold K, Trubel W, Schima H (1996) Numerical study of wall mechanics and fluid dynamics in end-to-side anastomoses and correlation to intimal hyperplasia. J Biomech 29:1297–1308
Houlind K, Stenbog EV, Sorensen KE, Emmertsen K, Hansen OK, Rybro L, Hjortdal VE (1999) Pulmonary and caval flow dynamics after total cavopulmonary connection. Heart 81:67–72
Hughes PE, How TV (1995) Flow structures at the proximal side-to-end anastomosis: influence of geometry and flow division. J Biomech Eng 117:224–236
Ibrahim J, Miyashiro JK, Berk BC (2003) Shear stress is differentially regulated among inbred rat strains. Circ Res 92:1001–1009
Inzoli F, Migliavacca F, Pennati G (1996) Numerical analysis of steady flow in aorto-coronary bypass 3-D model. J Biomech Eng 118:172–179
Jackson MJ, Bicknell CD, Zervas V, Cheshire NJ, Sherwin SJ, Giordana S, Peiro J, Papaharilaou Y, Doorly DJ, Caro CG (2003) Three-dimensional reconstruction of autologous vein bypass graft distal anastomoses imaged with magnetic resonance: clinical and research applications. J Vasc Surg 38:621–625
Kaazempur-Mofrad MR, Ethier CR (2001) Mass transport in an anatomically realistic human right coronary artery. Ann Biomed Eng 29:121–127
Karner G, Perktold K, Zehentner HP (2001) Computational modeling of macromolecule transport in the arterial wall. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 4:491–504
Khunatorn Y, Mahalingam S, DeGroff CG, Shandas R (2002) Influence of connection geometry and SVC-IVC flow rate ratio on flow structures within the total cavopulmonary connection: a numerical study. J Biomech Eng 124:364–377
Kim YH, Chandran KB (1993) Steady flow analysis in the vicinity of an end-to-end anastomosis. Biorheology 30:117–130
Kim YH, Chandran KB, Bower TJ, Corson JD (1993) Flow dynamics across end-to-end vascular bypass graft anastomoses. Ann Biomed Eng 21:311–320
Kim YH, Walker PG, Fontaine AA, Panchal S, Ensley AE, Oshinski J, Sharma S, Ha B, Lucas CL, Yoganathan AP (1995) Hemodynamics of the Fontan connection: an in-vitro study. J Biomech Eng 117:423–428
Kirpalani A, Park H, Butany J, Johnston KW, Ojha M (1999) Velocity and wall shear stress patterns in the human right coronary artery. J Biomech Eng 121:370–375
Kitagawa T, Katoh I, Fukumura Y, Masuda Y, Hori T (1995) Achieving optimal pulmonary blood flow in the first-stage palliation in early infancy for complex cardiac defects with hypoplastic left ventricles. Cardiol Young 5:21–27
Kleinstreuer C, Lei M, Archie JP Jr (1996) Flow input waveform effects on the temporal and spatial wall shear stress gradients in a femoral graft-artery connector. J Biomech Eng 118:506–510
Kleinstreuer C, Hyun S, Buchanan JR Jr, Longest PW, Archie JP Jr, Truskey GA (2001) Hemodynamic parameters and early intimal thickening in branching blood vessels. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 29:1–64
Korshunov VA, Berk BC (2004) Strain-dependent vascular remodeling: the “Glagov phenomenon” is genetically determined. Circulation 110:220–226
Krueger U, Zanow J, Scholz H (2000) Comparison of two different arteriovenous anastomotic forms by numerical 3D simulation of blood flow. Int J Angiol 9:226–231
Krueger U, Zanow J, Scholz H (2002) Computational fluid dynamics and vascular access. Artif Organs 26:571–575
Ku DN, Giddens DP, Zarins CK, Glagov S (1985) Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 5:293–302
Ku JP, Draney MT, Arko FR, Lee WA, Chan FP, Pelc NJ, Zarins CK, Taylor CA (2002) In vivo validation of numerical prediction of blood flow in arterial bypass grafts. Ann Biomed Eng 30:743–752
Kute SM, Vorp DA (2001) The effect of proximal artery flow on the hemodynamics at the distal anastomosis of a vascular bypass graft: computational study. J Biomech Eng 123:277–283
Laganà K, Dubini G, Migliavacca F, Pietrabissa R, Pennati G, Veneziani A, Quarteroni A (2002) Multiscale modelling as a tool to prescribe realistic boundary conditions for the study of surgical procedures. Biorheology 39:359–364
