Abstract
Objectives
Diabetes patients suffer from comorbid conditions and disease-related complications. Combined with demographic, clinical and treatment satisfaction variables, they have a confounding effect on health-related quality of life (HRQoL). This study compared the sensitivity of EQ-5D, SF-6D and 15D utilities to the specific effect of diabetes complications.
Methods
Utilities were compared in 319 type II diabetics with and without comorbidities and complications. Based on subsample size and confirmed diagnoses, coronary heart disease (CHD) and diabetic retinopathy (DR) were two complications chosen for further analysis. Significant EQ-5D, SF-6D and 15D predictors were identified with OLS regression and subsequently controlled for with ANCOVA.
Results
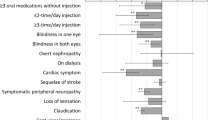
The presence of CHD resulted in utility decrements (P < 0.001) for all instruments, whereas DR only decreased 15D utilities (P < 0.05). Gender, age, treatment satisfaction, arthropathy and diabetic foot were significant predictors throughout, whereas BMI, neuropathy and CHD for at least two utilities. After controlling for these confounding variables, 15D still discriminated between diabetics with and without CHD (P < 0.01) and DR (P < 0.05), with seven and five dimensions affected, respectively.
Conclusions
After removing the effect of background variables, 15D utilities remain sensitive to CHD and DR. The obvious explanation is its richer descriptive system, which provides increased discriminative ability compared to EQ-5D and SF-6D, and this might be evidence for preferring the 15D in economic evaluations of interventions for diabetics. However, the need remains for further testing in other diabetes complications and more diverse patient samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wild, S., Roglic, G., Green, A., Sicree, R., King, H.: Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27, 1047–1053 (2004)
Stumvoll, M., Goldstein, B.J., van Haeften, T.W.: Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 365, 1333–1346 (2005)
Massi-Benedetti, M.: The cost of diabetes type II in Europe. The CODE-2 Study. Diabetologia 4, S1–S4 (2002)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National diabetes fact sheet: general information and national estimates on diabetes in the United States, 2007. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta (2008)
Holmes, J., McGill, S., Kind, P., Bottomley, J., Gillam, S., Murphy, M.: Health-related quality of life in type 2 diabetes (TARDIS-2). Value Health 3(1), 47–51 (2000)
Watkins, K., Connell, C.M.: Measurement of health-related QOL in diabetes mellitus. Pharmacoeconomics 22, 1109–1126 (2004)
Rose, M., Burkert, U., Scholler, G., Schirop, T., Danzer, G., Klapp, B.F.: Determinants of quality of life of patients with diabetes under intensified insulin therapy. Diabetes Care 21, 1876–1885 (1998)
Rubin, R.R., Peyrot, M.: Quality of life and diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 15, 205–218 (1999)
Anderson, R.M., Fitzgerald, J.T., Wisdom, K., Davis, W.K., Hiss, R.G.: A comparison of global versus disease-specific quality-of-life measures in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes Care 20, 299–305 (1997)
Woodcock, A.J., Julious, S.A., Kinmonth, A.L., Campbell, M.J.: Problems with the performance of the SF-36 among people with type 2 diabetes in general practice. Qual. Life Res. 10, 661–670 (2001)
Parkerson Jr., G.R., Connis, R.T., Broadhead, W.E., Patrick, D.L., Taylor, T.R., Tse, C.K.: Disease-specific versus generic measurement of health-related quality of life in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Med. Care 31, 629–639 (1993)
Brooks, R.: EuroQol: the current state of play. Health Policy 37, 53–72 (1996)
Dolan, P., Gudex, C., Kind, P., Williams, A.: The time trade-off method: results from a general population study. Health Econ. 5, 141–154 (1996)
Yfantopoulos, J.: The Greek version of the EuroQol (EQ-5D) instrument. Arch. Hell. Med. 18, 180–191 (2001)
Kontodimopoulos, N., Pappa, E., Niakas, D., Yfantopoulos, J., Dimitrakaki, C., Tountas, Y.: Validity of the EQ-5D instrument in a Greek general population. Value Health 11, 1162–1169 (2008)
Brazier, J., Roberts, J., Deverill, M.: The estimation of a preference-based measure of health from the SF-36. J. Health Econ. 21, 271–292 (2002)
