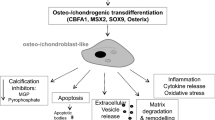
Abstract
Background
Vascular calcification is common in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, while erythropoietin (EPO) is widely used in the treatment of renal anemia in CKD patients, whether there is a link between the two is still not clear.
Methods
The primary rat vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and CKD rats were treated with EPO and the calcium deposition was observed by alizarin red staining, von Kossa staining and calcium quantification. Activation of JAK2/STAT3/BMP-2 axis and NF-κB signaling pathways was investigated by Western blotting.
Results
EPO-induced calcium deposition in VSMCs and significantly potentiated calcification in CKD rats. Furthermore, EPO activated JAK2/STAT3/BMP-2 axis, NF-κB pathway and the pro-calcification effect of EPO was partially blocked by the STAT3 inhibitor (Cryptotanshinone) or NF-κB inhibitor (BAY 11-7082), respectively, in vitro.
Conclusion
EPO could promote VSMCs calcification in vitro and in vivo and this effect may be achieved through the JAK2/STAT3/BMP-2 axis and NF-κB pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;32(5 Suppl 3):112-9.
Stenvinkel P, Carrero JJ, Axelsson J, Lindholm B, Heimburger O, Massy ZA. Emerging biomarkers for evaluating cardiovascular risk in the chronic kidney disease patient: how do new pieces fit into the uremic puzzle? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3(2):505–21.
Liabeuf S, Desjardins L, Diouf M, Temmar M, Renard C, Choukroun G, Massy ZA. The addition of vascular calcification scores to traditional risk factors improves cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with chronic kidney disease. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0131707.
Temmar M, Liabeuf S, Renard C, Czernichow S, Esper NE, Shahapuni I, et al. Pulse wave velocity and vascular calcification at different stages of chronic kidney disease. J Hypertens. 2010;28(1):163.
Sigrist MK, Taal MW, Bungay P, McIntyre CW. Progressive vascular calcification over 2 years is associated with arterial stiffening and increased mortality in patients with stages 4 and 5 chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2007; 2(6):1241–8.
Lau WL, Pai A, Moe SM, Giachelli CM. Direct effects of phosphate on vascular cell function. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011;18(2):105–12.
Shroff RC, McNair R, Figg N, et al. Dialysis accelerates medial vascular calcification in part by triggering smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Caircultion. 2008;118(17):1748–57.
Mody N, Parhami F, Sarafian TA, Demer LL. Oxidative stress modulates osteoblastic differentiation of vascular and bone cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001;31(4):509–19.
Byon CH, Javed A, Dai Q, et al. Oxidative stress induces vascular calcification through modulation of the osteogenic transcription factor Runx2 by AKT signaling. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(22):15319–27.
Hosaka N, Mizobuchi M, Ogata H, et al. Elastin degradation accelerates phosphate-induced mineralization of vascular smooth muscle cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 2009;85(6):523–9.
Pai A, Leaf EM, El-Abbadi M, Giachelli CM. Elastin degradation and vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype change precede cell loss and arterial medial calcification in a uremic mouse model of chronic kidney disease. Am J Pathol. 2011;178(2):764–73.
Paloian NJ, Giachelli CM. A current understanding of vascular calcification in CKD. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014;307(8):F891–900.
Kidney Disease: ImprovingGlobal Outcomes (KDIGO) Anemia Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney inter Suppl. 2012; 2:279–335.
Ammarguellat F, Gogusev J, Drtieke TB. Direct effect of erythropoietin on rat vascular smooth-muscle cell via a putative erythropoietin receptor. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 1996;11:687–92.
Kusano E, Akimoto T, Inoue M, et al. Human recombinant erythropoietin inhibits interleukin-1beta-stimulated nitric oxide and cyclic guanosine monophosphate production in cultured rat vascular smooth-muscle cells. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 1999;14(3):597–603.
Ito C, Kusano E, Furukawa Y, et al. Modulation of the erythropoietin-induced proliferative pathway by cAMP in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;283(6):C1715-21.
