Abstract
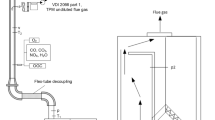
Wood pellet is a densified fuel with homogeneous physical properties suitable for use at various scales in domestic and industrial furnaces. A wood pellet stove is a small-scale furnace for domestic heat production that can replace conventional oil or gas boilers. Since the fuel properties of wood pellet are very different from those of oil or gas, the design of a wood pellet stove requires profound understanding of solid fuel combustion as well as of gas flow mixing and reactions. Due to limitations on the height of an installed furnace (~1 m), poor design of the furnace, air supply, fume extraction, or the heat exchanger may lead to excessive CO emissions or low energy efficiency. This study evaluated the design of an existing wood pellet stove with 30,000 kcal/h capacity, using experimental and computational techniques in order to optimize the furnace design. The results show that it is critical to minimize unused furnace volume and to enhance gaseous mixing for reduced CO emissions while maintaining sufficiently high temperatures for fast oxidation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alakangas E, Paju P (2002) Wood pellets in Finland—technology, economy, and market. OPET report 5, Finland
McKendry P (2002) Energy production from biomass (part1): overview of biomass. Bioresour Technol 83:37–46
Johansson LS, Leckner B, Gustavsson L, Cooper D, Tullin C, Potter A (2004) Atmospheric environment 38:4183–4195
Korea Energy Management Corporation (2009) Performance standard of wood pellet stoves (in Korean). http://www.kemco.or.kr. Accessed 1 Feb 2011
Yin C, Rosendahl LA, Kær SK (2008) Grate-firing of biomass for heat and power production. Progr Energy Combust Sci 34:725–754
Ståhl M, Wikstöm F (2009) Swedish perspective on wood fuel pellets for household heating: a modified standard for pellets could reduce end-user problems. Biomass Bioenergy 33:803–809
Korea Forest Service, List of companies qualified for the wood pellet stove supply (in Korean), June 2010, Korea. available from http://www.forest.go.kr. Accessed 1 Feb 2011
Fluent Inc. (2006) Fluent 6.3 user’s guide, Lebanon, New Hampshire
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the 2009 Collaboration Between Industry-Academy-Research Institute program of the Korea Small & Medium Business Administration (SMBA). This paper is based on a presentation given at the 6th I-CIPEC (International Conference on Incineration/Pyrolysis and Emission Control), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–29 July 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YW., Ryu, C., Lee, WJ. et al. Assessment of wood pellet combustion in a domestic stove. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 13, 165–172 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-011-0014-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-011-0014-0