Abstract
Background
There are many complex and rare mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) other than the two classical mutations of L858R and exon 19 deletional mutation. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical significance of rare and complex mutations, and the efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Methods
We analyzed 1,431 NSCLC patients who were treated with either gefitinib or erlotinib. Exons 18 to 21 of EGFR were analyzed by PCR and subjected to direct sequencing methods.
Results
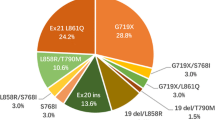
Of 306 patients who had EGFR mutation, 24 patients (7.3 %) had complex mutations. The frequency of rare mutations was 10.3 %. Four groups were categorized [group A (N = 269): classical mutation alone; group B (N = 16): complex mutation with classical mutation; group C (N = 16): rare mutation alone or complex mutation with rare mutation; group D (N = 5); classical mutation with T790M]; the response rate (RR) to TKI was significantly different between each group (RR = 74.8 % in group A vs. 68.8 % in group B vs. 25.0 % in group C vs. 80.0 % in group D, P < 0.001). Progression-free survival (PFS) was also poorer in rare mutations (median PFS: 11.9 vs. 8.1 vs. 1.4 vs. 8.0 months, respectively, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
NSCLC patients harboring rare mutations did not show consistent and favorable responses to EGFR TKI compared with those harboring classical mutations. However, complex mutations with classical mutations showed similar treatment efficacy toward EGFR TKI to that with classical mutations alone.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC et al (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R et al (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S et al (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361:947–957
Han SW, Kim TY, Hwang PG et al (2005) Predictive and prognostic impact of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin Oncol 23:2493–2501
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M et al (2004) EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13306–13311
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y et al (2010) Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 11:121–128
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K et al (2010) Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362:2380–2388
Wu JY, Yu CJ, Chang YC et al (2011) Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on “uncommon” epidermal growth factor receptor mutations of unknown clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17:3812–3821
Pallis AG, Voutsina A, Kalikaki A et al (2007) ‘Classical’ but not ‘other’ mutations of EGFR kinase domain are associated with clinical outcome in gefitinib-treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 97:1560–1566
Murray S, Dahabreh IJ, Linardou H et al (2008) Somatic mutations of the tyrosine kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor and tyrosine kinase inhibitor response to TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer: an analytical database. J Thorac Oncol 3:832–839
Gu D, Scaringe WA, Li K et al (2007) Database of somatic mutations in EGFR with analyses revealing indel hotspots but no smoking-associated signature. Hum Mutat 28:760–770
De Pas T, Toffalorio F, Manzotti M et al (2011) Activity of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring rare epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. J Thorac Oncol 6:1895–1901
Ma F, Sun T, Shi Y et al (2009) Polymorphisms of EGFR predict clinical outcome in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with Gefitinib. Lung Cancer 66:114–119
Centeno I, Blay P, Santamaria I et al (2011) Germ-line mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are rare but may contribute to oncogenesis: a novel germ-line mutation in EGFR detected in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 11:172
Yun CH, Mengwasser KE, Toms AV et al (2008) The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2070–2075
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY et al (2007) MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20932–20937
Zhang GC, Lin JY, Wang Z et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor double activating mutations involving both exons 19 and 21 exist in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 19:499–506
Huang SF, Liu HP, Li LH et al (2004) High frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations with complex patterns in non-small cell lung cancers related to gefitinib responsiveness in Taiwan. Clin Cancer Res 10:8195–8203
Hsieh MH, Fang YF, Chang WC et al (2006) Complex mutation patterns of epidermal growth factor receptor gene associated with variable responses to gefitinib treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 53:311–322
Hata A, Yoshioka H, Fujita S et al (2010) Complex mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5:1524–1528
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Kim YT, Kim TY, Lee DS et al (2008) Molecular changes of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and KRAS and their impact on the clinical outcomes in surgically resected adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 59:111–118
Wu JY, Wu SG, Yang CH et al (2008) Lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 mutations is associated with poor gefitinib treatment response. Clin Cancer Res 14:4877–4882
Yokoyama T, Kondo M, Goto Y et al (2006) EGFR point mutation in non-small cell lung cancer is occasionally accompanied by a second mutation or amplification. Cancer Sci 97:753–759
Wu SG, Chang YL, Hsu YC et al (2008) Good response to gefitinib in lung adenocarcinoma of complex epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations with the classical mutation pattern. Oncologist 13:1276–1284
Su KY, Chen HY, Li KC et al (2012) Pretreatment epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation predicts shorter EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor response duration in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 30:433–440
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korean Government (2010-0009563). We especially thank to our database manager Ju Yon Kim for her accurate data management. We also thank the members of Seoul National University Hospital Lung Study Group. This study was presented in part at the 48th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Chicago, IL, June 1–5, 2012.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Keam, B., Kim, DW., Park, J.H. et al. Rare and complex mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor, and efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 19, 594–600 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-013-0602-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-013-0602-1