Abstract
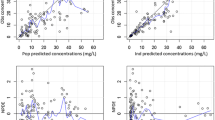
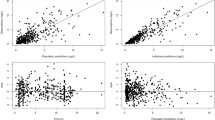
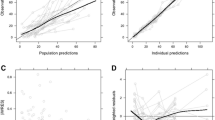
The aims of this study were to develop a population pharmacokinetic model for meropenem in Japanese pediatric patients, and to use this model to assess the pharmacodynamics of meropenem regimens against common bacterial populations. Pharmacokinetic data were pooled from nine separate studies (229 plasma samples and 61 urine samples from 40 infected children), modeled using the NONMEM program, and used for a pharmacodynamic simulation to estimate the probabilities of attaining the bactericidal target (40% of the time above the MIC for the bacterium). In the final population pharmacokinetic model, body weight (BW, kg) was the most significant covariate: Clr (l/h) = 0.254 × BW, Clnr (l/h) = 3.45, V c (l) = 0.272 × BW, Q (l/h) = 1.65, and V p (l) = 0.228 × BW, where Clr and Clnr are the renal and non-renal clearances, V p and V c are the volumes of distribution of the central and peripheral compartments, and Q is the intercompartmental (central–peripheral) clearance. In most typical patients (BW = 10, 20, and 30 kg), the approved regimens of 10–40 mg/kg, three times a day (0.5-h infusions), achieved a target attainment probability of >80% against Escherichia coli, Streptococcus pneumoniae, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. The results of this study provide a better understanding of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of meropenem in Japanese pediatric patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perez-Ruixo JJ, Zannikos P, Hirankarn S, Stuyckens K, Ludwig EA, Soto-Matos A, et al. Population pharmacokinetic meta-analysis of trabectedin (ET-743, Yondelis) in cancer patients. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46:867–84.
Chan PL, Weatherley B, McFadyen L. A population pharmacokinetic meta-analysis of maraviroc in healthy volunteers and asymptomatic HIV-infected subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;65(Suppl 1):76–85.
Nicolau DP. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of meropenem. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(Suppl 1):S32–40.
Fujita K, Murono K, Saijyo M, Yoshioka H, Maruyama S, Sakata H, et al. Clinical and pharmacokinetic evaluation of meropenem and its effect on fecal flora in children. Jpn J Antibiot. 1992;45:718–26.
Tsutsumi H, Chiba S. Clinical pharmacology and efficacy of meropenem. Jpn J Antibiot. 1992;45:727–33.
Tajima T, Negishi S, Kondo Y, Nishimura S, Higa A, Hagiwara N, et al. Pharmacokinetic, bacteriological and clinical studies on meropenem in children. Jpn J Antibiot. 1992;45:826–32.
Niinou K, Sato H, Nakazawa S. Studies of meropenem in pediatric infections. Jpn J Antibiot. 1992;45:833–44.
Toyonaga Y, Yamori K, Hatakeyama K, Ishihara T, Kawamura K, Seo K, et al. Pharmacokinetic and clinical studies on meropenem. Jpn J Antibiot. 1992;45:850–65.
Meguro H, Mori A, Fujii R, Terashima I, Kurosaki T, Toba T, et al. Clinical evaluation of a new carbapenem, meropenem, in infants and children. Jpn J Antibiot. 1992;45:866–79.
Kuno K, Ogawa A, Hayakawa F, Takeuchi H, Ito K, Takimoto Y, et al. Laboratory and clinical studies on meropenem in pediatrics. Jpn J Antibiot. 1992;45:880–8.
Haruta T, Kuroki S, Okura K, Nikami H, Nishio T, Kobayashi Y. Studies on meropenem in the field of pediatrics. Jpn J Antibiot. 1992;45:897–904.
Ikeda K, Ikawa K, Morikawa N, Miki M, Nishimura S, Kobayashi M. High-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection for real-time therapeutic drug monitoring of meropenem in plasma. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007;856:371–5.
Ikawa K, Morikawa N, Uehara S, Monden K, Yamada Y, Honda N, et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic target attainment analysis of doripenem in infected patients. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;33:276–9.
Iba K, Yoshitake A. Pharmacokinetics of [14C]meropenem in dogs and monkeys. Jpn J Chemother. 1992;40(Suppl 1):145–53.
Kanazawa K, Ueda Y. In vitro antimicrobial activity of meropenem against clinical isolates of various bacterial species from pediatric patients in Japan. Jpn J Chemother. 2004;52:1–16.
Parker EM, Hutchison M, Blumer JL. The pharmacokinetics of meropenem in infants and children: a population analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995;36(Suppl A):63–71.
Du X, Li C, Kuti JL, Nightingale CH, Nicolau DP. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of meropenem in pediatric patients. J Clin Pharmacol. 2006;46:69–75.
Ikawa K, Morikawa N, Ikeda K, Ohge H, Sueda T. Development of breakpoints of carbapenems for intraabdominal infections based on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in peritoneal fluid. J Infect Chemother. 2008;14:330–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ikawa, K., Morikawa, N., Ikeda, K. et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of meropenem in Japanese pediatric patients. J Infect Chemother 16, 139–143 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-009-0025-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-009-0025-0