Abstract
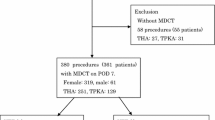
We prospectively evaluated the disease-specific features of the early postoperative plasma d-dimer value and the relationship with deep venous thrombosis and/or pulmonary thromboembolism (DVT/PE) in 95 patients following total knee arthroplasty. Patients in whom DVT/PE was highly suspected were diagnosed by high-resolution multi-detector row computed tomography scanning (MDCT). Forty-nine knees in 46 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA, 24 knees) or osteoarthritis (OA, 25 knees) were finally recruited. DVT/PE was detected in 28 (57.1%) of the 49 cases examined by diagnostic MDCT: 12 (50.0%) of the 24 cases of RA, and 16 (64.0%) of the 25 cases of OA. Of these, PE was found in 11 cases (39.2%), but none of them showed clinical symptomatic signs of dyspnea or chest pain. In both RA and OA cases, there were statistically significant differences in the d-dimer value on postoperative day 3 (P = 0.027) and after day 28 (P = 0.037) between the groups with and without DVT/PE. In OA cases, there were significant differences between the two groups on postoperative days 1 (P = 0.034), 3 (P = 0.020), 5 (P = 0.005), and 7 (P = 0.045), respectively. At the baseline, perioperative d-dimer levels in the RA group without DVT/PE were higher than in the OA group. However, multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that RA was not a significant risk factor of DVT/PE in comparison with OA. In conclusion, individual evaluation of the d-dimer level between RA and OA should provide a more precise predictive indicator of early postoperative DVT/PE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maynard MJ, Sculco TP, Ghelman B. Progression and regression of deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;1:125–30.
Schiff RL, Kahn SR, Shrier I, Strulovitch C, Hammouda W, Cohen E, et al. Identifying orthopedic patients at high risk for venous thromboembolism despite thromboprophylaxis. Chest. 2005;128:3364–71.
Kearon C. Duration of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after surgery. Chest. 2003;124:386S–92.
Kelly J, Hunt BJ. A clinical probability assessment and d-dimer measurement should be the initial step in the investigation of suspected venous thromboembolism. Chest. 2003;124:1116–9.
Stein PD, Hull RD, Patel KC, Olson RE, Ghali WA, Brant R, et al. d-dimer for the exclusion of acute venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:589–602.
Mukubo Y, Kawamata M. Higher preoperative d-dimer value remain high postoperatively in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with those with osteoarthrosis. J Anesth. 2006;20:51–3.
Parvizi J, Mui A, Purtill JJ, Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH. Total joint arthroplasty: when do fatal or near-fatal complications occur? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:27–32.
Helwig U, Schaub S, Berghold A, Ziervogel H. Coagulation parameters after retransfusion of unwashed blood. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21:385–91.
Nasu Y, Takeda K, Yorimitsu M, Abe N, Sato T, Hashizume H. d-dimer testing for a early screening for the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. J Jpn Knee Soc. 2005;30:120–3.
Shiota N, Sato T, Nishida K, Matsuo M, Takahara Y, Mitani S, et al. Changes in LPIA d-dimer levels after total hip or knee arthroplasty relevant to deep-vein thrombosis diagnosed by bilateral ascending venography. J Orthop Sci. 2002;7:444–50.
Siddiqui AU, Buchman TG, Hotchkiss RS. Pulmonary embolism as a consequence of applying sequential compression device on legs in a patient asymptomatic of deep vein thrombosis. Anesthesiology. 2000;92:880–2.
Fraser JD, Anderson DR. Deep venous thrombosis: recent advances and optimal investigation with US. Radiology. 1999;211:9–24.
Segal JB, Eng J, Tamariz LJ, Bass EB. Review of the evidence on diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Ann Fam Med. 2007;5:63–73.
Nakamura M. Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis in the perioperative period. Masui. 2006;55:1371–81.
Cham MD, Yankelevitz DF, Henschke CI. Thromboembolic disease detection at indirect CT venography versus CT pulmonary angiography. Radiology. 2005;234:591–4.
Loud PA, Katz DS, Bruce DA, Klippenstein DL, Grossman ZD. Deep venous thrombosis with suspected pulmonary embolism: detection with combined CT venography and pulmonary angiography. Radiology. 2001;219:498–502.
Perrier A, Roy PM, Sanchez O, Le Gal G, Meyer G, Gourdier AL, et al. Multidetector-row computed tomography in suspected pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1760–8.
Stein PD, Fowler SE, Goodman LR, Gottschalk A, Hales CA, Hull RD, et al. Multidetector computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2317–27.
Winer-Muram HT, Rydberg J, Johnson MS, Tarver RD, Williams MD, Shah H, et al. Suspected acute pulmonary embolism: evaluation with multi-detector row CT versus digital subtraction pulmonary arteriography. Radiology. 2004;233:806–15.
Caprini JA, Glase CJ, Anderson CB, Hathaway K. Laboratory markers in the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2004;109:I4–8.
Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, Forgie M, Kearon C, Dreyer J, et al. Evaluation of d-dimer in the diagnosis of suspected deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1227–35.
So AK, Varisco PA, Kemkes-Matthes B, Herkenne-Morard C, Chobaz-Peclat V, Gerster JC, et al. Arthritis is linked to local and systemic activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis pathways. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:2510–5.
Weinberg JB, Pippen AM, Greenberg CS. Extravascular fibrin formation and dissolution in synovial tissue of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991;34:996–1005.
Wallberg-Jonsson S, Cvetkovic JT, Sundqvist KG, Lefvert AK, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S. Activation of the immune system and inflammatory activity in relation to markers of atherothrombotic disease and atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2002;29:875–82.
Ichikawa Y, Yamada C, Horiki T, Hoshina Y, Uchiyama M. Serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 and fibrin degradation product levels correlate with clinical disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998;16:533–40.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Dr. Toru Miyoshi for critical reading of the manuscript, and in particular statistical analysis of the data. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshitaka, T., Abe, N., Minagawa, H. et al. Disease-specific screening for deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism using plasma d-dimer values after total knee arthroplasty. Mod Rheumatol 18, 359–365 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-008-0068-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-008-0068-6