Laganà K, Balossino R, Migliavacca F, Pennati G, Bove EL, de Leval MR, Dubini G (2005) Pulmonary and coronary perfusions in univentricular circulation assessed by CFD multiscale models. J Biomech (in press)
Lardo AC, Webber SA, Friehs I, del Nido PJ, Cape EG (1999a) Fluid dynamic comparison of intra-atrial and extracardiac total cavopulmonary connections. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 117:697–704
Lardo AC, Webber SC, Iyengar A, del Nido PJ, Friehs I, Cape EG (1999b) Bidirectional superior cavopulmonary anastomosis improves mechanical efficiency in dilated atriopulmonary connections. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 188:681–691
Lee D, Su JM, Liang HY (2001) A numerical simulation of steady flow fields in a bypass tube. J Biomech 34:1407–1416
Lei M, Kleinstreuer C, Archie JP Jr (1996) Geometric design improvements for femoral graft-artery junctions mitigating restenosis. J Biomech 29:1605–1614
Lei M, Kleinstreuer C, Archie JP (1997a) Hemodynamic simulations and computer-aided designs of graft-artery junctions. J Biomech Eng 119:343–348
Lei M, Archie JP, Kleinstreuer C (1997b) Computational design of a bypass graft that minimizes wall shear stress gradients in the region of the distal anastomosis. J Vasc Surg 25:637–646
Lei M, Giddens DP, Jones SA, Loth F, Bassiouny H (2001) Pulsatile flow in an end-to-side vascular graft model: comparison of computations with experimental data. J Biomech Eng 123:80–87
Lemmon JD, Yoganathan AP (2000) Three-dimensional computational model of left heart diastolic function with fluid-structure interaction. J Biomech Eng 122:109–117
Leuprecht A, Perktold K, Prosi M, Berk T, Trubel W, Schima H (2002) Numerical study of hemodynamics and wall mechanics in distal end-to-side anastomoses of bypass grafts. J Biomech 35:225–236
de Leval MR, McKay R, Jones M, Stark J, Macartney FJ (1981) Modified Blalock–Taussig shunt. Use of subclavian artery orifice as flow regulator in prosthetic systemic-pulmonary artery shunts. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 81:112–119
de Leval MR, Kilner P, Gewillig M, Bull C (1988) Total cavopulmonary connection: a logical alternative to atriopulmonary connection for complex Fontan operations. Experimental studies and early clinical experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 96:682–695
de Leval MR, Dubini G, Migliavacca F, Jalali H, Camporini G, Redington A, Pietrabissa R (1996) Use of computational fluid dynamics in the design of surgical procedures: application to the study of competitive flows in cavo-pulmonary connections. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 111:502–513
Longest PW, Kleinstreuer C (2000) Computational haemodynamics analysis and comparison study of arterio-venous grafts. J Med Eng Technol 24:102–110
Longest PW, Kleinstreuer C (2003a) Particle-hemodynamics modeling of the distal end-to-side femoral bypass: effects of graft caliber and graft-end cut. Med Eng Phys 25:843–858
Longest PW, Kleinstreuer C (2003b) Numerical simulation of wall shear stress conditions and platelet localization in realistic end-to-side arterial anastomoses. J Biomech Eng 125:671–681
Longest PW, Kleinstreuer C, Archie JP Jr (2003) Particle hemodynamics analysis of Miller cuff arterial anastomosis. J Vasc Surg 38:1353–1362
Loth F, Fischer PF, Arslan N, Bertram CD, Lee SE, Royston TJ, Shaalan WE, Bassiouny HS (2003) Transitional flow at the venous anastomosis of an arteriovenous graft: potential activation of the ERK1/2 mechanotransduction pathway. J Biomech Eng 125:49–61
Low HT, Chew YT, Lee CN (1993) Flow studies on atriopulmonary and cavopulmonary connections of the Fontan operations for congenital heart defects. J Biomed Eng 15:303–307
Lutostansky EM, Karner G, Rappitsch G, Ku DN, Perktold K (2003) Analysis of hemodynamic fluid phase mass transport in a separated flow region. J Biomech Eng 125:189–196
McGiffin DC, McGiffin PB, Galbraith AJ, Cross RB (1992) Aortic wall stress profile after repair of coarctation of the aorta. It is related to subsequent true aneurysm formation? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 104:924–931
