Abstract
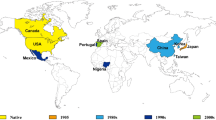
The pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, is the causative agent of pine wilt of Pinus thunbergii and P. densiflora in Japan. The nematode is vectored by cerambycid beetles of the genus Monochamus. It is inferred to have been introduced from North America early in the 1900s and then to have distributed in China, Korea, and Taiwan. Intensive and/or long-term studies of pine wilt systems have elucidated the pattern and mechanism of the nematode’s spread within a pine stand, dispersal of vector beetles, and spread pattern of pine wilt within a prefecture. The modeling of nematode spread over pine stands, which involves beetle reproduction within a pine stand, has been developing and should elucidate the factors influencing the rate at which the nematode range expands. In this review, we summarize the biologies of the nematode, beetle, and tree, and then characterize the spread of the nematode within a pine stand, locally over pine stands, and regionally over unit administrative districts. Local and regional spreading of the nematode is related primarily to long-distance dispersal by insect vectors and to the artificial transportation of pine logs infested with the nematode and its vector, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akasofu Y (1974) Infestation of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Monochamus alternatus in Toyama Prefecture (I) (in Japanese). Annu Rep Toyama Pref For Exp Stn 9:82–98
Akbulut S, Linit MJ (1999) Flight performance of Monochamus carolinensis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) with respect to nematode phoresis and beetle characteristics. Environ Entomol 28:1014–1020
Anbutsu H, Togashi K (2000) Deterred oviposition response of Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) to oviposition scars occupied by eggs. Agric For Entomol 2:217–223
Andow DA, Kareiva PM, Levin SA, Okubo A (1990) Spread of invading organisms. Landscape Ecol 4:177–188
Arakawa Y, Togashi K (2002) Newly discovered transmission pathway of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus from males of the beetle Monochamus alternatus to Pinus densiflora trees via oviposition wounds. J Nematol 34:396–404
Arakawa Y, Togashi K (2004) Presence of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, in the spermatheca of female Monochamus alternatus. Nematology 6:157–159
Beckenbach K, Smith MJ, Webster JM (1992) Taxonomic affinities and intra- and interspecific variation in Bursaphelenchus spp. as determined by polymerase chain reaction. J Nematol 24:140–147
Edwards OR, Linit MJ (1992) Transmission of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus through oviposition wounds of Monochamus carolinensis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J Nematol 24:133–139
Enda N (1977) Boarding of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus on Monochamus alternatus and its departure from vectors (in Japanese). In: Studies on the control of pine wilt disease. Secretariat of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Research Council, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Tokyo, pp 83–85
Fujioka H (1993) A report on the habitat of Monochamus alternatus Hope in Akita prefecture (in Japanese with English summary). Bull Akita For Tech Cent 2:40–56
Fujishita A (1978) Infestation of pine wilt disease in Shizuoka Prefecture (in Japanese). Trans 26th Annu Meet Chubu Bra Jpn For Soc:193–198
Fukuda K (1997) Physiological process of the symptom development and resistance mechanism in pine wilt disease. J For Res 2:171–181
Futai K (2003) Role of asymptomatic carrier trees in epidemic spread of pine wilt disease. J For Res 8:253–260
Gilbert M, Grégire J-C, Freise JF, Heitland W (2004) Long-distance dispersal and human population density allow the prediction of invasive patterns in the horse chestnut leafminer Cameraria ohridella. J Anim Ecol 73:459–468
Hagiwara Y, Ogawa S, Takeshita H (1975) Range expansion of pine wilt disease (in Japanese). Trans 28th Annu Meet Kyushu Bra Jpn For Soc:153–154
Hashimoto H, Sanui T (1974) Influence of inoculum quantity of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus on wilting disease development in Pinus thunbergii trees (in Japanese). Trans 85th Annu Meet Jpn For Soc: 251–253
Ido N, Kobayashi K (1977) Dispersal of Monochamus alternatus (in Japanese). In: Studies on the control of pine wilt disease. Secretariat of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Research Council, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Tokyo, pp 87–88
Ito K (1982) The tethered flight of the Japanese pine sawyer, Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J Jpn For Soc 64:395–397
Iwahori H, Tsuda K, Kanzaki N, Izui K, Futai K (1998) PCR-RFLP and sequencing analysis of ribosomal DNA of Bursaphelenchus nematodes related to pine wilt disease. Fundam Appl Nematol 21:655–666
Jikumaru S, Togashi K (2000) Temperature effects on the transmission of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nemata: Aphelenchoididae) by Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J Nematol 32:110–116
Kato R, Okudaira T (1977) Range expansion of the pinewood nematode in Aichi Prefecture (in Japanese). Trans 26th Annu Meet Chubu Bra Jpn For Soc:159–164
