Abstract
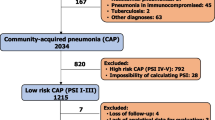
Community-acquired pneumonia remains one of the most important diseases associated with mortality. The aim of this study was to identify the risk factors for mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia in Japan. This prospective study was carried out at the Social Insurance Tagawa Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan. All patients were managed according to the 1993 American Thoracic Society guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia, after an evaluation of the risk class by the pneumonia Patient Outcome Research Team (PORT) study. A comparison of several factors, including demographic findings, clinical signs, underlying diseases, results of medical examinations, severity of diseases, and causative pathogens in both survival and fatal groups, was carried out from 227 episodes of community-acquired pneumonia in 208 hospitalized patients (128 men, mean age 67.7 years). The presence of a risk of aspiration, low systolic blood pressure, low PaO2/FIO2 ratio, a high pneumonia score, and the presence of severe congestive heart failure were found to be independent risk factors for mortality from community-acquired pneumonia. The mortality in risk classes IV and V was 17.5% and 54.2%, respectively, and there was a significant correlation between risk classes. The risk factors we identify here are generally similar to those given in previous reports in Western countries. According to the prediction rule of the pneumonia PORT study, the risk classes were strongly associated with the mortality, and would be suitable and helpful for the management of patients with community-acquired pneumonia in Japan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Organization of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Abridged life tables for Japan. Reported in 2003. http://www.mhlw.go.jp/English/database/db-hw/lifetb03/index.html
RA Garibaldi (1985) ArticleTitleEpidemiology of community-acquired respiratory tract infections in adults: incidence, etiology, and impact Am J Med 78 32–7 Occurrence Handle4014285 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0002-9343(85)90361-4 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2M3kvVGltg%3D%3D
MS Niederman SP Peters (1998) ArticleTitleUpdate in pulmonary medicine Ann Intern Med 128 208–15 Occurrence Handle9454529 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7gvVCgtA%3D%3D
MS Niederman JB Bass SuffixJr GD Campbell AM Fein RF Grossman LA Mandell et al. (1993) ArticleTitleGuidelines for the initial management of adults with community-acquired pneumonia: diagnosis, assessment of severity, and initial antimicrobial therapy Am Rev Respir Dis 148 1418–26 Occurrence Handle8239186 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2c%2FlslOhtw%3D%3D
JG Bartlett RF Breiman LA Mandell TM File SuffixJr (1998) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired pneumonia in adults: guidelines for management Clin Infect Dis 26 811–38 Occurrence Handle9564457 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3isFKntg%3D%3D
G Huchon (1998) ArticleTitleWoodhead M, and the European Study on Community-Acquired Pneumonia Committee. Management of adult community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections Eur Respir Rev 8 391–426
Matsushima T and the Japanese Respiratory Society Community-Acquired Pneumonia Treatment Guideline Creation Committee. Diagnostic and treatment guideline formulation committee for community-acquired pneumonia of the Japanese Respiratory Society (in Japanese). Tokyo: Japanese Respiratory Society; 2000
MS Niederman LA Mandell A Anzueto JB Bass WA Broughton GD Campbell et al. (2001) ArticleTitleGuidelines for the management of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. Diagnosis, assessment of severity, antimicrobial therapy, and prevention Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163 1730–54 Occurrence Handle11401897 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mzjtl2qsA%3D%3D
MJ Fine TE Auble DM Yealy BH Hanusa LA Weissfeld DE Singer et al. (1997) ArticleTitleA prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia N Engl J Med 336 243–50 Occurrence Handle8995086 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199701233360402 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s7js1Gguw%3D%3D
PB Hasley MN Albaum YH Li CR Fuhrman CA Britton TJ Marrie et al. (1996) ArticleTitleDo pulmonary radiographic findings at presentation predict mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia? Arch Intern Med 156 2206–12 Occurrence Handle8885819 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archinte.156.19.2206 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s%2FktVGjtA%3D%3D
