Abstract
Background
Pozzi et al. reported the effectiveness of steroid pulse therapy (Pozzi’s regimen) in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). The present study was performed to clarify the predictive factors for IgAN patients treated with Pozzi’s regimen.
Methods
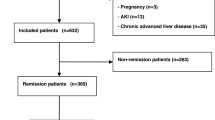
One hundred nine IgAN patients treated by Pozzi’s regimen were observed for up to 112.6 (median 39.7) months, and remission of proteinuria (PR) and disappearance of urinary abnormalities [complete remission (CR)] after Pozzi’s regimen were analyzed. Predictive factors for the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) slopes for up to 5 years were analyzed among 81 patients who were observed for at least 2 years. The outcome of a 50 % increase in sCr was compared between the CR and non-CR groups within 2 years.
Results
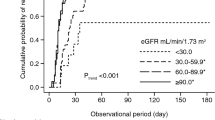
Cumulative PR and CR rates increased rapidly until 2 years (54.5 and 46.8 % at 2 years), and then slowly but steadily up to 6 years (72.8 and 66.4 % at 6 years). Baseline characteristics of the CR and non-CR groups within 2 years were similar except for proteinuria. GFR slope was steeper in the non-CR group than in the CR group (−2.44 ± 5.12 vs. −0.32 ± 3.34 ml/min/1.73 m2/year). On multivariate analysis, sex and CR within 2 years were associated with GFR slope. Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated a better survival rate in CR group patients without a 50 % increase in sCr (p = 0.024).
Conclusions
Among IgAN patients treated with Pozzi’s regimen, CR within 2 years predicts a good prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger J, Hinglais N. Les depots intercapillaires d’IgA-IgG. J Urol Nephrol (Paris). 1968;74:694–5.
D’Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987;245:709–27.
Donadio James V, Grande Joseph P. IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:738–48.
Hiki Y, Odani H, Takahashi M, Yasuda Y, Nishimoto A, Iwase H, et al. Mass spectrometry proves under-O-glycosylation of glomerular IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2001;59:1077–85.
Yasuda Y, Horie A, Odani H, Iwase H, Hiki Y. Application of mass spectrometry to IgA nephropathy: structural and biological analyses of underglycosylated IgA1 molecules. Contrib Nephrol. 2004;141:170–88.
Koyama A, Igarashi M, Kobayashi M, Coworkers of the Research Group on Progressive Renal Diseases. Natural history and risk factors for immunoglobulin A nephropathy in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;29:526–32.
D’Amico G. Natural history of idiopathic IgA nephropathy and factors predictive of disease outcome. Semin Nephrol. 2004;24:179–96.
Wakai K, Kawamura T, Endoh M, Kojima M, Tomino Y, Tamakoshi A, et al. A scoring system to predict renal outcome in IgA nephropathy: from a nationwide prospective study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:2800–8.
Wakai K, Kawamura T, Matsuo S, Hotta N, Ohno Y. Risk factors for IgA nephropathy: a case-control study in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;33:738–45.
Radford MG Jr, Donadio JV Jr, Bergstralh EJ, Grande JP. Predicting renal outcome in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:199–207.
Kobayashi Y, Hiki Y, Kokubo T, Horii A, Tateno S. Steroid therapy during the early stage of progressive IgA nephropathy. A 10-year follow-up study. Nephron. 1996;72:237–42.
Pozzi C, Bolasco PG, Fogazzi GB, Andrulli S, Altieri P, Ponticelli C, et al. Corticosteroids in IgA nephropathy: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 1999;353:883–7.
Pozzi C, Andrulli S, Del Vecchio L, Melis P, Fogazzi GB, Altieri P, et al. Corticosteroid effectiveness in IgA nephropathy: long-term results of a randomized, controlled trial. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:157–63.
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16:31–41.
Locatelli F, Pozzi C, Del Vecchio L, Andrulli S, Bolasco P, Fogazzi G, et al. New therapeutic approaches in primary IgA nephropathy. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1999;29:73–91.
