Abstract
Background
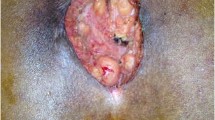
Failures of flap rotation, flap necrosis, recurrence of the disease, maceration at the incisional line and insufficient or late healing of flap corners which can be associated with ischemia appear to be the main problems associated with the closing techniques during the surgical treatment of this disease. We describe a simple, effective and incision protective repair method for excision of the pilonidal cyst.
Methods
Data from 17 (12 males and 5 females) consecutive patients who had elective surgery for chronic pilonidal sinus disease with wide excision of all the sinuses and a new flap technique closure with adipo-fascio-cutaneous flaps which was used in our series for the treatment of pilonidal sinus disease were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
Satisfactory results were achieved with this flap rotation technique in 17 patients. There were no flap rotation failures, flap necrosis, disease recurrence, incisional line maceration, or delayed wound healing.
Conclusion
As a result, presented technique provides avoidance of flap necrosis, maceration on the incision and insufficient or late healing of the flap. We describe a technique which has a minimal amount of scar across the midline natal cleft and fewer flap corners resulting in a lower chance of margin necrosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cihan A, Mentes BB, Tatlıcıoğlu E, Özmen S, Leventoğlu S, Ucan BH (2004) Modified Limberg flap reconstruction compares favourably with primary repair for pilonidal sinus surgery. ANZ J Surg 74:238–242
Kapan M, Kapan S, Pekmezci S, Durgun V (2002) Sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease with Limberg flap repair. Tech Coloproctol 6:27–32
Rao AC (2006) Cutting seton for pilonidal disease: a new approach. Tech Coloproctol 10:242–244
Muzi MG, Milito G, Nigro C, Cadeddu F, Farinon AM (2009) A modification of primary closure for the treatment of pilonidal disease in Day-Care setting. Colorectal Dis 11:84–88
Bascom J (2008) Surgical treatment of pilonidal disease. BMJ 336:842–843
Zimmerman CE (1984) Outpatient excision and primary closure of pilonidal cysts and sinuses. Long-term follow-up. Am J Surg 148:658–659
Khaira HS, Brown JH (1995) Excision and primary suture of pilonidal sinus. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 77:242–244
Topgül K, Ozdemir E, Kiliç K, Gökbayir H, Ferahköşe Z (2003) Long-term results of Limberg flap procedure for treatment of pilonidal sinus: a report of 200 cases. Dis Colon Rectum 46:1545–1548
Ersoy OF, Karaca S, Kayaoglu HA, Ozkan N, Celik A, Ozum T (2007) Comparison of different surgical options in the treatment of pilonidal disease: retrospective analysis of 175 patients. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 23:67–70
Petersen S, Aumann G, Kramer A, Doll D, Sailer M, Hellmich G (2007) Short-term results of Karydakis flap for pilonidal sinus disease. Tech Coloproctol 11:235–240
Mentes Ö, Bagci M, Bilgin T, Coskun I, Ozgul Ö, Ozdemir M (2005) Management of pilonidal sinus disease with oblique excision and primary closure: results of 493 patients. Dis Colon Rectum 49:104–108
Singh R, Pavithran NM (2005) Adipo-fascio-cutaneous flaps in the treatment of pilonidal sinus: experience with 50 cases. Asian J Surg 28:198–201
Sondenaa K, Andersen E, Nesvik I, Soreide JA (1995) Patient characteristics and symptoms in chronic pilonidal sinus disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 10:39–42
Hurst DW (1984) The evolution of management of pilonidal sinus disease. Can J Surg 27:603–605
Miocinovic M, Horzic M, Bunoza D (2001) The prevalence of anaerobic infection in pilonidal sinus of the sacrococcygeal region and its effect on the complications. Acta Med 55:87–90
McCallum IJD, King PM, Bruce J (2008) Healing by primary closure versus open healing after surgery for pilonidal sinus: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 336:868–871
Petersen S, Koch R, Stelzner S, Wendlandt T, Ludwig K (2002) Primary closure techniques in chronic pilonidal sinus: a survey of results of different surgical approaches. Dis Colon Rectum 45:1458–1467
Spivak H, Brooks V, Nussbaum M, Friedman I (1996) Treatment of chronic pilonidal disease. Dis Colon Rectum 39:1136–1139
Akıncı OF, Coskun A, Uzunkoy A (2000) Simple and effective surgical treatment of pilonidal sinus: asymmetric excision and primary closure using suction drain and subcuticular skin closure. Dis Colon Rectum 43:701–706
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ekçi, B., Gökçe, Ö. A new flap technique to treat pilonidal sinus. Tech Coloproctol 13, 205–209 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-009-0500-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-009-0500-8