Akimoto T, Kusano E, Inaba T, Iimura O, et al. Erythropoietin regulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis by a phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase-dependent pathway. Kidney Int. 2000;58(1):269–82.
Neusser M, Tepel M, Zidek W. Erythropoietin increases cytosolic free calcium concentration in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. 1993;27(7):1233–6.
Patel JJ, Modes JE, Flanagan CL, et al. Dual delivery of EPO and BMP2 from a novel modular Poly-ɛ-Caprolactone Construct to Increase the bone formation in prefabricated bone flaps. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21(9):889–97.
Lin Wan F, Zhang Q, He, et al. EPO promotes bone repair through enhanced cartilaginous callus formation and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102010.
Shiozawa Y, Jung Y, Anne M, et al. Erythropoietin couples hematopoiesis with bone formation. PLoS One. 2010;5(5):e10853.
Koulouridis I, Alfayez M, Trikalinos TA, Balk EM, Jaber BL. Dose of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and adverse outcomes in CKD: a metaregression analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;61(1):44–56.
Szczech LA, Barnhart HX, Inrig JK, et al. Secondary analysis of the CHOIR trial epoetin-alpha dose and achieved hemoglobin outcomes. Kidney Int. 2008;74(6):791–8.
Takenaka T, Itaya Y, Ishikawa I, Kobayashi K, Tsuchiya Y. Skeletal effects of erythropoietin in hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol. 2003;35(3):407–13.
Koury MJ, Bondurant MC. The mechanism of erythropoietin action. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991;18(4 Suppl 1):20–3.
Klingmüller U. The role of tyrosine phosphorylation in proliferation and maturation of erythroid progenitor cells–signals emanating from the erythropoietin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1997;249(3):637–47.
Rong Ma J, Huang HC, et al. JAK2/STAT5/Bcl-xL signalling is essential for erythropoietin-mediated protection against apoptosis induced in PC12 cells by the amyloid β—peptide Aβ25-35. Br J Pharmacol. 2014;171(13):3234–45.
Li C, Shi C, Kim J. Y, et al. Erythropoietin promotes bone formation through EphrinB2/EphB4 signaling. J Dent Res. 2015;94(3):455–63.
Jia G, Stormont RM, Gangahar DM, Agrawal DK. Role of matrix Gla protein in angiotensin II-induced exacerbation of vascular calcification. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;303(5):H523-32.
Watson KE, Bostrom K, Ravindranath R, et al. TGF-beta-1 and 25-hydroxycholesterol stimulate osteoblast-like vascular cells to calcify. J Clin Invest. 1994;93(5):2106–13.
Hautmann MB, Thompson MM, Swartz EA, et al. Angiotensin II-induced stimulation of smooth muscle α-actin expression by serum response factor and the homeodomain transcription factor MHox. Circ Res. 1997;81(4):600–10.
Deaton RA, Su C, Valencia TG, Grant SR, Deaton RA. Transforming growth factor-β1-induced expression of smooth muscle marker genes involves activation of PKN and p38 MAPK. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(35):31172–81.
Zhao G, Xu MJ, Zhao MM, et al. Activation of nuclear factor-kappa B accelerates vascular calcification by inhibiting ankylosis protein homolog expression. Kidney Int. 2012;82(1):34–44.
Zhao MM, Xu MJ, Cai Y, et al. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote p65 nuclear translocation mediating high-phosphate-induced vascular calcification in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int. 2011;79(10):1071–9.
Digicaylioglu M, Lipton SA. Erythropoietin-mediated neuroprotection involves cross-talk between Jak2 and NF-kappaB signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;412(6847):641–7.
Moore E. Bellomo R. Erythropoietin (EPO) in acute kidney injury. Ann Intensive Care. 2011;1(1):3.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Human and animal rights
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Animal Care and Use Committee of Chongqing Medical University.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Zhong, X., Zhao, L. et al. JAK2/STAT3/BMP-2 axis and NF-κB pathway are involved in erythropoietin-induced calcification in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Clin Exp Nephrol 23, 501–512 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-018-1666-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-018-1666-z