Abstract
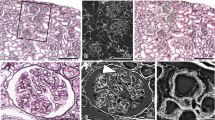
Background. It is known that abnormal lipid depositions are shown in some renal glomerular diseases. Electron microscopic findings have shown materials with varying degrees of intracytoplasmic electron density, but it has been difficult to prove that they are truly lipids.
Methods. Routinely processed Epon-embedded specimens from seven patients with known renal diseases were utilized in this study. Ultrathin sections were cut, and examined by electron microscopy. Then serial 1-μm-thick sections were made stained with Sudan IV.
Results. Several patterns of lipid deposition with varying electron densities within the glomeruli were observed by electron microscopy. These lipid depositions were positive for Sudan IV, but showed different colors according to their electron density.
Conclusions. The procedure used in the study enables us to recognize light- and electron-microscopic findings of abnormal lipid depositions in serial sections, and may be useful in helping us to simultaneously evaluate the site and nature of these histopathological phenomena.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: February 5, 2001 / Accepted: June 14, 2001
About this article
Cite this article
Mochizuki, S., Moriya, T., Naganuma, H. et al. Significance of fat stains in serial sections from Epon-embedded tissue samples for electron microscopy in renal diseases. Clin Exp Nephrol 5, 240–245 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-001-8020-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-001-8020-5