Abstract
Background
In some settings, specific techniques for open reduction and internal fixation are preferred based on the eminence of a surgeon or professional organization. An emphasis on technical aspects of surgery that are not proved superior and vary substantially from surgeon to surgeon can be confusing for trainees. This study applied a numerical grading of the technical aspects of tension band wire (TBW) fixation for olecranon fracture; assessed the interobserver agreement of each criterion; and measured the correlation of the technical grading and objective and subjective long-term outcomes.
Materials and methods
Forty observers were invited to rate the technical aspects of TBW fixation of the olecranon on 26 post-operative radiographs. The interobserver reliability of the rating was measured using the intra-class correlation coefficient. The correlation between the rating and motion, Mayo elbow performance index, and disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand score was tested with the Spearman’s rank correlation test.
Results
None of the figure-of-eight TBW constructs were considered perfect according to the numerical grading: the majority of observers found three deviations per fixation. The interobserver agreement was only fair for the total number of deviations and no correlation between the number of deviations and long-term objective and subjective outcome was found.
Conclusions
A rating of the technical aspects of TBW for olecranon fractures was unreliable and did not correlate with subjective and objective outcomes. Emphasis on specific technical aspects of fixation might be confusing for trainees and could distract them from the principles of effective treatment.
Level of evidence
Level IV diagnostic study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Operative fixation is indicated for most olecranon fractures-especially displaced olecranon fractures in healthy, active patients [15]. Operative treatment of displaced, transverse, non-comminuted fracture of the olecranon is associated with good to excellent elbow function in retrospective short-term follow-up studies [2, 14]. Moreover, satisfactory clinical results are durable over time [6, 10].
The tension band principle as applied to transverse olecranon fractures fixed by tension band wiring (TBW) is based on the premise that distraction forces on the outer cortex of the ulna during elbow flexion are converted to compression forces on the articular surface of the olecranon at the fracture site [14]. The specific technical aspects of the TBW for simple olecranon fracture are subject to ongoing debate as there is little evidence to support any specific technique [5, 9, 13, 14]. Nevertheless, the specific surgical technique or technical aspects of the procedure are preferred based more upon the eminence of the surgeon or group rather than the data. For instance, the AO technique emphasizes parallel and intramedullary Kirschner wires, but it is not clear that those specific technical aspects confer an advantage [5, 9, 13, 14].
Surgeons mostly agree with themselves (good to excellent intra-observer reliability), but not so much with each other (poor interobserver reliability) (Claessen et al. unpublished data). An emphasis on technical aspects of surgery that are not proved superior and vary substantially from surgeon to surgeon can be confusing and demoralizing for trainees. For example, some surgeons prefer intramedullary Kirschner wires and others transcortical fixation. A discussion of the variations is instructive, but criticism for not following one surgeon’s preferences sends the wrong message.
Schneider et al. [14] described ten criteria for evaluating surgical treatment of olecranon fractures based on ten operative imperfections: (1) nonparallel K-wires, (2) long K-wires, (3) K-wires extending radially outwards, (4) insufficient fixation of the proximal ends of the K-wires, (5) intramedullary K-wires, (6) perforation of the joint surface, (7) single wire knot, (8) jutting wire knot(s), (9) loose figure-of-eight configuration, and (10) incorrect repositioning to evaluate radiographs of olecranon fractures.
This study applied a numerical grading of the technical aspects of TBW fixation for olecranon fracture based on the Schneider criteria [14]; assessed the interobserver agreement of the rating; and measured the correlation of the technical grading and objective and subjective long-term outcomes. We hypothesized that the average number of observed technical deviations according to the Schneider criteria per TBW will be at least three. Our secondary hypothesis is that interobserver agreement on the total number of technical deviations is poor. We also hypothesized that there is no correlation between technical deviations of the TBW surgical technique and long-term objective and subjective clinical outcome.