MS Houston MD Silverstein VJ Suman (1997) ArticleTitleRisk factors for 30-day mortality in elderly patients with lower respiratory tract infection: community-based study Arch Intern Med 157 2190–5 Occurrence Handle9342995 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archinte.157.19.2190 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2Fgt1Gisw%3D%3D
RR Muder (1998) ArticleTitlePneumonia in residents of long-term care facilities: epidemiology, etiology, management, and prevention Am J Med 105 319–30 Occurrence Handle9809694 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9343(98)00262-9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FisFGltA%3D%3D
LI Iezzoni MA Moskowitz (1998) ArticleTitleA clinical assessment of MedisGroups JAMA 260 3159–63 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.260.21.3159
A Saito F Miki K Oizumi N Rikitomi A Watanabe H Koga et al. (1999) ArticleTitleClinical evaluation methods for new antimicrobial agents to treat respiratory infections. Report of the Committee for the Respiratory System, Japan Society of Chemotherapy J Infect Chemother 5 110–23 Occurrence Handle11810502 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s101560050020
DF Boerner P Zwadyk (1982) ArticleTitleThe value of the sputum Gram's stain in community-acquired pneumonia JAMA 247 642–5 Occurrence Handle6172607 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.247.5.642 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL387gtFamsw%3D%3D
T Ishida T Hashimoto M Arita I Ito M Osawa (1998) ArticleTitleEtiology of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients: a 3-year prospective study in Japan Chest 114 1588–93 Occurrence Handle9872193 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FoslWqug%3D%3D
PH Edelstein RD Meyer SM Finegold (1980) ArticleTitleLaboratory diagnosis of Legionnaires' diseases Am Rev Respir Dis 121 317–27 Occurrence Handle6987923 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL3c7ltFOhsg%3D%3D
L Brade H Brunnemann M Ernst (1994) ArticleTitleOccurrence of antibodies against chlamydial lipopolysaccharide in human sera as measured by ELISA using an artificial glycoconjugate antigen FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 8 27–41 Occurrence Handle7512399 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1574-695X.1994.tb00422.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXjt1Srtrc%3D
T Kishimoto Y Kubota T Matsushima H Izutsu A Matsumoto R Soejima et al. (1996) ArticleTitleAssay of specific anti-Chlamydia pneumoniae antibodies by the ELISA method: evaluation of ELISA kit using outer membrane complex (in Japanese) Kansenshogaku Zasshi 70 821–9 Occurrence Handle8890550 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s%2FksFGjtA%3D%3D
J Horner EW Massey SR Brazer (1990) ArticleTitleAspiration in bilateral stroke patients Neurology 40 1686–8 Occurrence Handle2234422 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M%2FktlGguw%3D%3D
C Gonzalez M Rubio J Romero-Vivas M Gonzalez JJ Picazo (1999) ArticleTitleBacteremic pneumonia due to Staphylococcus aureus: a comparison of disease caused by methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible organisms Clin Infect Dis 29 1171–7 Occurrence Handle10524959 Occurrence Handle10.1086/313440 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MvlsVKmsQ%3D%3D
K Hasegawa (1990) ArticleTitleThe clinical issues of age-related dementia Tohoku J Exp Med 161 S28–38
PA Poole-Wilson (1989) Chronic heart failure: causes, pathophysiology, prognosis, clinical manifestations, investigations. Diseases of the heart Baillière Tindall London 48–57
InstitutionalAuthorNameResearch Committee of the British Thoracic Society and Public Health Service (1987) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired pneumonia in adults in British hospitals in 1982–1983: a survey of aetiology, mortality, prognostic factors and outcome Q J Med 62 195–219
MJ Fine BH Hanusa JR Lave DE Singer RA Stone LA Weissfeld et al. (1995) ArticleTitleComparison of a disease-specific and generic severity of illness measure for patients with community-acquired pneumonia J Gen Intern Med 10 359–68 Occurrence Handle7472683 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02599830 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28%2Fms1SlsA%3D%3D
A Ortqvist G Sterner J Axel Nilsoson (1985) ArticleTitleSevere community-acquired pneumonia: factors influencing need of intensive care treatment and prognosis Scand J Infect Dis 17 377–86 Occurrence Handle4089544 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL287it1KrsA%3D%3D
M Levy F Dromer N Brion F Letuedu C Carbon (1988) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired pneumonia: importance of initial noninvasive bacteriologic and radiographic investigations Chest 92 43–8
