Abstract
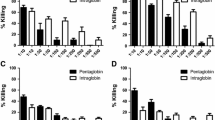
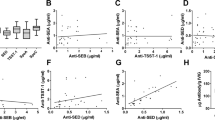
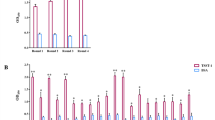
Human-origin intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) collected from healthy individuals was tested for its neutralizing activity against the hemolysin, toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1), and enterotoxins, produced by laboratory strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The hemolytic activity of the culture supernatant against sheep red blood cells was reduced from 100% to 5.5% relative hemolysis in the presence of 0.156 mg protein/ml of IVIG. The maximum dilution endpoint of the culture supernatant for TSST-1-mediated latex aggregation was 32-fold. This level of TSST-1 activity was reduced to eightfold dilution by 0.78 mg protein/ml of IVIG, and the latex aggregation activity of undiluted TSST-1 in the culture supernatant was inhibited by 1.56 mg protein/ml of IVIG. Similarly, the enterotoxin A-mediated latex aggregation titer appeared to be a 320-fold dilution. This toxin activity was reduced to an 80-fold dilution and below a tenfold dilution by 0.049 through 0.78 and 1.56 mg protein/ml, respectively, of IVIG. These results show that IVIG has powerful neutralizing activity against hemolysin, TSST-1, and enterotoxin A. Therefore, IVIG may be useful for passive immunization therapy in patients suffering from diseases caused by MRSA exotoxins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HJ Knopf (1997) ArticleTitleNosocomial infections caused by multiresistant pathogens. Clinical management exemplified by multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus Urologe A 36 248–54 Occurrence Handle9265346 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s001200050099 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2szksVensw%3D%3D
HF Chambers (2001) ArticleTitleThe changing epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Emerg Infect Dis 7 178–82 Occurrence Handle11294701 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzpsFShtQ%3D%3D
A Marchese GC Schito EA Debbia (2000) ArticleTitleEmergence of drug-resistant gram-positive pathogenic bacteria (in Italian) J Chemother 12 12–4 Occurrence Handle11428095
MM Dinges PM Orwin PM Schlievert (2000) ArticleTitleExotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus Clin Microbiol Rev 13 16–34 Occurrence Handle10627489 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXntFagtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1128/CMR.13.1.16-34.2000
T Katayama T Mino C Inaoka F Fujiwara T Miyamichi M Nakayama (2005) ArticleTitleCoagulase typing, production of toxin, drug sensibility, Staphylococcus aureus (in Japanese) J Osaka Med-Center & Res Inst Mater-Child-Health 21 24–7
FJ Schmitz CR MacKenzie R Geisel S Wagner H Idel J Verhoef et al. (1997) ArticleTitleEnterotoxin and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 production of methicillin resistant and methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus strains Eur J Epidemiol 13 699–708 Occurrence Handle9324218 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1007357206672 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmvFentb0%3D
GM Wiseman (1975) ArticleTitleThe hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteriol Rev 39 317–44 Occurrence Handle1108866 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28XhtVShtL4%3D
C Piao T Karasawa K Totsuka T Uchiyama K Kikuchi (2005) ArticleTitleProspective surveillance of community-onset and healthcare-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from a university-affiliated hospital in Japan Microbiol Immunol 49 959–70 Occurrence Handle16301806 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtlektbjK
A Bernel T Proft JD Fraser DN Posnett (1999) ArticleTitleSuperantigens in human disease J Clin Immunol 19 149–57 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020547509410
NJ Labrecque J Thibodeau RP Sékaly (1993) ArticleTitleInteractions between staphylococcal superantigens and MHC class II molecules Semin Immunol 5 23–32 Occurrence Handle8467091 Occurrence Handle10.1006/smim.1993.1004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXmt1emsLg%3D
T Uchiyama XJ Yan K Imanishi J Yagi (1994) ArticleTitleBacterial superantigens–mechanism of T cell activation by the superantigens and their role in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases Microbiol Immunol 38 245–56 Occurrence Handle7935042 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXkvVSnsr8%3D
JM Hurley R Shimonkevitz A Hanagan K Enney E Boen S Malmstrom et al. (1995) ArticleTitleIdentification of class II major histocompatibility complex and T cell receptor binding sites in the superantigen toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 J Exp Med 181 2229–35 Occurrence Handle7760008 Occurrence Handle10.1084/jem.181.6.2229 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXlvFSjur4%3D
T Nakae F Hirayama M Hashimoto (2002) ArticleTitleNeutralizing activity of human immunoglobulin preparation against toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (in Japanese) Kansenshogaku Zasshi 76 195–202 Occurrence Handle11974889
F Aarestrup H Larsen N Eriksen C Elsberg N Jensen (1999) ArticleTitleFrequency of α- and β-hemolysin in Staphylococcus aureus of bovine and human origin APMIS 107 425–30 Occurrence Handle10230698 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXivFeku7w%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1699-0463.1999.tb01576.x
M Mehrotra G Wang WM Johnson (2000) ArticleTitleMultiplex PCR for detection of genes for Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin 1, and methicillin resistance J Clin Microbiol 38 1032–5 Occurrence Handle10698991 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXitVemu74%3D
K Kitamura Y Mikami (2002) ArticleTitleAnalysis of the physicochemical and biochemical property of various intravenous immunoglobulin preparations Biotherapy 16 467–76 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XotlajsL8%3D
C Rayner WJ Munckhof (2005) ArticleTitleAntibiotics currently used in the treatment of infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus Intern Med J 35 3–16 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1444-0903.2005.00976.x
PM Schlievert (1993) ArticleTitleRole of superantigens in human disease J Infect Dis 167 997–1002 Occurrence Handle8486972 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXks12rtLg%3D
AL Panlilio DH Culver RP Gaynes S Banerjee TS Henderson JS Tolson et al. (1992) ArticleTitleMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in U.S. hospitals, 1975–1991 Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 13 582–6 Occurrence Handle1469266 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s7gslKgtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1086/646432
JK Todd (2005) ArticleTitleStaphylococcal infections Pediatr Rev 26 444–50 Occurrence Handle16327025
UB Schaad (1985) ArticleTitleSyndromes caused by staphylococcal toxins (in German) Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax 22 IssueID74 1175–9
T Syuji KA Yogesh MW Sharyn (1993) ArticleTitleIntravenous immunoglobulin contains specific antibodies inhibitory to activation of T cells by staphylococcal toxin superantigens J Clin Invest 91 602–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yanagisawa, C., Hanaki, H., Natae, T. et al. Neutralization of staphylococcal exotoxins in vitro by human-origin intravenous immunoglobulin. J Infect Chemother 13, 368–372 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-007-0551-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-007-0551-6