Materials and methods
Study design
Our local Medical Ethics Committee approved this interobserver study to evaluate 26 postoperative-anonymized radiographs of patients treated for olecranon fractures at the Academic Medical Center between 1974 and 1997, with subjective and objective outcome scores available after 10–30 years follow-up [6]. From 1974, all trauma patients treated and admitted to our level I trauma center were prospectively documented in a trauma database classified according to the arbeitsgemeinschaft für osteosynthesefragen (AO) comprehensive classification of fractures.
We previously reported on the long-term subjective (DASH) and objective outcomes (Broberg and Morrey elbow arthritis score, range of motion) of 41 patients [6].
Inclusion criteria were: (1) traumatic non-pathological simple olecranon fracture, and (2) age 18 years or older. Patients were excluded if no post-operative lateral and anterior–posterior radiograph was available.
Of those 41 patients, 26 patients had a traumatic non-pathological simple olecranon fracture and a post-operative lateral and anterior–posterior radiograph.
All included patients underwent open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) for transverse noncomminuted olecranon fractures between 1977 and 1997. During this time period, our general indication for performing ORIF was greater than 2 mm displacement. In this study, indication for TBW was a simple transverse noncomminuted olecranon fracture.
The average age of the included patients was 34 years (range: 19–72 years). Nine patients were female (35%) and 17 were male (65%). The average follow-up time was 18 years (range 9–33). The average flexion extension arc was 139 degrees (range 95–150). The average postoperative DASH score was nine (range 0–65). Eight of 26 patients had a DASH score of greater than ten points (13; 14; 17; 17; 25; 30; 37; 65 points, respectively). The average elbow arthritis score according to Broberg and Morrey was 0.2 (range, grade 0–1). All patients started with passive range of motion exercises within 1 week.
Members of the Shoulderelbowplatform, an online collaboration of shoulder and elbow surgeons from all over the world, were invited to evaluate the radiographs on a web-based study platform including DICOM viewer. Members of the Shoulderelbowplatform are fully trained, actively practicing surgeons and residents from around the world. The goals of the Shoulderelbowplatform are to: (1) facilitate online interobserver reliability and diagnostic accuracy studies about orthopedic shoulder and elbow injuries, (2) offer a platform to educate residents.
Participants
Sixty-three senior orthopaedic residents and orthopaedic surgeons started to evaluate 26 radiographs on the platform (www.shoulderelbowplatform.com), of which 40 observers finished the study (63% of the initial responders). Twenty-one orthopaedic residents and 19 orthopaedic surgeons completed the study. Thirty-five percent of the observers were less than 3 years in practice and the majority of the observers were involved in resident training (53%) (Table 1).
Study description
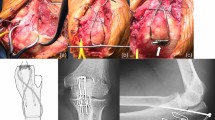
After login, postoperative radiographs (standard anterior–posterior and lateral views) of 26 treated olecranon fractures were presented to the observers. Observers were asked to critique the following details of applied surgical technique of the “classic” TBW construct on 26 post-operative radiographs based on the written description in the recent paper by Schneider et al. that we would like to coin the Schneider criteria [14] (Table 2). In total 10 points per TBW construct could be obtained. A point was given for each of the 10 Schneider criteria that did not meet expectations.
The following Schneider’s criteria for evaluating TBW of olecranon fractures were subject of interpretation: oversized Kirschner wires in terms of length, loose figure-of-eight configuration (i.e. the wire cerclage not ‘flush’ to the bone), incorrect reduction (i.e. congruent joint articular surface), prominent wire knot(s) (i.e. twisted ends not sufficiently bent back into direct contact with the bone) (Figs. 1, 2).
Observers were also asked if they (1) would have performed the fixation differently and (2) advised a revision surgery.
One case had to be completed to be able to continue with the next case. The observers completed the study at their own pace and in their own time on various computers if necessary.
