Abstract.
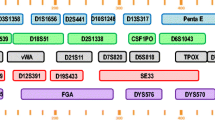
The individual differences in the repeat count of several bases, short tandem repeat (STR), among all of the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) base sequences, can be used as unique DNA information for a personal identification (ID). We propose a method to generate a personal identifier (hereafter referred to as a “DNA personal ID”) by specifying multiple STR locations (called “loci”) and then sequencing the repeat count information. We also conducted a validation experiment to verify the proposed principle based on actual DNA data.
We verified that the matching probability of DNA personal IDs becomes exponentially smaller, to about 10-n, as n stages of loci are used and that no correlation exists among the loci.
Next, we considered the various issues that will be encountered when applying DNA personal IDs to information security systems, such as biometric personal authentication systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published online: 9 April 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itakura, Y., Hashiyada, M., Nagashima, T. et al. Proposal on personal identifiers generated from the STR information of DNA . IJIS 1, 149–160 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10207-002-0013-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10207-002-0013-1