McQueen DM, Peskin CS, Yellin EL (1982) Fluid dynamics of the mitral valve: physiological aspects of a mathematical model. Am J Physiol 242:H1095–H1110
Melbin J, Ho PC (1997) Stress reduction by geometric compliance matching at vascular graft anastomoses. Ann Biomed Eng 25:874–881
Migliavacca F, de Leval MR, Dubini G, Pietrabissa R (1996) A computational pulsatile model of the bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis: the influence of pulmonary forward flow. J Biomech Eng 118:520–528
Migliavacca F, Dubini G, Pietrabissa R, de Leval MR (1997) Computational transient simulations with varying degree and shape of pulmonic stenosis in models of the bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis. Med Eng Phys 19:394–403
Migliavacca F, de Leval MR, Dubini G, Pietrabissa R, Fumero R (1999b) Computational fluid dynamic simulations of cavopulmonary connections with an extracardiac lateral conduit. Med Eng Phys 23:187–193
Migliavacca F, Kilner PJ, Pennati G, Dubini G, Pietrabissa R, Fumero R, de Leval MR (1999a) Computational fluid dynamic and magnetic resonance analyses of flow distribution between lungs after total cavopulmonary connection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 46:393–399
Migliavacca F, Yates R, Pennati G, Dubini G, Fumero R, de Leval MR (2000b) Calculating blood flow from Doppler measurements in the systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt. A method based on computational fluid dynamics. Ultrasound Med Biol 26:209–219
Migliavacca F, Dubini G, Pennati G, Pietrabissa R, Fumero R, Hsia T-Y, de Leval MR (2000a) Computational model of the fluid dynamics in systemic-to-pulmonary shunts. J Biomech 33:549–557
Migliavacca F, Pennati G, Dubini G, Pietrabissa R, Fumero R, Urcelay G, Bove EL, Hsia T-Y, de Leval MR (2001) Modeling of the Norwood circulation: effects of shunt size vascular resistances and heart rate. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280:H2076–H2086
Migliavacca F, Pennati G, Di Martino E, Dubini G, Pietrabissa R (2002) Pressure drops in a distensible model of end-to-side anastomosis in systemic-to-pulmonary shunts. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 5:243–248
Migliavacca F, Dubini G, Bove EL, de Leval MR (2003) Computational fluid dynamics simulations in realistic 3-D geometries of the total cavopulmonary anastomosis: the influence of the inferior caval anastomosis. J Biomech Eng 125:805–813
Moore JA, Steinman DA, Prakash S, Johnston KW, Ethier CR (1999) A numerical study of blood flow patterns in anatomically realistic and simplified end-to-side anastomoses. J Biomech Eng 121:265–272
Moyle K (2003) Heamodynamics of the Fontan connection. PhD Thesis, Auckland
Myers JG, Moore JA, Ojha M, Johnston KW, Ethier CR (2001) Factors influencing blood flow patterns in the human right coronary artery. Ann Biomed Eng 29:109–120
Ojha M (1994) Wall shear stress temporal gradient and anastomotic intimal hyperplasia. Circ Res 74:1227–1231
Ojha M, Cobbold RS, Johnston KW (1993) Hemodynamics of a side-to-end proximal arterial anastomosis model. J Vasc Surg 17:646–655
Papaharilaou Y, Doorly DJ, Sherwin SJ (2002a) The influence of out-of-plane geometry on pulsatile flow within a distal end-to-side anastomosis. J Biomech 35:1225–1239
Papaharilaou Y, Doorly DJ, Sherwin SJ, Peiro J, Griffith C, Cheshire N, Zervas V, Anderson J, Sanghera B, Watkins N, Caro CG (2002b) Combined MR imaging and numerical simulation of flow in realistic arterial bypass graft models. Biorheology 39:525–531
Pennati G, Fiore GB, Migliavacca F, Lagana’ K, Fumero R, Dubini G (2001) In vitro steady-flow analysis of systemic-to-pulmonary shunt haemodynamics. J Biomech 34:23–30
Perktold K, Rappitsch G (1995) Mathematical modeling of arterial blood flow and correlation to atherosclerosis. Technol Health Care 3:139–151