Post hoc power analysis
Post hoc power analysis, performed with the use of nQuery Advisor software, revealed that 17 fractures evaluated by 34 observers would provide 80% power (\(\alpha\) = 0.05, \(\beta\) = 0.20) to detect a clinically significant difference [8].
Explanatory and outcome measures
The outcome measures were the number of technical deviations according to the Schneider criteria, the interobserver agreement and long-term subjective (DASH) and objective outcomes (Broberg and Morrey elbow arthritis score, range of motion). Technical deviation was defined as a presumed technical error as proposed by Schneider et al. [14]. However, no clinical data exist that the listed technical deviations are indeed errors or mistakes, as we these have not been associated with worse clinical outcome in clinical series to date.
The explanatory variables were TBW technique characteristics.
Statistical analysis
We assessed an intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) two-way mixed-effects model. ICC is a measure of agreement between observers, adjusted for agreement due to chance alone used for comparison of continuous numeric data. Potential ICC values ranging from 0 (no agreement) to 1 (perfect agreement). ICC values representing poor agreement are 0.00–0.20; fair agreement, 0.21–0.40; moderate agreement, 0.41–0.60; substantial agreement, 0.61–0.80; and almost perfect agreement, greater than 0.80 [3, 12].
The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was done to correlate the number of technical deviations based on consensus agreement (>50% of observers) to the DASH score, the range of motion and the Broberg and Morrey elbow arthritis score.
Results
Numerical grading
The average number of observed technical deviations on the guideline per TBW construct was 3.0 (range 1.5–4.7) and no fixation was considered perfect (Table 3). Moreover, the observers recommended performing 96% of the fixations differently (based on the question would you have performed the fixation differently).
In almost all 26 patients, at least one observer identified one of the respective technical deviations. In other words, all potential deviations on the guideline were seen by at least one surgeon in each patient; even conflicting potential technical deviations like scoring both intramedullary Kirschner wires and Kirschner wires protruding radially in the same TBW construct by different surgeons exemplifies the fact that surgeons mostly agree with themselves (good to excellent intra-observer reliability), but not so much with each other (poor interobserver reliability) in most studies [4, 7, 16].
Only one patient had implant failure and reoperation (patient 20). There were four potential technical deviations in this TBW construct according to a consensus agreement of more than 50% of the observers: (1) non-parallel Kirschner wires (2) too long Kirschner wires (3) insufficient fixation of the proximal ends of the Kirschner wires (4) intramedullary Kirschner wires. However, the majority of surgeons in this study advised no revision of internal fixation for this patient.
Interobserver agreement
The interobserver agreement on the total number of deviations was fair (ICC = 0.32) (reference value 0.21–0.40) (Table 4). The interobserver agreement was fair for all subgroups. For example, the interobserver agreement was not higher if the observer had more than 6 years of experience compared to less than 6 years of experience. This included a consecutive series of ratings by experts in the field of elbow surgery.
Correlation number of potential technical deviations TBW and long-term objective- and subjective outcomes
There was no correlation between technical deviations of the TBW surgical technique and long-term objective and subjective outcomes [6]. No correlation between the DASH score and the number of technical deviations was seen (p = 0.64). There was also no correlation between the elbow arthritis score according to Broberg and Morrey and the number of technical deviations (p = 0.99) [1]. However, elbow arthritis was correlated to a higher DASH score in this patient group p = 0.02). With the numbers available, there was no significant correlation between the number of technical deviations and range of motion: flexion (p = 0.06), extension (p = 0.07), supination (p = 0.23), and pronation (p = 0.76).
Discussion
There is little data to support one technique over the other for TBW of olecranon fractures [5, 9, 13, 14]. In this study we applied a numerical grading of the technical aspects of TBW fixation for olecranon fracture; assessed the interobserver agreement of each criterion; and measured the correlation of the technical grading and objective and subjective long-term outcomes.
