Abstract
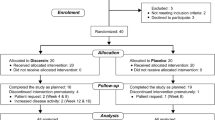
The superiority of the combination therapy of methotrexate (MTX) and anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) biological agents over anti-TNF monotherapy in MTX-naïve patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been demonstrated. We investigated the efficacy and safety of continuation versus discontinuation of MTX at the commencement of etanercept (ETN) in patients with active RA despite MTX therapy. In total, 151 patients with active RA despite treatment with MTX were randomized to either ETN 25 mg twice a week and MTX 6–8 mg/week (the E + M group) or ETN alone (the E group). Co-primary endpoints included the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) good response rate and the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 50 response rate at week 24. Demographic and clinical features between groups at baseline were similar. The EULAR good response rates were significantly higher in the E + M group (52%) than in the E group (33%) at week 24 (p = 0.0001). Although the ACR50 response rate, one of the co-primary endpoints, and the ACR70 response rate at week 24 were not significantly greater in the E + M group (64 and 38%, respectively) than in the E group (48 and 26%, respectively), the ACR20 response rate was significantly greater in the E + M group (90%) than in the E group (64%; p = 0.0002). Safety profiles were similar for the groups. Thus, MTX should be continued at the commencement of ETN therapy, even in RA patients who show an inappropriate response to MTX.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keystone EC. Strategies to control disease in rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor antagonists—an opportunity to improve outcomes. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006;2:594–601.
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, Weisman MH, Emery P. New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2007;370:1861–74.
Moreland LW, Baumgartner SW, Schiff MH, Tindall EA, Fleischmann RM, Weaver AL, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75)-Fc fusion protein. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:141–7.
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, et al. A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1586–93.
Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, Bulpitt KJ, Fleischmann RM, Fox RI, et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:253–9.
Klareskog L, van der Heijde D, de Jager JP, Gough A, Kalden J, Malaise M, et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double-blind randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2004;363:675–81.
van Riel PLCM, Taggart AJ, Sany J, Gaubitz M, Nab HW, Pedersen R, et al. Efficacy and safety of combination etanercept and methotrexate versus etanercept alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to methotrexate: the ADORE study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1478–83.
Miyasaka N, Takeuchi T, Eguchi K. Guidelines for the proper use of etanercept in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:63–7.
Kameda H, Sekiguchi N, Nagasawa H, Amano K, Takei H, Suzuki K, et al. Development and validation of handy rheumatoid activity score with 38 joints (HRAS38) in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving infliximab. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:381–8.
Choy EH. Two is better than one? Combination therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2004;43:1205–7.
Goekoop-Ruiterman YPM, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, van Zeben D, Kerstens PJSM, Hazes JMW, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt Study). Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3381–90.
Combe B, Codreanu C, Fiocco U, Gaubitz M, Geusens PP, Kvien TK, et al. Etanercept and sulfasalazine, alone and combined, in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite receiving sulfasalazine: a double-blind comparison. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1357–62.
van der Heijde D, Klareskog L, Rodriguez-Valverde V, Codreanu C, Bolosiu H, Melo-Gomes J. Comparison of etanercept and methotrexate, alone and combined, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Two-year clinical and radiographic results from the TEMPO study, a double-blind, randomized trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1063–74.
Kameda H, Amano K, Sekiguchi N, Takei H, Ogawa H, Nagasawa H, et al. Factors predicting the response to low-dose methotrexate therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a better response in male patients. Mod Rheumatol. 2004;14:442–6.
Yamanaka H, Tanaka Y, Sekiguchi N, Inoue E, Saito K, Kameda H, et al. Retrospective study on the notable efficacy and related factors of infliximab therapy in a rheumatoid arthritis management group in Japan (RECONFIRM). Mod Rheumatol. 2007;17:28–32.
Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Inoue E, Saito K, Sekiguchi N, Sato E, et al. Retrospective study on the notable efficacy and related factors of infliximab therapy in a rheumatoid arthritis management group in Japan: one-year clinical outcome (RECONFIRM-2). Mod Rheumatol. 2008;18:146–52.