Kiritani K (1998 ) Exotic insects in Japan. Entomol Sci 1:291–298
Kishi Y (1995). The pine wood nematode and the Japanese pine sawyer. Thomas Company, Tokyo
Kiyohara T, Tokushige Y (1971) Inoculation experiments of a nematode, Bursaphelenchus sp., onto pine trees. J Jpn For Soc 53:210–218
Kondo K, Foundin A, Linit M, Smith M, Bolla R, Winter R, Dropkin V (1982) Pine wilt disese-nematological, entomological, and biochemical investigations. Univ Missouri-Columbia Agric Exp Stn SR 282:1–56
Kuniyoshi S (1974) Occurrence of the pinewood nematode in Okinawa Prefecture (in Japanese). For Pests 23:40–42
Liebhold AM, MacDonald WL, Bergdahl D, Mastro VC (1995) Invasion by exotic forest pests: a threat to forest ecosystems. For Sci Monograph 30:1–49
Linit MJ (1988) Nematode-vector relationships in the pine wilt disease system. J Nematol 20:227–235
Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol Appl 10:689–710
Maehara N Futai K (1996) Factors affecting both the numbers of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae), carried by the Japanese pine sawyer, Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), and the nematode’s life history. Appl Entomol Zool 31:443–452
Mamiya Y (1975) The life history of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus lignicolus (in Japanese with English summary). Jpn J Nematol 5:16–25
Mamiya Y (1976) Pine wilting disease caused by the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus lignicolus, in Japan. Jpn Agric Res Q 10:206–212
Mamiya Y (1983) Pathology of the pine wilt disease caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Annu Rev Phytopathol 21:201–220
Mamiya Y (1988) History of pine wilt disease in Japan. J Nematol 20:219–226
Mamiya Y, Enda N (1972) Transmission of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) by Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Nematologica 18:159–162
Mamiya Y, Kiyohara T (1972) Description of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus n. sp. (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from pine wood and histopathology of nematode-infested trees. Nematologica 18:120–124
Matsubara I (1976) Observations of the epidemic mortality of pine trees in Chiba prefecture (in Japanese). Trans 87th Annu Meet Jpn For Soc 307–308
Matsueda A (1975) Infestation of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Monochamus alternatus in Ishikawa Prefecture (in Japanese). Bull Ishikawa For Exp Stn 6:43–62
Morimoto K, Iwasaki A (1972) Role of Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) as a vector of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) (in Japanese with English summary). J Jpn For Soc 54:177–183
Morimoto K, Iwasaki A (1974a) Studies on the Japanese pine sawyer (X). Larval molting (in Japanese). Trans 85th Annu Meet Jpn For Soc: 227–228
Morimoto K, Iwasaki A (1974b) Studies on the Japanese pine sawyer (IX). Density effects on the emergence rate (in Japanese). Trans 85th Annu Meet Jpn For Soc: 299–300
Morimoto K, Iwasaki A, Taniguchi A (1972) Studies on Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) XIV–Relationship between proportion of beetles staying on a tree in a day and air temperature (in Japanese). Trans Annu Meet Kyushu Bran Jpn For Soc 28:199–200
Mota MM, Braasch H, Bravo MA, Penas AC, Burgermeister W, Metge K, Sousa E (1999) First report of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Portugal and in Europe. Nematology 1:727–734
Necibi S, Linit MJ (1998) Effect of Monochamus carolinensis on Bursaphelenchus xylophilus dispersal stage formation. J Nematol 30:246–254
Nickle WR, Golden AM, Mamiya Y, Wergin WP (1981) On the taxonomy and morphology of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer 1934) Nickle 1970. J Nematol 13:385–392
Sakai AK, Allendorf FW, Holt JS, Lodge DM, Molofsky J, With KA, Baughman S, Cabin RJ, Cohen JE, Ellstrand NC, McCauley DE, O’Neil P, Parker IM, Thompson JN, Weller SG (2001) The population biology of invasive species. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 32:305–332
Sato H, Sakuyama T, Kobayashi M (1987) Transmission of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner et Buhrer) Nickle (Nematoda, Aphelenchoididae) by Monochamus saltuarius (Gebler) (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae) (in Japanese with English summary). J Jpn For Soc 69:492–496
Shibata E (1986) Dispersal movement of the adult Japanese pine sawyer, Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in a young pine forest. Appl Entomol Zool 21:184–186
Shigesada N, Kawasaki K (1997) Biological invasions: theory and practice. Oxford Univ Press, Oxfrod
Shigesada N, Kawasaki K, Takeda Y (1995) Modeling stratified diffusion in biological invasions. Am Nat 146:229–251
Sousa E, Bravo MA, Pires J, Naves P, Penas AC, Bonifacio L, Mota MM (2001) Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda; Aphelenchoididae) associated with Monochamus galloprovincialis (Coleoptera; Cerambycidae) in Portugal. Nematology 3:89–91
Suarez AV, Holway DA, Case TJ (2001) Patterns of spread in biological invasions dominated by long-distance jump dispersal: Insight from Argentine ants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1095–1100
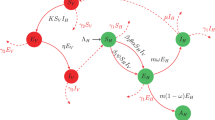
