Abstract
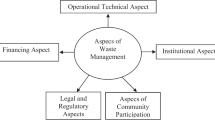
With the rapid growth of healthcare waste and improvement of people’s environment awareness, the sustainability of healthcare waste management is becoming increasingly important. However, there is no research on the identification of key factors that influence sustainable healthcare waste management using the quantitative methods in the existing literature. Based on an in-depth analysis of the existing literature, we found out 15 factors influencing sustainable healthcare waste management. Then we used the interval-valued fuzzy DEMATEL (Decision Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory) method to analyze these factors. Finally, we presented a case study to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. We found that sound legal framework supporting sustainability, strengthening sustainable management training or education programs and positive attitude and perception towards sustainable healthcare waste management are the top three most important factors. This study contributes to the literature on sustainable healthcare waste management and helps to improve the sustainability of healthcare waste management.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moscelli G, Siciliani L, Gutacker N, Cookson R (2018) Socioeconomic inequality of access to healthcare: does choice explain the gradient. J Health Econ 57:290–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhealeco.2017.06.005
Aung TS, Luan SJ, Xu QY (2019) Application of multi-criteria-decision approach for the analysis of medical waste management systems in Myanmar. J Clean Prod 222:733–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.049
Caniato M, Tudor T, Vaccari M (2015) International governance structures for health-care waste management: a systematic review of scientific literature. J Environ Manag 153:93–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.01.039
Li H, Li JL, Zhang ZB et al (2020) Establishing an interval-valued fuzzy decision-making method for sustainable selection of healthcare waste treatment technologies in the emerging economies. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 22:501–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00943-0
Azmal M, Kalhor R, Dehcheshmeh NF (2014) Going toward green hospital by sustainable healthcare waste management: Segregation, treatment and safe disposal. Health 6:2632–2640. https://doi.org/10.4236/health.2014.619302
Hong JM, Zhan S, Yu ZH et al (2018) Life-cycle environmental and economic assessment of medical waste treatment. J Clean Prod 174:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.206
Apergis N, Bhattacharya M, Hadhri W (2020) Health care expenditure and environmental pollution: a cross-country comparison across different income groups. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:8142–8156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07457-0
Bui TD, Tsai FM, Tseng ML, Ali MH (2020) Identifying sustainable solid waste management barriers in practice using the fuzzy Delphi method. Resour Conserv Recycl 154:104625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104625
Salman RA, Beller E, Kagan J et al (2014) Increasing value and reducing waste in biomedical research regulation and management. Lancet 383(9912):176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62297-7
Martens ML, Carvalho MM (2017) Key factors of sustainability in project management context: a survey exploring the project managers’ perspective. Int J Proj Manag 35(6):1084–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2016.04.004
Cavicchi C, Vagnoni E (2017) Does intellectual capital promote the shift of healthcare organizations towards sustainable development? Evidence from Italy. J Clean Prod 153:275–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.175
Li H, Li JL, Zhu JR (2019) Intervention mechanism of healthcare service goods based on social welfare maximization in China. PLoS ONE 14(3):e0214655. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214655
Maria FD, Sisani F, Contini S et al (2020) Is the policy of the European Union in waste management sustainable? An assessment of the Italian context. Waste Manage 103:437–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.01.005
Xu Y, Yeh CH, Yang SP (2020) Risk-based performance evaluation of improvement strategies for sustainable e-waste management. Resour Conserv Recycl 155:104664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104664
Romano G, Senante MM (2020) Factors affecting eco-efficiency of municipal waste services in Tuscan municipalities: an empirical investigation of different management models. Waste Manage 105:384–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.02.028
Bartolacci F, Paolini A, Quaranta AG et al (2018) Assessing factors that influence waste management financial sustainability. Waste Manage 79:571–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.07.050
Cesaro A, Belgiorno V (2017) Sustainability of medical waste management in different sized health care facilities. Waste Biomass Valor 8:1819–1827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9730-y