The average figure-of-eight TBW construct of a displaced-transverse-non-comminuted olecranon fracture in this series had at least three out of ten potential technical deviations according to a consensus agreement of greater than 50% of 40 observers [14]. In other words, pearls and pitfalls of TBW technique for simple olecranon fractures will remain a subject of ongoing debate, which can be confusing to the trainee. The point of discussion should be the lack of consensus and the dearth of evidence, not the preferences of any given surgeon. Schneider et al. evaluated 233 TBW constructs for ten potential technical deviations—the Schneider criteria [14]. They found an average of 4.24 imperfections per TBW construct and concluded that TBW is not as easy as surgeons and published reports suggest [14].
We would have expected higher than fair agreement on the total number of technical deviations per TBW construct given that some potential technical deviations were not subject to interpretation, such as single wire knot and prominent wire knot(s).
The lack of correlation between technical deviations and outcomes suggest that most of the Schneider criteria [14] are irrelevant from the patient’s perspective. The range of motion of the elbow in our study is also discording from the number of surgeons who suggested a revision surgery (in several patients an inferior ROM corresponded to a better judgment on radiographs, and vice versa). Perhaps olecranon fractures have a wide margin for error and a good outcome is likely except for technical mistakes and severe non-compliance. The evidence that nonoperative treatment and olecranon nonunion lead to good function in most patients supports this idea [2, 14]. In any case, the clinical outcome cannot be predicted based on postoperative radiographs.
This study should be interpreted in light of several limitations. First of all, this interobserver reliability lacks a reference standard, as the configuration of a “perfect” TBW construct is unknown and therefore accuracy data could not be calculated. The radiographs were all made according to hospital protocol, but were not otherwise standardized. However, this represents our daily clinical practice. A high proportion of the observers were residents and young surgeons. However, the interobserver agreement was fair for all subgroups. Observers had no information regarding patient characteristics or injury. Also, we did not give observers any training or reference values on technique specifics, only the written description as above. Perforation of the surface joint might be underestimated on plain films and the gold standard here in case of doubt might be computed tomography in any future reference study. Due to low number of implant loosening or breakage (one patient, 4%) we lack power to correlate any potential technical deviations to loss of fixation. According to a post hoc power analysis a 25% complication rate was needed to detect any correlation between technical deviations and loss of fixation.
A numerical grading of technical aspects of the TBW fixation for olecranon fracture was unreliable and did not correlate with objective and subjective long-term outcomes. In other words, technic specifics of the TBW fixation will remain a subject of ongoing debate, which might be confusing to the trainee and might distract them from the principles of effective treatment. The discussion should be focused on the lack of consensus and the minimal evidence, not the preferences of the surgeon.
Change history
06 September 2018
Unfortunately, after publication of this article [1], it was noticed that the author J. Carel Goslings was tagged incorrectly during the production process. This resulted in the PubMed display of the author name as ‘J Carel Goslings’. The correct display is ‘Goslings JC’. This correction contains the correct tagging.