Takasu F, Yamamoto N, Kawasaki K, Togashi K, Kishi Y, Shigesada N (2000) Modeling the expansion of an introduced tree disease. Biol Invasions 2:141–150
Tamura H (1983) Infection of pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, via fused roots (in Japanese). Trans 27th Annu Meet of Jpn Soc Appl Entomol Zool:163
Tares S, Abad P, Bruguier N, de Guiran G (1992) Identification and evidence for relationships among geographical isolates of Bursaphelenchus spp. (pinewood nematode) using homologous DNA probes. Heredity 68:157–164
Togashi K (1985) Transmission curves of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from its vector, Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), to pine trees with reference to population performance. Appl Entomol Zool 20:246–251
Togashi K (1986) Effects of the initial density and natural enemies on the survival rate of the Japanese pine sawyer, Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), in pine logs. Appl Entomol Zool 21:244–251
Togashi K (1989a) Development of Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in relation to oviposition time (in Japanese with English summary). Jpn J Appl Entomol Zool 33:1–8
Togashi K (1989b) Development of Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in Pinus thunbergii trees weakened at different times (in Japanese with English summary). J Jpn For Soc 71:383–386
Togashi K (1989c) Studies on population dynamics of Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) and spread of pine wilt disease caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) (in Japanese with English summary). Bull Ishikawa For Exp Stn 20:1–142
Togashi K (1989d) Temporal pattern of the occurrence of weakened Pinus thunbergii trees and causes for mortality. J Jpn For Soc 71:323–328
Togashi K (1989e) Population density of Monochamus alternatus adults (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) and incidence of pine wilt disease caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae). Res Popul Ecol 30:177–192
Togashi K (1989f) Variation in external symptom development of pine wilt disease in field grown Pinus thunbergii. J Jpn For Soc 71:442–448
Togashi K (1990a) Life table for Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) within dead trees of Pinus thunbergii. Jpn J Entomol 58:217–230
Togashi K (1990b) Change in the activity of adult Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in relation to age. Appl Entomol Zool 25:153–159
Togashi K (1990c) A field experiment on dispersal of newly emerged adults of Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Res Popul Ecol 32:1–13
Togashi K (1991) Spatial pattern of pine wilt disease caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) within a Pinus thunbergii stand. Res Popul Ecol 33:245–256
Togashi K, Arakawa Y (2003) Horizontal transmission of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus between sexes of Monochamus alternatus. J Nematol 35:7–16
Togashi K, Magira H (1981) Age-specific survival rate and fecundity of the adult Japanese pine sawyer, Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), at different emergence times. Appl Entomol Zool 16:351–361
Togashi K, Sekizuka H (1982) Influence of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus lignicolus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae), on longevity of its vector, Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Appl Entomol Zool 17:160–165
Togashi K, Chung YJ, Shibata E (2004) Spread of an introduced tree pest organism—the pinewood nematode. In: Hong SK, Lee JA, Ihm B-S, Farina A, Son Y, Kim E-S, Choe JC (eds) Ecological issues in a changing world—status, response and strategy. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 173–188
Togashi K, Nakamura K, Takahashi F (1992) An index of susceptibility of pine stands to pine wilt disease. Appl Entomol Zool 27:341–347
Yamamoto N, Takasu F, Kawasaki K, Togashi K, Kishi Y, Shigesada N (2000) Local dynamics and global spread of pine wilt disease (in Japanese). Jpn J Ecol 50:269–276
Yoshimura A, Kawasaki K, Takasu F, Togashi K, Futai K, Shigesada N (1999) Modeling the spread of pine wilt disease caused by nematodes with pine sawyers as vector. Ecology 80:1691–1702
Veit RR, Lewis MA (1996) Dispersal, population growth, and the Allee effect: dynamics of the house finch invasion of eastern North America. Am Nat 148:255–274
Warren JE, Linit MJ (1993) Effect of Monochamus calorinensis on the life history of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J Nematol 25:703–709
Wingfield MJ, Blanchette RB (1983) The pine-wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, in Minnesota and Wisconsin: Insect associates and transmission studies. Can J For Res 13:1068–1076
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the kind permission of the American Society of Ecology and the Springer Science and Business Media for the use of the figures and table. This study was supported in part by a grand-in-aid for scientific research from JSPS (no. 18208013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Togashi, K., Shigesada, N. Spread of the pinewood nematode vectored by the Japanese pine sawyer: modeling and analytical approaches. Popul Ecol 48, 271–283 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10144-006-0011-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10144-006-0011-7