L Daley C Jenchs D Draper G Lenhart N Thomas J Walker (1988) ArticleTitlePredicting hospital-associated mortality for Medicare patients: a method for patients with stroke, pneumonia, acute myocardial infarction, and congestive heart failure JAMA 260 3617–24 Occurrence Handle3057251 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.260.24.3617 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1M%2Fls1Sjsw%3D%3D
MJ Fine JJ Orloff D Arisumi GD Fang VC Arena BH Hanusa et al. (1990) ArticleTitlePrognosis of patients hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia Am J Med 88 1N–8N Occurrence Handle2195886 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3czhtlOrsA%3D%3D
EN Vergis C Brennen M Wagener RR Muder (2001) ArticleTitlePneumonia in long-term care: a prospective case-control study of risk factors and impact on survival Arch Intern Med 161 2378–81 Occurrence Handle11606155 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archinte.161.19.2378 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mnks1ygsA%3D%3D
TJ Marrie KC Carriere Y Jin DH Johnson (2003) ArticleTitleFactors associated with death among adults <55 years of age hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia Clin Infect Dis 36 413–21 Occurrence Handle12567298 Occurrence Handle10.1086/346037
O Takashi (2005) ArticleTitlePreventive strategies for aspiration pneumonia in elderly disabled persons Tohoku J Exp Med 207 3–12 Occurrence Handle10.1620/tjem.207.3
ML Jackson KM Neuzil WW Thompson DK Shay O Yu CA Hanson et al. (2004) ArticleTitleThe burden of community-acquired pneumonia in seniors: results of a population-based study Clin Infect Dis 39 1642–50 Occurrence Handle15578365 Occurrence Handle10.1086/425615
A Torres J Serra-Batlles A Ferrer P Jimenez R Celis E Cobo et al. (1999) ArticleTitleSevere community-acquired pneumonia: epidemiology and prognostic factors Am Rev Respir Dis 144 312–8
P Moine JB Vercken S Chevret C Chastang P Gajdos (1994) ArticleTitleSevere community-acquired pneumonia: etiology, epidemiology and prognostic factors Chest 105 1478–95
FL Brancati JW Chow MM Wagener SJ Vacarello VL Yu (1993) ArticleTitleIs pneumonia really the old man's friend? Two-year prognosis after community-acquired pneumonia Lancet 342 30–3 Occurrence Handle8100295 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0140-6736(93)91887-R Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3szgt1CjsQ%3D%3D
J Rello R Rodriguez P Jubert B Alvarez (1996) ArticleTitleSevere community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly: epidemiology and prognosis Clin Infect Dis 23 723–8 Occurrence Handle8909834 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s%2Fms1emsQ%3D%3D
R Riquelme A Torres M El-Ebiary JP de la Ballacasa R Estruch J Mensa et al. (1996) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired pneumonia in the elderly: a multivariate analysis of risk and prognostic factors Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154 1450–5 Occurrence Handle8912763 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s%2FmvFOrsQ%3D%3D
P Vekatesan J Gladman JT Macfarlane D Barer P Berman W Kinnear et al. (1990) ArticleTitleA hospital study of community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly Thorax 45 254–8 Occurrence Handle10.1136/thx.45.4.254
JP Jassens L Gauthey F Hermann L Tkatch JP Michel (1996) ArticleTitleCommunity-acquired pneumonia in older patients J Am Geriatric Soc 44 539–44
S Horiuchi JR Wilmoth (1998) ArticleTitleDeceleration in the age pattern of mortality at older ages Demography 35 391–412 Occurrence Handle9850465 Occurrence Handle10.2307/3004009 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FmslCmsw%3D%3D
MH Kollef A Shorr YP Tabak V Gupta LZ Liu RS Johannes (2005) ArticleTitleEpidemiology and outcomes of health-care-associated pneumonia: results from a large US database of culture-positive pneumonia Chest 128 3854–62 Occurrence Handle16354854 Occurrence Handle10.1378/chest.128.6.3854
MH Kollef ST Micek (2006) ArticleTitleMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a new community acquired pathogen? Curr Opin Infect Dis 19 161–8 Occurrence Handle16514341 Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.qco.0000216627.13445.e2
Matsushima T and the Committee for the JRS Guidelines in Management of Respiratory Infections. In: The JRS guideline for the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults (in Japanese). Tokyo: Japanese Respiratory Society; 2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiki, R., Kawayama, T., Ueyama, T. et al. The risk factors for mortality of community-acquired pneumonia in Japan. J Infect Chemother 13, 157–165 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-007-0512-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-007-0512-0