Oña J, Oña R, Calvo FJ (2012) A classification tree approach to identify key factors of transit service quality. Expert Syst Appl 39:11164–11171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.03.037
Pietzsch N, Ribeiro JLD, Medeiros JF (2017) Benefits, challenges and critical factors of success for zero waste: a systematic literature review. Waste Manage 67:324–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.05.004
Hsu CH, Chang AY, Luo W (2017) Identifying key performance factors for sustainability development of SMEs e integrating QFD and fuzzy MADM methods. J Clean Prod 161:629–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.063
Vardopoulos I (2019) Critical sustainable development factors in the adaptive reuse of urban industrial buildings. A fuzzy DEMATEL approach. Sustain Cities Soc 50:101684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101684
Singh PK, Sarkar P (2020) A framework based on fuzzy Delphi and DEMATEL for sustainable product development: a case of Indian automotive industry. J Clean Prod 246:118991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118991
Mahmoudi S, Jalali A, Ahmadi M et al (2019) Identifying critical success factors in Heart Failure Self-Care using fuzzy DEMATEL method. Appl Soft Comput 84:105729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105729
Kuo MS (2011) A novel interval-valued fuzzy MCDM method for improving airlines’ service quality in Chinese cross-strait airlines. Transport Res E-LOG 47(6):1177–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2011.05.007
Ashtiani B, Haghighirad F, Makui A et al (2009) Extension of fuzzy TOPSIS method based on interval-valued fuzzy sets. Appl Soft Comput 9(2):457–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2008.05.005
Wang ZF, Ren JZ, Goodsite ME et al (2018) Waste-to-energy, municipal solid waste treatment, and best available technology: comprehensive evaluation by an interval-valued fuzzy multi-criteria decision making method. J Clean Prod 172:887–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.184
Chen SM, Li TS (2013) Evaluating students’ answerscripts based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Inform Sciences 235:308–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2012.12.031
Gorzałczany MB (1987) A method of inference in approximate reasoning based on interval-valued fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 21(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(87)90148-5
Türkşen İB, Bilgiç T (1996) Interval valued strict preference with Zadeh triples. Fuzzy Sets Syst 78(2):183–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(95)00167-0
Cornelis C, Kerre EE (2006) Advances and challenges in interval-valued fuzzy logic. Fuzzy Sets Syst 157(5):622–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2005.10.007
Wang GJ, Li XP (1998) The applications of interval-valued fuzzy numbers and interval-distribution numbers. Fuzzy Sets Syst 98(3):331–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(96)00368-5
Gabus A, Fontela F (1972) World problems, an invitation to further thought within the framework of DEMATEL. Geneva, Switzerland, Geneva Research Center
Kumar A, Dixit G, Prabhakar D (2016) Analyzing the factors affecting the sustainable municipal solid waste management (MSWM). Indian J Sci Technol 9(47):1–7. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i47/105286
Chauhan A, Singh A (2016) A hybrid multi-criteria decision making method approach for selecting a sustainable location of healthcare waste disposal facility. J Clean Prod 139:1001–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.098
Ezeah C, Roberts CL (2012) Analysis of barriers and success factors affecting the adoption of sustainable management of municipal solid waste in Nigeria. J Environ Manage 103:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.02.027
Chen Y, Li PJ, Carlo L et al (2009) Sustainable management measures for healthcare waste in China. Waste Manage 29(6):1996–2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.11.031
Ko S, Kim W et al (2020) The economic value of sustainable recycling and waste management policies: the case of a waste management crisis in South Korea. Waste Manage 104:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.01.020
Lee S, Vaccari M, Tudor T (2016) Considerations for choosing appropriate healthcare waste management treatment technologies: a case study from an East Midlands NHS Trust, in England. J Clean Prod 135:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.166
Phillips J, Mondal MK (2014) Determining the sustainability of options for municipal solid waste disposal in Varanasi. India. Sustain Cities Soc 10:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2013.04.005
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 71432002, 71972012) and Chinese Government Scholarship of China Scholarship Committee (Grant No. 201906030126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Dietl, H. & Li, J. Identifying key factors influencing sustainable element in healthcare waste management using the interval-valued fuzzy DEMATEL method. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 23, 1777–1790 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01233-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01233-4