Takeuchi T, Yamanaka H, Inoue E, Nagasawa H, Nawata M, Ikari K, et al. Retrospective clinical study on the notable efficacy and related factors of infliximab therapy in a rheumatoid arthritis management group in Japan: one-year outcome of joint destruction (RECONFIRM-2J). Mod Rheumatol. 2008;18:447–52.
Maini E, St clair EW, Breedveld F, Furst D, Kalden J, Weisman M, et al. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomized phase III trial. Lancet. 1999;354:1932–9.
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DMFM, St. Claire EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1594–602.
St. Clair EW, van der Heijde DMFM, Smolen JS, Maini RN, Bathon JM, Emery P. Combination of infliximab and methotrexate therapy for early rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3432–43.
van Vollenhoven RF, Ernestam S, Harju A, Bratt J, Klareskog L. Etanercept versus etanercept plus methotrexate: a registry-based study suggesting that the combination is clinically more efficacious. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5:R347–51.
Hyrich KL, Symmons DPM, Watson KD, Silman AJ, on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Comparison of the response to infliximab or etanercept monotherapy with response to cotherapy with methotrexate or another disease-modifying antirheumatic drug in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1786–94.
Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollenhoven R, et al. The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:26–37.
Zachariae C, Mørk NJ, Reunala T, Lorentzen H, Falk E, Karvonen SL, et al. The combination of etanercept and methotrexate increases the effectiveness of treatment in active psoriasis despite inadequate effect of methotrexate therapy. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88:495–501.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the following investigators, their staff and sites: Shiozawa K. (Konan Hospital Foundation, Kakogawa Hospital), Kobayashi S. (Juntendo University School of Medicine, Koshigaya Hospital), Tamura N. (Juntendo University School of Medicine, Juntendo Hospital), Sawada T. (The University of Tokyo Hospital), Yamana S. (Higashihiroshima Memorial Hospital), Honda Y. (Kurume University Hospital), Kojima T. (Nagoya University Hospital), Takahashi H. (Sapporo Medical University Hospital), Sugiyama T. (Shimoshizu National Hospital), Taniguchi A. (Tokyo Women’s Medical University, Institute of Rheumatology), Nannki T. (Tokyo Medical & Dental University, Hospital Faculty of Medicine), Yamamura M. (Aich Medical University Hospital), Kurasawa K. (Dokkyo Medical University Hospital), Chiba K. (Fukushima Daiich Hospital), Kato K. (Fujita Health University Hospital), Ezawa K. (Kurashiki Kousai Hospital), Fujii T. (Kyoto University Hospital), Nakata S. (Matsuyama Red Cross Hospital), Tamachi S. (Mie Chuou Medical Center), Kawabe Y. (National Hospital Organization, Ureshino Medical Center), Yano R. (Okayama University Hospital), Kuroiwa T. (The Hospital of Hyogo College of Medicine), Kubota A. (Toho University Omori Medical Center), Kanbe K. (Tokyo Women’s Medical University Medical Center East); Hyogo Prefectural General Rehabilitation Center; Konan Hospital Foundation, Rokko Island Hospital; Kurume University Medical Center; Nagasaki University Hospital of Medicine and Dentistry; Nihon University Itabashi Hospital; Niigata University Medical and Dental Hospital; Osaki Citizen Hospital; Saiseikai Takaoka Hospital; St. Marianna University School of Medicine Hospital; Taihakusakura Hospital; Tohoku Kosei Nenkin Hospital; Tohoku University Hospital; Tsukuba University Hospital. This study was supported by the Advanced Clinical Research Organization (ACRO, Japan) and by research grants from the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
Conflict of interest statement
HK, TH, TA and YT received honoraria from Wyeth. SS received an unrestricted research grant from Wyeth. SN, MT, TK and TT received unrestricted research grants and honoraria from Wyeth.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kameda, H., Ueki, Y., Saito, K. et al. Etanercept (ETN) with methotrexate (MTX) is better than ETN monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite MTX therapy: a randomized trial. Mod Rheumatol 20, 531–538 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-010-0324-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-010-0324-4