Pappa, E., Kontodimopoulos, N., Niakas, D.: Validating and norming of the Greek SF-36 Health Survey. Qual. Life Res. 14, 1433–1438 (2005)
Anagnostopoulos, F., Niakas, D., Pappa, E.: Construct validation of the Greek SF-36 Health Survey. Qual. Life Res. 14, 1959–1965 (2005)
Kontodimopoulos, N., Niakas, D.: A cost-utility analysis in renal replacement therapy based on patients’ expected remaining life years. Health Policy 86, 85–96 (2008)
Kontodimopoulos, N., Pappa, E., Papadopoulos, A.A., Tountas, Y., Niakas, D.: Comparing SF-6D and EQ-5D utilities across groups differing in health status. Qual. Life Res. 18, 87–97 (2009)
Sintonen, H.: The 15D Instrument of health-related quality of life: properties and applications. Ann. Med. 33, 328–336 (2001)
Yfantopoulos, J.: Validation and measurement of quality of life in Greece using EQ-15D. Arch. Hell. Med. 18, 279–287 (2001)
Aletras, V.H., Kontodimopoulos, N., Niakas, D.A., Vagia, M.G., Pelteki, H.J., Karatzoglou, G.I., et al.: Valuation and preliminary validation of the Greek 15D in a sample of patients with coronary artery disease. Value Health 12, 574–579 (2009)
Lewis, K.S., Bradley, C., Knight, G., Boulton, A.J., Ward, J.D.: A measure of treatment satisfaction designed specifically for people with insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabet. Med. 5, 235–242 (1988)
Stavem, K., Froland, S.S., Hellum, K.B.: Comparison of preference-based utilities of the 15D, EQ-5D and SF-6D in patients with HIV/AIDS. Qual. Life Res. 14, 971–980 (2005)
Kontodimopoulos, N., Aletras, V.H., Paliouras, D., Niakas, D.: Mapping the cancer-specific EORTC QLQ-C30 instrument to preference-based EQ-5D, SF-6D and 15D indices. Value Health 12, 1151–1157 (2009)
Lillegraven, S., Kristiansen, I.S., Kvien, T.K.: Comparison of utility measures and their relationship with other health status measures in 1041 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 1762–1767 (2010)
Barton, G.R., Sach, T.H., Avery, A.J., Jenkinson, C., Doherty, M., Whynes, D.K., et al.: A comparison of the performance of the EQ-5D and SF-6D for individuals aged ≥45 years. Health Econ. 17, 815–832 (2008)
Drummond, M.F.: Introducing economic and quality of life measures into clinical studies. Ann. Med. 33, 344–349 (2001)
de Groot, V., Beckerman, H., Lankhorst, G.J., Bouter, L.M.: How to measure comorbidity. A critical review of available methods. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 56, 221–229 (2003)
Xuan, J., Kirchdoerfer, L.J., Boyer, J.G., Norwood, G.J.: Effects of comorbidity on health-related quality-of-life scores: an analysis of clinical trial data. Clin. Ther. 21, 383–403 (1999)
de Visser, C.L., Bibo, H.J., Groenier, K.H., de Visser, W., Jong Meyboom-de, B.: The influence of cardiovascular disease on quality of life in type 2 diabetics. Qual. Life Res. 11, 249–261 (2002)
Lloyd, A., Sawyer, W., Hopkinson, P.: Impact of long-term complications on quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes not using insulin. Value Health 4, 392–400 (2001)
Wee, H.L., Cheung, Y.B., Li, S.C., Fong, K.Y., Thumboo, J.: The impact of diabetes mellitus and other chronic medical conditions on health-related Quality of Life: is the whole greater than the sum of its parts? Health Qual. Life Outcomes 3, 2 (2005)
Rose, M., Burkert, U., Scholler, G., Schirop, T., Danzer, G., Klapp, B.F.: Determinants of the quality of life of patients with diabetes under intensified insulin therapy. Diabetes Care 21, 1876–1885 (1998)
Longworth, L., Bryan, S.: An empirical comparison of EQ-5D and SF-6D in liver transplant patients. Health Econ. 12, 1061–1067 (2003)
Gerard, K., Nicholson, T., Mullee, M., Mehta, R., Roderick, P.: EQ-5D versus SF-6D in an older, chronically ill patient group. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 3, 91–102 (2004)
Lamers, L.M., Bouwmans, C.A., van Straten, A., Donker, M.C., Hakkaart, L.: Comparison of EQ-5D and SF-6D utilities in mental health patients. Health Econ. 15, 1229–1236 (2006)
Xie, F., Li, S.C., Luo, N., Lo, N.N., Yeo, S.J., Yang, K.Y., et al.: Comparison of the EuroQol and short form 6D in Singapore multiethnic Asian knee osteoarthritis patients scheduled for total knee replacement. Arthritis Rheum. 57, 1043–1049 (2007)
van Stel, H.F., Buskens, E.: Comparison of the SF-6D and the EQ-5D in patients with coronary heart disease. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 4, 20 (2006)
