Abstract
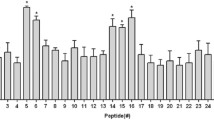
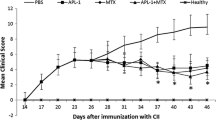
We reported that peripheral blood mononuclear cells from HLA-DRB1*0101 Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were highly reactive to 256–271 peptide of type II collagen (CII). Similar to RA, T cells reactive to CII (AA256–271) play a crucial role in the generation of arthritis in CII-induced arthritis mouse (I-Aq). In the present study, we regulated the CII reactivity of T cells from CIA mouse with I-Aq by altered peptide ligand (APL). Eight different APLs were designed and screened for their antagonistic activity using CII reactive cytokine production assay. Four APLs of CII 256–271 exhibited antagonistic activity in CII-reactive T cells. Moreover, intraperitoneally injected APL-5 (G262A) significantly suppressed CII-induced arthritis in mice, whereas the other three APLs did not. Compared with the control, APL-5 suppressed interleukin (IL)-17 production by T cells from CII-induced arthritis mice. These results suggest that CII APL is a potentially suitable therapeutic strategy for the control of RA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Struyk L, Hawes GE, Dolhain RJ, van Scherpenzeel A, Godthelp B, Breedveld FC, et al. Evidence for selective in vivo expansion of synovial tissue-infiltrating CD4+CD45RO+T lymphocyte on the basis of CDR3 diversity. Int Immunol. 1994;6:897–907.
Fugger L, Svejgaard A. Association of MHC and rheumatoid arthritis. HLA-DR4 and rheumatoid arthritis: studies in mice and human. Arthritis Res Ther. 2000;2:208–11.
Londei M, Savill CM, Verhoef A, Brennan F, Leech ZA, Duance V, et al. Persistence of collagen type II-specific T cell clones in the synovial membrane of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:636–40.
Saeki T, Kato T, Masuko-Hongo K, Nakamura H, Yoshino S, Nishioka K, et al. Type II collagen is a target antigen of clonally expanded T cells in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58:446–50.
Luross JA, Williams NA. The genetic and immunopathological processes underlying collagen-induced arthritis. Immunology. 2001;103:407–16.
Magistris MTD, Alexander J, Coggeshall M, Altman A, Gaeta FC, Grey HM, et al. Antigen analog-major histocompatibility complexes act as antagonists of the T cell receptor. Cell. 1992;68:625–34.
Pfeiffer C, Stein J, Aouthwood S, Ketelaar H, Sette A, Bottomly K. Altered peptide ligands can control CD4 T lymphocyte differentiation in vivo. J Exp Med. 1995;181:1569–74.
Ohnishi Y, Tsutsumi A, Matsumoto I, Goto D, Ito S, Kuwana M, et al. Altered peptide ligands control type II collagen-reactive T cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:226–8.
Wraith DC, Smilek DE, Mitchell DJ, Steinman L, McDevitt HO. Antigen recognition in autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the potential for peptide-mediated immunotherapy. Cell. 1989;59:247–55.
Myers LK, Rosloniec EF, Seyer JM, Stuart JM, Kang AH. A synthetic peptide analogue of a determinant of type II collagen prevents the onset of collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 1993;150:4652–8.
Miller SD, Turley DM, Podojil JR. Antigen-specific tolerance strategies for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:665–77.
Nakae S, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwakura Y. Suppression of immune induction of collagen-induced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2003;171:6173–7.
Myers LK, Tang B, Rosloniec EF, Stuart JM, Chiang TM, Kang AH. Characterization of a peptide analogue of a determinant of type II collagen that suppress collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 1998;161:3589–95.
Zhao J, Li R, He J, Shi J, Long L, Li Z. Mucosal administration of an altered CII263–272 peptide inhibits collagen-induced arthritis by suppression of Th1/Th17 cells and expansion of regulatory T cells. Rheumatol Int. 2008;29:9–16.
Vermeire K, Heremans H, Vandeputte M, Huang S, Billiau A, Matthys P. Accelerated collagen-induced arthritis in IFN-gamma receptor-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1997;158:5507–13.
Coppieters K, Van Beneden K, Jacques P, Dewint P, Vervloet A, Vander Cruyssen B, et al. A single early activation of invariant NK T cells confers long-term protection against collagen-induced arthritis in ligand-specific manner. J Immunol. 2007;179:2300–9.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by a Research Grant from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, and the Research Grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors confirm that they have no conflicts of interest with regard to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
E. Wakamatsu is a research fellow of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
About this article
Cite this article
Wakamatsu, E., Matsumoto, I., Yoshiga, Y. et al. Altered peptide ligands regulate type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Mod Rheumatol 19, 366–371 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0174-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0174-0