Abstract
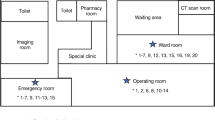
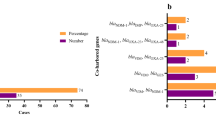
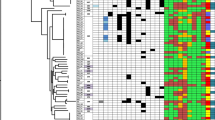
We witnessed outbreaks of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa at a hospital in Tokyo, Japan, during the period September 2004 through May 2005. The first outbreak occurred in September and October 2004. Three isolates of MDR P. aeruginosa were identified from urine samples obtained from three nonambulatory immunodeficient patients in one ward. After 3 weeks, another outbreak of P. aeruginosa occurred in the hematology ward on the same floor of the hospital. During the outbreaks, environmental surveys were conducted twice in each of the two wards, at 2-week intervals, to identify the sources of the pathogens. A total of 23 P. aeruginosa isolates, including 11 from environmental sources, were analyzed for chromosomal DNA typing by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, for O-antigen serotyping, and for other typing. Results revealed two causative clones, as well as environmental contamination by P. aeruginosa clones on the surfaces of urine volume-measuring devices in rooms where urine is handled, which may have been sources of the pathogens during the outbreaks. To prevent further outbreaks, we performed the following: (a) environmental surface monitoring for drug-resistant P. aeruginosa, (b) active surveillance of specimens, (c) strict isolation of infected patients or carriers of MDR P. aeruginosa, (d) rigorous contact precautions, and (e) disinfection with 70% alcohol on the surfaces of apparatuses contaminated by MDR or drug-resistant P. aeruginosa and in the rooms where urine is handled. As a result, the outbreaks were contained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T Kirikae O Tokunaga Y Inoue T Fujino K Saruta H Yoshikura et al. (2004) ArticleTitleMolecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens in a long-term care facility for patients with severe motor and intellectual disabilities Jpn J Infect Dis 57 226–8 Occurrence Handle15507784 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXitFOhtg%3D%3D
ME Falagas PK Koletsi IA Bliziotis (2006) ArticleTitleThe diversity of definitions of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and pandrug-resistant (PDR) Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa J Med Microbiol 55 1619–29 Occurrence Handle17108263 Occurrence Handle10.1099/jmm.0.46747-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXislGmtA%3D%3D
J Sekiguchi T Asagi T Miyoshi-Akiyama A Kasai Y Mizuguchi M Araake et al. (2007) ArticleTitleOutbreaks of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in community hospitals in Japan J Clin Microbiol 45 979–89 Occurrence Handle17122009 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JCM.01772-06 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXktFOgtL0%3D
InstitutionalAuthorNameClinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2006) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically EditionNumber6th ed Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Wayne, PA
J Sekiguchi T Asagi T Miyoshi-Akiyama T Fujino I Kobayashi K Morita et al. (2005) ArticleTitleMultidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain that caused an outbreak in a neurosurgery ward and its aac(6′)-Iae gene cassette encoding a novel aminoglycoside acetyltransferase Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49 3734–42 Occurrence Handle16127047 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AAC.49.9.3734-3742.2005 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXpvFKltb0%3D
E Osano Y Arakawa R Wacharotayankun M Ohta T Horii H Ito et al. (1994) ArticleTitleMolecular characterization of an enterobacterial metallo beta-lactamase found in a clinical isolate of Serratia marcescens that shows imipenem resistance Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38 71–8 Occurrence Handle8141584 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXitFWgu7c%3D
FH Camaron DJ Groot Obbink VP Ackerman RM Hall (1986) ArticleTitleNucleotide sequence of the AAD(2″) aminoglycoside adenylyltransferase determinant aadB. Evolutionary relationship of this region with those surrounding aadA in R538-1 and dhfrII in R388 Nucleic Acids Res 14 8625–35 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/14.21.8625
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sekiguchi, Ji., Teruya, K., Horii, K. et al. Molecular epidemiology of outbreaks and containment of drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Tokyo hospital. J Infect Chemother 13, 418–422 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-007-0560-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-007-0560-5