Grieve, R., Grishchenko, M., Cairns, J.: SF-6D versus EQ-5D: reasons for differences in utility scores and impact on reported cost-utility. Eur. J Health Econ. 10, 15–23 (2004)
Brazier, J., Roberts, J., Tsuchiya, A., Busschbach, J.: A comparison of the EQ-5D and SF-6D across seven patient groups. Health Econ. 13, 873–884 (2004)
Petrou, S., Hockley, C.: An investigation into the empirical validity of the EQ-5D and SF-6D based on hypothetical preferences in a general population. Health Econ. 14, 1169–1189 (2005)
Bharmal, M., Thomas 3rd, J.: Comparing the EQ-5D and the SF-6D descriptive systems to assess their ceiling effects in the US general population. Value Health 9, 262–271 (2006)
Papadopoulos, A.A., Kontodimopoulos, Ν., Niakas, D.: Health related quality of life in type II diabetes patients: Assessing socio-demographic and clinical variables. In: Hoffmann, E.C. (ed.) Health-Related Quality of Life. Nova Science, New York (2009)
Papadopoulos, A.A., Kontodimopoulos, N., Frydas, A., Ikonomakis, E., Niakas, D.: Predictors of health-related quality of life in type II diabetic patients in Greece. BMC Public Health 7, 186 (2007)
Dennett, S.L., Boye, K.S., Yurgin, N.R.: The impact of body weight on patient utilities with or without type 2 diabetes: a review of the medical literature. Value Health 11, 478–486 (2008)
Redekop, W.K., Koopmanschap, M.A., Stolk, R.P., Rutten, G.E., Wolffenbuttel, B.H., Niessen, L.W.: Health-related quality of life and treatment satisfaction in Dutch patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 25, 458–463 (2002)
Nicolucci, A., Cucinotta, D., Squatrito, S., Lapolla, A., Musacchio, N., Leotta, S., et al.: Clinical and socio-economic correlates of quality of life and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 19, 45–53 (2009)
Wandell, P.E.: Quality of life of patients with diabetes mellitus. An overview of research in primary health care in the Nordic countries. Scand. J. Prim. Health Care 23, 68–74 (2005)
U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group: Quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients is affected by complications but not by intensive policies to improve blood glucose or blood pressure control (UKPDS 37). Diabetes Care 22, 1125–1136 (1999)
Wandell, P., Brorsson, B., Aberg, H.: Functioning and wellbeing of patients with type 2 diabetes or angina pectoris, compared with the general population. Diabetes Metab. 26, 465–471 (2000)
Ahola, A.J., Saraheimo, M., Forsblom, C., Hietala, K., Sintonen, H., Groop, P.H., et al.: Health-related quality of life in patients with type 1 diabetes–association with diabetic complications (the FinnDiane Study). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 25, 1903–1908 (2010)
Halkoaho, A., Kavilo, M., Pietilä, A.M., Huopio, H., Sintonen, H., Heinonen, S.: Does gestational diabetes affect women’s health-related quality of life after delivery? Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 148, 20–43 (2010)
Patrick, D.L., Deyo, R.A.: Generic and disease-specific measures in assessing health status and quality of life. Med. Care 27(3 Suppl), S217–S232 (1989)
Bryan, S., Longworth, L.: Measuring health-related utility: why the disparity between EQ-5D and SF-6D? Eur. J. Health Econ. 6, 253–260 (2005)
Solli, O., Stavem, K., Kristiansen, I.S.: Health-related quality of life in diabetes: the associations of complications with EQ-5D scores. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 8, 18 (2010)
Hahl, J., Hämäläinen, H., Sintonen, H., Simell, T., Arinen, S., Simell, O.: Health-related quality of life in type 1 diabetes without or with symptoms of long-term complications. Qual. Life Res. 11, 427–436 (2002)
Lubetkin, E.I., Jia, H., Franks, P., Gold, M.R.: Relationship among sociodemographic factors, clinical conditions, and health-related quality of life: Examining the EQ-5D in the U.S. general population. Qual. Life Res 14, 2187–2196 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kontodimopoulos, N., Pappa, E., Chadjiapostolou, Z. et al. Comparing the sensitivity of EQ-5D, SF-6D and 15D utilities to the specific effect of diabetic complications. Eur J Health Econ 13, 111–120 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-010-0290-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-010-0290-y