Abstract
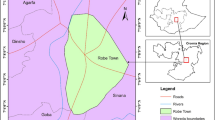
The installation of an olive mill wastewater (OMW) disposal site without well-defined standards and constraints may cause undesirable long-term effects on soils and groundwater. In Tunisia and other developing countries, there are no solid waste control regulations to control the location selection of disposal sites. In this study, the OMW disposal site criteria established in Greece, Turkey, and China’s regulations were used to select the best location for the OMW disposal site in the Sidi Bouzid region of Tunisia. The multi-criteria analysis was performed using a geographic information system (GIS) combined with the different functions of the fuzzy set method for suitability criteria. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) was used to assign the weight of selected criteria and the weighted linear combination (WLC) aggregation method is displayed to create the final OMW disposal site. The obtained results show that the selection of suitable OMW disposal sites is based on different norms, given the spatial differences of the selected areas. The final decision is based on the selection of the strictest solid waste control regulations which takes into consideration environmental and socio-economic effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jarboui R, Hadrich B, Gharsallah N, Ammar E (2010) Olive mill wastewater disposal in evaporation ponds in Sfax (Tunisia): moisture content effect on microbiological and physical chemical parameters. Biodegradation 20:845–858
Lopes M, Araujo C, Aguedo M, Gomes N, Gonçalves C, Teixeira JA, Belo I (2009) The use of olive mill wastewater by wild type Yarrowia lipolytica strains: medium supplementation and surfactant presence effect. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84(4):533–537
Ammar E, Mekki H, Ueno S, Ben Zina M (2004) Traitement de l’effluent des huileries d’olive et son inte´gration dans des briques de construction – optimisation des proprie´te´sphysico-me´caniques par analyse statistique. Annal Chimie Sci Mate´r 29:33–46 (treatment of olive mill effluent and its integration in building bricks – optimization of physico-mechanical properties by statistical analysis).
Kavvadias V, Doula MK, Komnitsas K, Liakopoulou N (2010) Disposal of olive oil mill wastes in evaporation ponds: effects on soil properties. J Hazard Mater 182:144–155
Komnitsas K, Zaharaki D (2012) Pre-treatment of olive mill wastewaters at laboratory and mill scale and subsequent use in agriculture: legislative framework and proposed soil quality indicators. Resour Conserv Recycl 69:82–89
Roig A, Cayuela ML, Sànchez-Monedero MA (2006) An overview on olive mill wastes and their valorization methods. Waste Manage 26:960–969
Shabou R, Zairi M, Kallel A, Aydi A, Ben Dhia H (2009) Assessing the effect of an olive mill wastewater evaporation pond in Sousse, Tunisia. Environ Geol 58:679–686
Aydi A, Zairi M, Ben Dhia H (2013) Minimization of environmental risk of landfill site using fuzzy logic, analytical hierarchy process, and weighted linear combination methodology in a geographic information system environment. Environ Earth Sci 68(5):1375–1389
Zamorano M, Molero E, Hurtado A, Grindlay A, Ramos A (2008) Evaluation of a municipal landfill site in southern Spain with GIS-aided technology. J Hazardous Mater 160:473–481
Ersoy H, Bulut F (2009) Spatial and multi-criteria decision analysis based methodology for landfill site selection in growing urban regions. J Waste Manag Res 27:489–500
Vatalis K, Manoliadis O (2002) A two-level multicriteria DSS for landfill site selection using GIS: case study in Western Macedonia, Greece. J Geogr Inf Decis Anal 6:49–56
Kontos TD, Komilis DP, Halvadakis CP (2003) Siting MSW landfills on Lesvos Island with a GIS-based methodology. Waste Manage Res 21:262–277
Ahmad SZ, Ahamad MSS, Wan Hussin WMA (2011) Comparative site selection process based on different policies and guidelines for municipal solid waste landfill site. In: 10th International symposium & exhibition on geoinformation 2011 (ISG 2011), Selangor, Malaysia, 27–29 September 2011
INS (Institut National de la Statistique) (2011) Données générales sur la population: données démographiques et sociales. http://www.ins.nat.tn
Lazzez A, Vichi S, Kammoun NG, Arous MN, Khlif M, Romero A, Cossentini M (2011) A four year study to determine the optimal harvesting period for Tunisian Chemlali olives. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 113:796–807
Regional Commission for Agricultural Development of Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia (2015) Projet les cartes agricoles, données numériques
Eldrandaly KA (2013) Developing a GIS – based MCE site selection tool in ArcGIS using COM technology. Int Arab J Inf Technol 10(3):276–282
Aydi A, Zairi M, Ben Dhia H (2012) Apport du SIG et des méthodes d’analyse multicritère pour le choix de site de stockage de margines. Revue Géomatique Expert N° 86
Aydi A (2018) Evaluation of groundwater vulnerability to pollution using a GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis. Groundw Sustain Dev 7:204–211
Huanga Y, Lanb Y, ThomsonaSJ FA, Hoffmannb WC, Laceyd RE (2010) Development of soft computing and applications in agricultural and biological engineering. Comput Electron Agric 71:107–127