Perktold K, Leuprecht A, Prosi M, Berk T, Czerny M, Trubel W, Schima H (2002) Fluid dynamics wall mechanics and oxygen transfer in peripheral bypass anastomoses. Ann Biomed Eng 30:447–460
Pietrabissa R, Inzoli F, Fumero R (1990) Simulation study of the fluid dynamics of aorto-coronary bypass. J Biomed Eng 12:419–424
Pietrabissa R, Mantero S, Marotta T, Menicanti L (1996) A lumped parameter model to evaluate the fluid dynamics of different coronary bypasses. Med Eng Phys 18:477–484
Pittaccio S, Migliavacca F, Dubini G, Pedersen EM, Fründ ET, Hjortdal V, Xu Y, de Leval M (2003) Fluid-structure interaction and rigid wall CFD-MRI combined study of aortic coarctation repairs. In: Proceedings of 2003 summer bioengineernig ASME conference. ISBN No. 0-9742492–0–3 (http://www.tulane.edu/~sbc2003/), pp 509–510
Qiu Y, Tarbell JM (1996) Computational simulation of flow in the end-to-end anastomosis of a rigid graft and a compliant artery. ASAIO J 42:M702–M709
Quarteroni A, Ragni S, Veneziani A (2001) Coupling between lumped and distributed models for blood flow problems. Comput Vis Sci 4:111–124
Quarteroni A, Veneziani A, Zunino P (2002) A domain decomposition method for advection-diffusion processes with application to blood solutes. SIAM J Sci Comput 23:1959–1980
Rachev A, Manoach E, Berry J, Moore JE Jr (2000) A model of stress-induced geometrical remodeling of vessel segments adjacent to stents and artery/graft anastomoses. J Theor Biol 206:429–443
Rappitsch G, Perktold K (1996) Computer simulation of convective diffusion processes in large arteries. J Biomech 29:207–215
Redaelli A, Montevecchi FM (1996) Computational evaluation of intraventricular pressure gradients based on a fluid-structure approach. J Biomech Eng 118:529–537
Redaelli A, Maisano F, Ligorio G, Cattaneo E, Montevecchi FM, Alfieri O (2004) Flow dynamics of the St Jude Medical Symmetry aortic connector vein graft anastomosis do not contribute to the risk of acute thrombosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 128:117–123
Redington AN, Penny D, Shinebourne EA (1991) Pulmonary blood flow after total cavopulmonary shunt. Br Heart J 65:213–217
Ryu K, Healy TM, Ensley AE, Sharma S, Lucas C, Yoganathan AP (2001) Importance of accurate geometry in the study of the total cavopulmonary connection computational simulations and in vitro experiments. Ann Biomed Eng 29:844–853
Salacinski HJ, Goldner S, Giudiceandrea A, Hamilton G, Seifalian AM, Edwards A, Carson RJ (2001) The mechanical behavior of vascular grafts: a review. J Biomater Appl 15:241–278
Sano S, Ishino K, Kawada M, Arai S, Kasahara S, Asai T, Masuda Z, Takeuchi M, Ohtsuki S (2003) Right ventricle-pulmonary artery shunt in first-stage palliation of hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 126:504–509
Scheltes JS, van Andel CJ, Pistecky PV, Borst C (2003) Coronary anastomotic devices: blood-exposed non-intimal surface and coronary wall stress. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 126:191–199
Schwartz LB, O’Donohoe MK, Purut CM, Mikat EM, Hagen PO, McCann RL (1992) Myointimal thickening in experimental vein grafts is dependent on wall tension. J Vasc Surg 15:176–186
Selezov I, Avramenko O, Fratamico G, Pallotti G, Pettazzoni P, De Sanctis LB, Coli L, Stefoni S, Bonomini V (1998) Mechanical effects of heart pulse propagation on a vessel-graft suture line stress. Int J Artif Organs 21:114–118
Sharma S, Goudy S, Walker P, Panchal S, Ensley A, Kanter K, Tam V, Fyfe D, Yoganathan A (1996) In vitro flow experiments for determination of optimal geometry of total cavopulmonary connection for surgical repair of children with functional single ventricle. J Am Coll Cardiol 27:1264–1269
Sherwin SJ, Shah O, Doorly DJ, Peiro J, Papaharilaou Y, Watkins N, Caro CG, Dumoulin CL (2000) The influence of out-of-plane geometry on the flow within a distal end-to-side anastomosis. J Biomech Eng 122:86–95
Sherwin SJ, Doorly DJ, Franke P, Peiro J (2002) Unsteady near wall residence times and shear exposure in model distal arterial bypass grafts. Biorheology 39:365–371
