Abstract
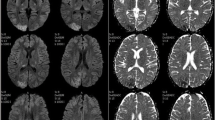
A 42-year-old female end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patient with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) post-transfusion during initiation of hemodialysis is reported. Eleven days after the onset of illness, we diagnosed encephalopathy as a grand mal seizure resulting from diffuse cerebral edema. One reason for the delayed diagnosis was that her symptom, a throbbing headache that occurred during her first dialysis, indicated dialysis disequilibrium syndrome. We must bear in mind that a small amount of transfusion could cause RPLS even during the first dialysis. To our knowledge, this is the first case report on RPLS after blood transfusion in an ESRD patient.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krishnan AV, Kiernan MC, Medscape. Neurological complications of chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2009;5(10):542–51.
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:494–500.
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23:1038–48.
Huang Y-C, Tsai P-L, Yeh J-H, Chen W-H. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome caused by blood transfusion: a case report. Acta Neurologica Taiwan. 2008;17:258–62.
Heo K, Park SA, Lee JY, Lee BI, Lee SK. Post-transfusion posterior leukoencephalopathy with cytotoxic and vasogenic edema precipitated by vasospasm. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003;15:230–3.
Boughammoura A, Touze E, Oppenheim C, Trystram D, Mas JL. Reversible angiopathy and encephalopathy after blood transfusion. J Neurol. 2003;250:116–8.
Ito Y, Niwa H, Iida T, Nagamatsu M, Yasuda T, Yanagi T, Sobue G. Post-transfusion reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome with cerebral vasoconstriction. Neurology. 1997;49:1174–5.
Lee VH, Eelco FM, Manno EM, Rabinstein AA. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2008;65(2):205–10.
Brown AL, Tucker B, Baker LRI, Raine AEG. Seizure related to blood transfusion and erythropoietin treatment in patients undergoing dialysis. BMJ. 1989;299:1258–9.
Delanty N, Vaughan C, Frucht S, Stubgen P. Erythropoietin-associated hypertensive posterior leukoencephalopathy. Neurology. 1997;49:686–9.
Hare GM, Mazer CD, Mak W, Gorczynski RM, Hum KM, Kim SY, et al. Hemodilutional anemia is associated with increased cerebral neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene expression. J Appl Physiol. 2003;94:2058–67.
LaManna JC, Chavez JC, Pichiule P. Structural and functional adaptation to hypoxia in the rat brain. J Exp Biol. 2004;207:3163–9.
LaManna JC, McCracken KA, Strohl KP. Changes in regional cerebral blood flow and sucrose space after 3–4 weeks of hypobaric hypoxia (0.5 ATM). Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;248:471–7.
Serrano J, Encinas JM, Salas E, Fernandez AP, Castro-Blanco S, Fernandez-Vizarra P, et al. Hypobaric hypoxia modifies constitutive nitric oxide synthase activity and protein nitration in the rat cerebellum. Brain Res. 2003;976:109–19.
Serrano J, Encinas JM, Fernandez AP, Rodrigo J, Martinez A. Effects of acute hypobaric hypoxia on the nitric oxide system of the rat cerebral cortex: protective role of nitric oxide inhibitors. Neuroscience. 2006;142:799–808.
Marzo F, Lavorgna A, Coluzzi G, Santucci E, Tarantino F, Rio TC, et al. Erythropoietin in heart and vessels: focus on transcription and signaling pathways. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2008;26:183–7.
Sheth KN, Wu GF, Messé SR, Wolf RL, Kasner SE. Dialysis disequilibrium: another reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome? Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2003;105(4):249–52.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, Y., Hirose, M., Inoue, Y. et al. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome after blood transfusion in a patient with end-stage renal disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 15, 942–947 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0515-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0515-0