Feizizadeh B, Blaschke T (2013) GIS-multi criteria decision analysis for landslide susceptibility mapping: comparing three methods for the Urmia lake basin, Iran. Nat Hazards 65:2105–2128
Kaufmann A (1975) Introduction to the theory of fuzzy subsets: vol. 1 - Fundamental theoretical elements. Academic Press, New York, pp 409
Kandel A (1982) Fuzzy techniques in pattern recognition. John Wiley and Sons, New York, p 356
Dubois D, Prade H (1980) Fuzzy sets and systems: Theory and application. Academic Press, New York, p 393
Eastman JR, Kyem PAK, Toledano J (1993) A procedure for multi-objective decision making in GIS under conditions of conflicting objectives. In Proceedings of European Conference on Geographical Information Systems, EGIS’93 (Utrecht: EGIS Foundation) 438–448
Eastman JR (2003) IDRISI Kilimanjaro: Guide to GIS and Image Processing. Clark University: Worcester, 1, 87–131. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2002.802519
Aydi A, Abichou T, Hamdi Nasr I, Louati M, Zairi M (2016) Assessment of land suitability for Olive mill wastewater Disposal Site Selection by integrating fuzzy logic, AHP and WLC in a GIS. Environ Monit Assess 188:59
Unal M, Cilek A, Guner ED (2020) Implementation of fuzzy, Simos and strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats analysis for municipal solid waste landfill site selection: Adana City case study. Waste Manag Res. 38 (1_suppl): 45–64
Saaty TL (1977) A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J Math Psychol 15(3):234–281
Saaty TL (2008) Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Serv Sci 1(1):83–97
Sharifi M, Hadidi M, Vessali E, Mosstafakhani P, Taheri K, Shahoie S, Khodamoradpour M (2009) Integrating multi-criteria decision analysis for a GIS-based hazardous waste landfill sitting in Kurdistan Province Western Iran. Waste Manag 29(10):2740–2758
Sener B, Suzen L, Doyuran V (2006) Landfill site selection by using geographic information systems. Environm Geol 49:376–388
Eskandari M, Homaee M, Mahmodi S (2012) An integrated multi criteria approach for landfill siting in a conflicting environmental, economical and socio-cultural area. Waste Manag 32:1528–1538
Saaty T, Vargas L (2001) Models, methods, concepts and applications of the analytic hierarchy process. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Edition, Boston
Rezaei-Moghaddam K, Karami E (2008) A multiple criteria evaluation of sustainable agricultural development models using AHP. Environ Dev Sustain 10:407–426
Bhushan N, Rai K (2004) Strategic Decision Making: Applying the AnalyticHierarchy Process. Springer-Verlag, New York, p 172
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26
Eastman JR (2006) IDRISI Andes Guide to GIS and Image Processing Manual Version 15.00. Clark University, Worcester, Massachusetts
Eastman JR (2006) IDRISI Andes Tutorial Manual Version 15.00. Clark University, Worcester, Massachusetts
Khodaparast M (2017) Municipal solid waste landfill siting by using GIS and analytical hierarchy process (AHP): a case study in Qom city, Iran. Environm Earth Sci 77:52
Psonis K, Latsoudas C, Skourtsis-Koroneou V, Varti-Mataranga M, Petridou V (1982) Geologic Map of Greece, Scale 1:50,000. Kardhamili sheet, Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration (IGME)
Dorhofer G, Siebert H (1998) The search for landfill sites—requirements and implementation in Lower Saxony, Germany. Environm Geol 35(1):55–65
Nas B, Karabork H, Ekercin S, Berktay A (2008) Mapping chlorophyll-a through in-situ measurements and Terra ASTER satellite data. Environm Monitor Assessm 157:375–382
Greek Governmental Ministry Decision 114218/97 (1997) Document 1016 B’/17 –11-97 “Framework of Specifications and General Planning for Solid Wastes, in Greek
European Council Directive 1999/31/EC, Document L 182 (1999) Landfilling of Solid Wastes. Off. J. L 182, 16/07/1999 P. 0001 - 0019
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) (2014) National Air Quality Index. Central Pollution -Control Board, Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Government of India
Ministry of Environment and Forestry of Turkey (2000) Control list of site selection criteria for landfill sites. Ankara http://www.atikyonetimi.cevreorman.gov.tr/evsel/2.doc (Accessed 15.04.09)
Antonakos AK, Lambrakis NJ (2007) Development and testing of three hybrid methods for the assessment of aquifer vulnerability to nitrates, based on the drastic model, an example from NE Korinthia, Greece. J Hydrol 333(2):288–304
Cinelli M, Coles SR, Kirwan K (2014) Analysis of the potentials of multi criteria decision analysis methods to conduct sustainability assessment. Ecol Ind 46:138–148
Leao S, Bishop I, Evans D (2001) Assessing the demand of solid waste disposal in urban region by urban dynamics modelling in a GIS environment. Resour Conserv Recycl 33(4):289–313
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Issaoui, W., Aydi, A., Mahmoudi, M. et al. GIS-based multi-criteria evaluation for olive mill wastewater disposal site selection. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 23, 1490–1502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01231-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01231-6