Steinman DA, Ethier CR (1994) The effect of wall distensibility on flow in a two-dimensional end-to-side anastomosis. J Biomech Eng 116:294–301
Steinman DA, Vinh B, Ethier CR, Ojha M, Cobbold RS, Johnston KW (1993) A numerical simulation of flow in a two-dimensional end-to-side anastomosis model. J Biomech Eng 115:112–118
Stewart SF, Lyman DJ (2004) Effects of an artery/vascular graft compliance mismatch on protein transport: a numerical study. Ann Biomed Eng 32:991–1006
Tacy TA, Whitehead KK, Cape EG (1998) In vitro Doppler assessment of pressure gradients across modified Blalock–Taussig shunts. Am J Cardiol 81:1219–1223
Tada S, Tarbell JM (2000) Interstitial flow through the internal elastic lamina affects shear stress on arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278:H1589–H1597
Tada S, Tarbell JM (2001) Fenestral pore size in the internal elastic lamina affects transmural flow distribution in the artery wall. Ann Biomed Eng 29:456–466
Tada S, Tarbell JM (2002) Flow through internal elastic lamina affects shear stress on smooth muscle cells (3D simulations). Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 282:H576–H584
Tada S, Tarbell JM (2004) Internal elastic lamina affects the distribution of macromolecules in the arterial wall: a computational study. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H905–H913
Tang D, Yang J, Yang C, Ku DN (1999) A nonlinear axisymmetric model with fluid-wall interactions for steady viscous flow in stenotic elastic tubes. J Biomech Eng 121:494–501
Tang D, Yang C, Kobayashi S, Ku DN (2001) Steady flow and wall compression in stenotic arteries: a three-dimensional thick-wall model with fluid-wall interactions. J Biomech Eng 123:548–557
Tang D, Yang C, Kobayashi S, Ku DN (2004) Effect of a lipid pool on stress/strain distributions in stenotic arteries: 3-D fluid-structure interactions (FSI):models. J Biomech Eng 126:363–370
Taylor CA, Draney MT (2004) Experimental and computational methods in cardiovascular fluid mechanics. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36:197–231
Taylor CA, Hughes TJR, Zarins CK (1996) Computational investigations in vascular disease. Comp Phys 10:224–232
Thubrikar MJ, Robicsek F (1995) Pressure-induced arterial wall stress and atherosclerosis. Ann Thorac Surg 59:1594–1603
Van Haesdonck JM, Mertens L, Sizaire R, Montas G, Purnode B, Daenen W, Crochet M, Gewillig M (1995) Comparison by computerized numeric modeling of energy losses in different Fontan connections. Circulation 92:II322–II326
Vignon IE, Taylor CA (2004) Outflow boundary condition for one-dimensional finite element modeling of blood flow and pressure waves in arteries. Wave Motion 39:361–374
Walsh MT, Kavanagh EG, O’Brien T, Grace PA, McGloughlin T (2003) On the existence of an optimum end-to-side junctional geometry in peripheral bypass surgery—a computer generated study. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 26:649–656
Wang DM, Tarbell JM (1995) Modeling interstitial flow in an artery wall allows estimation of wall shear stress on smooth muscle cells. J Biomech Eng 117:358–363
White SS, Zarins CK, Giddens DP, Bassiouny H, Loth F, Jones SA, Glagov S (1993) Hemodynamic patterns in two models of end-to-side vascular graft anastomoses: effects of pulsatility flow division Reynolds number and hood length. J Biomech Eng 115:104–111
Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto Y, Liu H (2000) Computational mechanical model studies on the spontaneous emergent morphogenesis of the cultured endothelial cells. J Biomech 33:115–126
Zidi M, Cheref M (2003) Mechanical analysis of a prototype of small diameter vascular prosthesis: numerical simulations. Comput Biol Med 33:65–75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Migliavacca, F., Dubini, G. Computational modeling of vascular anastomoses. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 3, 235–250 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-005-0070-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-005-0070-2