Pozzi C, Andrulli S, Pani A, Scaini P, Del Vecchio L, Fogazzi G, et al. Addition of azathioprine to corticosteroids does not benefit patients with IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:1783–90.
Reich HN, Troyanov S, Scholey JW, Cattran DC. Toronto glomerulonephritis registry: remission of proteinuria improves prognosis in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:3177–83.
Vivante A, Afek A, Frenkel-Nir Y, Tzur D, Farfel A, Golan E, et al. Persistent asymptomatic isolated microscopic hematuria in Israeli adolescents and young adults and risk for end-stage renal disease. JAMA. 2011;17(306):729–36.
Szeto CC, Lai FM, To KF, Wong TY, Chow KM, Choi PC, et al. The natural history of immunoglobulin a nephropathy among patients with hematuria and minimal proteinuria. Am J Med. 2001;110:434–7.
Kim BS, Kim YK, Shin YS, Kim YO, Song HC, Kim YS, et al. Natural history and renal pathology in patients with isolated microscopic hematuria. Korean J Intern Med. 2009;24:356–61.
Hotta O, Miyazaki M, Furuta T, Tomioka S, Chiba S, Horigome I, et al. Tonsillectomy and steroid pulse therapy significantly impact on clinical remission in patients with IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38:736–43.
Komatsu H, Fujimoto S, Hara S, Sato Y, Yamada K, Kitamura K. Effect of tonsillectomy plus steroid pulse therapy on clinical remission of IgA nephropathy: a controlled study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:1301–7.
Tomino Y, Sakai H. Special Study Group (IgA Nephropathy) on Progressive glomerular disease. Clinical guidelines for immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy in Japan, second version. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2003;7:93–7.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:982–92.
Fujimi-Hayashida A, Ueda S, Yamagishi S, Kaida Y, Ando R, Nakayama Y, et al. Association of asymmetric dimethylarginine with severity of kidney injury and decline in kidney function in IgA nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. 2011;33:1–6.
Ballardie FW, Roberts IS. Controlled prospective trial of prednisolone and cytotoxics in progressive IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:142–8.
Ando M, Minami H, Ando Y, Saka H, Sakai S, Yamamoto M, et al. Multi-institutional validation study of carboplatin dosing formula using adjusted serum creatinine level. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:4733–8.
Imai E, Horio M, Yamagata K, Iseki K, Hara S, Ura N, et al. Slower decline of glomerular filtration rate in the Japanese general population: a longitudinal 10-year follow-up study. Hypertens Res. 2008;31:433–41.
Goto M, Wakai K, Kawamura T, Masahiko A, Masayuki E, Yasuhiko T. A scoring system to predict renal outcome in IgA nephropathy: a nationwide 10-year prospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:3068–74.
Bjørneklett R, Vikse BE, Bostad L, Iversen BM. Long-term risk of ESRD in IgAN; validation of Japanese prognostic model in a Norwegian cohort. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27:1485–91
Lv J, Zhang H, Chen Y, Li G, Jiang L, Singh AK, et al. Combination therapy of prednisone and ACE inhibitor versus ACE-inhibitor therapy alone in patients with IgA nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:26–32.
Manno C, Torres DD, Rossini M, Pesce F, Schena FP. Randomized controlled clinical trial of corticosteroids plus ACE-inhibitors with long-term follow-up in proteinuric IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:3694–701.
Xie Y, Nishi S, Ueno M, Imai N, Sakatsume M, Narita I, et al. The efficacy of tonsillectomy on longterm renal survival in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2003;63:1861–7.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Study Group on IgA Nephropathy and by a Grant-in-Aid for Progressive Renal Diseases Research, Research on Intractable Disease, from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tatematsu, M., Yasuda, Y., Morita, Y. et al. Complete remission within 2 years predicts a good prognosis after methylprednisolone pulse therapy in patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol 16, 883–891 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0644-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0644-0