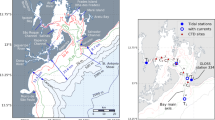
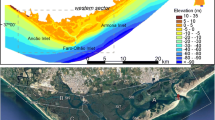
Abstract
This paper deals with the interaction and small-scale processes occurring around the inlets that connect the Venice Lagoon with the Northern Adriatic Sea. In a previous paper, barotropic processes have been investigated, whereas here, the focus is on the baroclinic processes. The hydrodynamics of the area are studied by means of a 3D shallow water hydrodynamic finite-element model, suitable to describe areas of complex morphology such as the coasts and the interaction channels. This is the first work that models the 3D interaction between the Venice Lagoon and the Adriatic Sea. Three different sets of simulations have been carried out to identify the physics behind the small-scale processes and the influence of the main forcings on the study area. The first imposes different idealized forcings, such as tides, wind, and river runoff. The vorticity maps of the first two layers show the predominance of wind forcing in the coastal area and tidal forcing in the three inlets of the Lagoon. Bora wind acts homogeneously, increasing the littoral currents, while Sirocco wind mainly impacts near Chioggia inlet, with a coastal current reversal, inducing its detachment offshore. Freshwater patterns are present along the coast, near the river mouths. Rivers do not directly influence the circulation close to the coast in front of the Venice Lagoon, except for the area near Chioggia inlet, where the Brenta river action can be seen. The second set of simulations deals with a sensitivity analysis to define the importance of the advection and of the baroclinic pressure gradient terms in the creation of persistent structures, such as small-scale coastal vortices seen along the littoral very close to the inlets. This analysis shows how advection is the main physical process responsible for the persistence of the positive vorticity structures close to the coast between the inlets, while the negative vorticity structures, also seen by the HF Radar, are due to the baroclinic-advective interaction. Finally, a real case, year 2004, has been simulated both to validate the model with observations and to identify the occurrence during the year of the characteristic hydrodynamic features attributable to the main forcings. The action of Bora wind characterizes the surface current patterns of February and November 2004, while Sirocco influences the month of May 2004. During periods of weak wind, the model reproduces the small-scale vortical structures close to the littoral.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajo M, Zampato L, Umgiesser G, Cucco A, Canestrelli P (2007) A finite element operational model for the storm surge prediction in Venice. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 75:236–249
Bellafiore D, Umgiesser G, Cucco A (2008) Modelling the water exchanges between the Venice Lagoon and the Adriatic Sea. Ocean Dyn 58:397–413
Bergamasco A, Carniel S, Pastres R, Pecenik G (1998) A unified approach to the modelling of the Venice Lagoon-Adriatic Sea ecosystem. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 46:483–492
Book JW, Perkins HT, Cavaleri L, Doyle JD, Pullen JD (2005) ADCP observations of the western Adriatic Slope current during winter 2001. Prog Oceanogr 66:270–286
Burchard H, Petersen O (1999) Models of turbulence in the marine environment—a comparative study of two equation turbulence models. J Mar Syst 21:29–53
Cucco A, Umgiesser G (2006) Modeling the Venice Lagoon residence time. Ecol Model 193(1–2):34–51
Franco P, Jeftić L, Rizzoli PM, Michelato A, Orlić M (1982) Descriptive model of the Northern Adriatic. Oceanol Acta 5(3):379–389
Gatto P (1984) Il cordone litoraneo della laguna di Venezia e e cause del suo degrado. Istituto Veneto di Scienze Lettere e Arti, Rapporti e Studi IX, 163–193
Gačić M, Kovačević V, Mazzoldi A, Paduan JD, Arena F, Mosquera IM, Gelsi G, Arcari G (2002) Measuring water exchange between the Venetian Lagoon and the open sea. EOS, Transaction, American Geophysical Union 83(20):217–222
Gačić M, Mosquera IM, Kovačević V, Mazzoldi A, Cardin V, Arena F, Gelsi G (2004) Temporal variations of water flow between the Venetian lagoon and the open sea. J Mar Syst 51:33–47
Kovačević V, Gačić M, Mosquera IM, Mazzoldi A, Marinetti S (2004) Hf radar observation in the northern Adriatic: surface current field in front of the Venetian Lagoon. J Mar Syst 51(1–4):95–122
Melaku Canu D, Umgiesser G, Solidoro C (2001) Short term simulations under winter conditions in the lagoon of Venice: a contribution to the environmental impact assessment of a temporary closure of the inlets. Ecol Model 138(1–3):215–230
Mosquera IM, Gačić M, Kovačević V, Mazzoldi A, Paduan JD, Yari S (2007) Surface current patterns in front of the Venetian Lagoon and their variability at different wind regimes. In: Scientific research and safeguarding of Venice—CORILA research programme 2004–2006, vol VI. Venice, Italy, pp 441–451
Paduan JD, Gačić M, Kovačević V, Mosquera IM, Mazzoldi A (2003) Vorticity pattern offshore of the venetian lagoon from hf radar observations. In: Scientific research and safeguarding of Venice - CORILA research programme 2001–2003, vol II. Venice, Italy, pp 361–372
Pinardi N, Allen I, Demirov E, De Mey P, Korres G, Lascaratos A, Le Traon PY, Mailaard C, Manzella G, Tziavos C (2003) The Mediterranean ocean forecasting system: first phase of implementation (1998-2001). Ann Geophys 21:3–20
Polli S (1960) La propagazione delle maree nell’Alto Adriatico. Publications of the Istituto Sperimentale Talassografico - Trieste 370
Tomasin A (2005) The software Polifemo for tidal analysis. Technical Note 202, ISMAR-CNR Institute of Marine Science Venice
Umgiesser G (2000) Modeling residual currents in the Venice Lagoon. In: Interaction between estuaries, coastal seas and shealf seas. Terra scientific publishing company (TERRAPUB), Tokyo, pp 107–124
Umgiesser G, Bergamasco A (1995) Outline of a primitive equation finite element model. In: Rapporto e Studi, vol XII. Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti, Venice, Italy, pp 291–320
Umgiesser G, Canu DM, Cucco A, Solidoro C (2004) A finite element model for the Venice Lagoon. Development, set-up, calibration and validation. J Mar Syst 51:123–145
Wells MG, Heijst G (2003) A model of tidal flushing on an estuary by dipole formation. Dyn Atmos Ocean 37:223–244
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank EuroMediterranean Centre for Climate Change (CMCC) and VECTOR Project for the partial funding of this work. Thanks to ECMWF for providing wind data. Thanks to MFStep for providing temperature and salinity data. Thanks to Dr. Mancero Mosquera for providing and treating the HF Radar data used for the study, Dr. Kovačević for the handling of HF Radar info, and Dr. Gačić for the help in the physical interpretation of processes. Thanks also to Dr. Sarretta for the GIS support in finding the best map representation for the analysis. Thanks to Dr. Proctor for the careful editing of the document and his suggestions. Thanks also to two anonymous reviewers that allowed us to improve this paper with their comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roger Proctor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellafiore, D., Umgiesser, G. Hydrodynamic coastal processes in the North Adriatic investigated with a 3D finite element model. Ocean Dynamics 60, 255–273 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-009-0254-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-009-0254-x