Abstract
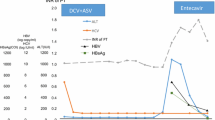
A 51-year-old man who was hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-negative and positive for anti-hepatitisB surface antigen (anti-HBs) and anti-hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc), during rituximab therapy for chronic Lymphocytic leukemia, developed reactivation of hepatitisB virus (HBV) infection with hepatitis that proceededtowards hepatic failure and death in spite of lamivudine therapy. HBsAg remained persistently negative, notwithstanding a high HBV-DNA titer. Our observation, following other cases of fatal reactivation of HBV infection in patients receiving rituximab, suggests that, in all patients with previous markers of HBV infection, lamivudine prophylaxis should be considered during rituximab therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W Yeo PK Chan S Zhong WM Ho JL Steinberg JS Tam et al. (2000) ArticleTitleFrequency of hepatitis B virus reactivation in cancer patientsundergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy: a prospective study of 626patients with identification of risk factors J Med Virol 62 299–307 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1096-9071(200011)62:3<299::AID-JMV1>3.0.CO;2-0 Occurrence Handle11055239
T Kawatani T Suou F Tajima K Ishiga H Omura A Endo et al. (2001) ArticleTitleIncidence of hepatitis virus infection and severe liver dysfunction in patients receiving chemotherapy for hematologic malignancies Eur J Haematol 67 45–50 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0609.2001.067001045.x Occurrence Handle11553266
J-A Hernandéz R Diloy D Salat N Del Rio X Martinez J-M Castelli (2003) ArticleTitleFulminant hepatitis subsequent to reactivation of precore mutant hepatitis B virus in a patient with lymphoma treated with chemotherapy and rituximab Haematologica 88 ECR22 Occurrence Handle12801855
C Skrabs C Mueller H Agis C Mannhalter U Jaeger (2002) ArticleTitleTreatment of HBV-carrying lymphoma patients with rituximab and CHOP: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge Leukemia 16 1884–6 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.leu.2402567 Occurrence Handle12200717
M Persico F De Marino G Di Giacomo Russo A Severino B Palmentieri M Picardi et al. (2002) ArticleTitleEfficacy of lamivudine to prevent hepatitis reactivation in hepatitis-B virus infected patients treated for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma Blood 99 724–5 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood.V99.2.724 Occurrence Handle11799967
O Shibolet Y Ilan S Gillis A Hubert D Shouval R Safadi (2002) ArticleTitleLamivudine therapy for prevention of immunosuppressive-induced hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatitis B surface carriers Blood 100 391–6 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood.V100.2.391 Occurrence Handle12091327
G Rossi (2003) ArticleTitleProphylaxis with lamivudine of hepatitis B virus reactivation in chronic HBsAg carriers with hemato-oncological neoplasia treated with chemotherapy Leuk Lymphoma 44 759–66 Occurrence Handle10.1080/104281903100006351 Occurrence Handle12802911
Medscape Alert Oct 9, 2004. Rituximab may be associated with HBV reactivation and fulminant hepatitis. http://www.medscape.com/infectiousdiseases. Cited Oct, 9, 2004.
I Dervite D Hober P Morel (2001) ArticleTitleAcute hepatitis B in a patient with antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen who was receiving rituximab N Engl J Med 344 68–9 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM200101043440120
TH Westhoff F Jochimsen A Schmittel M Stoffler-Meilicke JH Schafer W Zidek et al. (2003) ArticleTitleFatal hepatitis B virus reactivationby an escape mutant following rituximab therapy Blood 102 1930 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood-2003-05-1403 Occurrence Handle12930732
AL Mason L Xu L Guo M Kuhns R Perrillo (1998) ArticleTitleMolecular basis for persistent hepatitis B virus infection in the liver after clearance of serum hepatitis B surface antigen Hepatology 27 1736–42 Occurrence Handle10.1002/hep.510270638 Occurrence Handle9620351
JP Allain (2004) ArticleTitleOccult hepatitis B infection Transfus Clin Biol 11 18–25 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.tracli.2003.11.007 Occurrence Handle14980545
WF Carman J Korula L Wallace R MacPhee L Mimms R Decker (1995) ArticleTitleFulminant reactivation of hepatitis B due to envelope protein mutant that escaped detection by monoclonal HBsAg ELISA Lancet 345 1406–7 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(95)92599-6 Occurrence Handle7539089
X Yang T Xiao-Peng L Jian-Hua L Hong-YU Z Yong-Hong (2003) ArticleTitleA novel stop codon mutation in HBsAg gene identified in a hepatitis B virus strain associated with cryptogenic cirrhosis World J Gastroenterol 9 1516–20 Occurrence Handle12854154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sarrecchia, C., Cappelli, A. & Aiello, P. HBV reactivation with fatal fulminating hepatitis during rituximab treatment in a subject negative for HBsAg and positive for HBsAb and HBcAb. J Infect Chemother 11, 189–191 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-005-0385-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-005-0385-z