References
Broberg MA, Morrey BF (1986) Results of delayed excision of the radial head after fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am 68:669–674
Chalidis BE, Sachinis NC, Samoladas EP, Dimitriou CG, Pournaras JD (2008) Is tension band wiring technique the “gold standard” for the treatment of olecranon fractures? A long term functional outcome study. J Orthop Surg Res 3:9
Cole RJ, Bindra RR, Evanoff BA, Gilula LA, Yamaguchi K, Gelberman RH (1997) Radiographic evaluation of osseous displacement following intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: reliability of plain radiography versus computed tomography. J Hand Surg Am 22:792–800
Doornberg J, Lindenhovius A, Kloen P, van Dijk CN, Zurakowski D, Ring D (2006) Two and three-dimensional computed tomography for the classification and management of distal humeral fractures. Evaluation of reliability and diagnostic accuracy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88:1795–1801
Doring AC, Nota SP, Hageman MG, Ring DC (2014) Measurement of upper extremity disability using the patient-reported outcomes measurement information system. J Hand Surg 39:1160–1165
Flinterman HJ, Doornberg JN, Guitton TG, Ring D, Goslings JC, Kloen P (2014) Long-term outcome of displaced, transverse, noncomminuted olecranon fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(6):1955–1961
Futamura K, Baba T, Homma Y, Mogami A, Kanda A, Obayashi O, Sato K, Ueda Y, Kurata Y, Tsuji H, Kaneko K (2016) New classification focusing on the relationship between the attachment of the iliofemoral ligament and the course of the fracture line for intertrochanteric fractures. Injury 47(8):1685–1691
Guitton TG, Ring D, Science of Variation G (2011) Interobserver reliability of radial head fracture classification: two-dimensional compared with three-dimensional CT. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:2015–2021
Jones JT, Nelson SL, Wootton J, Ying J, Ying J, Liberio B, Greenler AJ, Wiley K, Lee J, Huggins JL, LE Schanberg, Hermine B (2014) A134: validation of patient reported outomes measurement information system modules for use in childhood—onset lupus. Arthr Rheumatol 66(Suppl 11):S176–S177
Karlsson MK, Hasserius R, Karlsson C, Besjakov J, Josefsson PO (2002) Fractures of the olecranon: a 15 to 25-year followup of 73 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res 403:205–212
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Menendez ME, Bot AG, Hageman MG, Neuhaus V, Mudgal CS, Ring D (2013) Computerized adaptive testing of psychological factors: relation to upper-extremity disability. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95:e149
Rommens PM, Kuchle R, Schneider RU, Reuter M (2004) Olecranon fractures in adults: factors influencing outcome. Injury 35:1149–1157
Schneider MM, Nowak TE, Bastian L, Katthagen JC, Isenberg J, Rommens PM, Muller LP, Burkhart KJ (2014) Tension band wiring in olecranon fractures: the myth of technical simplicity and osteosynthetical perfection. Int Orthop 38:847–855
Wiegand L, Bernstein J, Ahn J (2012) Fractures in brief: olecranon fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:3637–3641
Yoon KH, Tak DH, Park JS, Joo YB, Lee S (2016) Medial synovial fold of the posterior cruciate ligament on knee magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopy: retrospective investigation of impingement. J Comput Ass Tomogr 40(5):799–802
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank prof. Dr. David Ring for his valuable comments regarding the manuscript.
Collaborators: E. Hoebink, P. Nolte, P. Eggen, R. Blokzijl, D. Haverkamp, D. L. van Deurzen, A. Vochteloo, T. Kraal, A. Peters, E. E. J. Raven, M. M. Campo, A. Heijink, E. Mutsaerts, S. A. F. Tulner, J. R. Lansdaal, J. Jenner, C. C. J. Jaspars, R. A. van den Wijngaard, A. J. M. Janus, E. M. Nelissen, M. van der Pluijm, H. van der Bracht, R. van Hove, D. Broekhuis, M. P. Somford, P. J. Damen, P. Scholten, J. J. Wiegerinck, C. Schonhuth, D. van Kampen, D. Eygendaal, B. van Ooij, L. Plaat, T. G. Guitton, S. B. Schouten, J. Hermans, E. W. Zwitser, R. J. P. van der Wal, G. A. Buijze, A. van Tongel, D. van Oostveen, S. van de Velde.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no non-financial competing interests (political, personal, religious, ideological, academic, intellectual, commercial or any other) to declare in relation to this manuscript.
Patient consent
Obtaining the informed consent from involved patients was waived by the Research Ethics Committee.
Ethical approval
All procedures involving human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee.
Funding
No funding was obtained.
Additional information
Members of the Shoulder elbow platform listed in the acknowledgements.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Claessen, F.M., van den Bekerom, M.P., van Dijk, C.N. et al. Tension band wiring for simple olecranon fractures: evaluation of surgical technique. J Orthop Traumatol 18, 275–281 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10195-017-0450-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10195-017-0450-2