Abstract
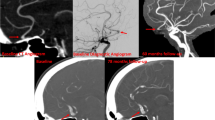
Fusiform intracranial aneurysms (FIA) are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. We carried out a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data with propensity score adjustment to compare the functional and angiographic outcomes between surgical and endovascular approaches to FIA. We conducted a systematic review for articles on the treatment of FIA with individual patient-level detailing. Data from patients treated for FIA in our institution from 2010 to 2018 were also collected. The primary studied outcome was morbidity, and secondary outcomes were angiographic results and retreatment. Propensity score–adjusted mixed-effects logistic regression models evaluated treatment options, stratified by anatomical location. Compiling original and published data, there were 312 cases, of which 79 (25.3%) had open surgery, and 233 (74.5%) were treated with endovascular procedures. There were no differences between treatment groups, for neither cavernous ICA (OR 1.04, 95% CI 0.05–23.6) nor supraclinoid aneurysms (OR 7.82, 95% CI 0.65–94.4). Both size (OR 1.11, 95% CI 1.03–1.19) and initial mRS (OR 2.0, 95% CI 1.2–3.3) were risk factors for morbidity, independent of location. Neither age nor rupture status influenced the odds of posterior morbidity. Unfavorable angiographic outcomes were more common in the endovascular group for supraclinoid and vertebrobasilar aneurysms (χ2, P < 0.01). There were no differences between morbidity of surgical and endovascular treatments for FIA, regardless of aneurysm location. Size and initial mRS were correlated with functional outcomes, whereas age and rupture status were not. Microsurgery seems to yield better long-term angiographic results compared to endovascular procedures.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Zaid G, Guo B, Deeks JJ, Debray TPA, Steyerberg EW, Moons KGM, Riley RD (2013) Individual participant data meta-analyses should not ignore clustering. J Clin Epidemiol 66:865–873.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.12.017
Alreshidi M, Cote DJ, Dasenbrock HH, Acosta M, Can A, Doucette J, Simjian T, Hulou MM, Wheeler LA, Huang K, Zaidi HA, Du R, Aziz-sultan MA, Mekary RA, Smith TR (2018) Coiling versus microsurgical clipping in the 0:1–11. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyx623/4847331
Byoun HS, Yi HJ, Choi KS, Chun HJ, Ko Y, Bak KH (2016) Comparison of endovascular treatments of ruptured dissecting aneurysms of the intracranial internal carotid artery and vertebral artery with a review of the literature. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 59:449–457. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.5.449
Chiaradio JC, Guzman L, Padilla L, Chiaradio MP (2002) Intravascular graft stent treatment of a ruptured fusiform dissecting aneurysm of the intracranial vertebral artery: technical case report. Neurosurgery 50:213–217. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200201000-00034
Dabus G, Lin E, Linfante I (2014) Endovascular treatment of fusiform intracranial vertebral artery aneurysms using reconstructive techniques. J Neurointerv Surg 6:589–594. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010897
Day AL, Gaposchkin CG, Yu CJ, Rivet DJ, Dacey RG (2003) Spontaneous fusiform middle cerebral artery aneurysms: characteristics and a proposed mechanism of formation. J Neurosurg 99:228–240. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.99.2.0228
Debray TPA, Moons KGM, van Valkenhoef G, Efthimiou O, Hummel N, Groenwold RHH, Reitsma JB (2015) Get real in individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis: a review of the methodology. Res Synth Methods 6:293–309. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1160
Deshmukh VR, Kakarla UK, Figueiredo EG, Zabramski JM, Spetzler RF (2006) Long-term clinical and angiographic follow-up of unclippable wrapped intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 58:434–441. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000199158.02619.99
Drake CG, Peerless SJ (1997) Giant fusiform intracranial aneurysms: review of 120 patients treated surgically from 1965 to 1992. J Neurosurg 87:141–162. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1997.87.2.0141
Ertl L, Holtmannspötter M, Patzig M, Brückmann H, Fesl G (2014) Use of flow-diverting devices in fusiform vertebrobasilar giant aneurysms: a report on periprocedural course and long-term follow-up. Am J Neuroradiol 35:1346–1352. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3859
Findlay JM, Hao C, Emery D (2002) Non-atherosclerotic fusiform cerebral aneurysms. Can J Neurol Sci 29:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0317167100001700
Flemming KD, Wiebers DO, Brown RD, Link MJ, Huston J, McClelland RL, Christianson TJH (2005) The natural history of radiographically defined vertebrobasilar nonsaccular intracranial aneurysms. Cerebrovasc Dis 20:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1159/000087710
Flemming KD, Wiebers DO, Brown RD, Link MJ, Nakatomi H, Huston J, McClelland R, Christianson TJH (2004) Prospective risk of hemorrhage in patients with vertebrobasilar nonsaccular intracranial aneurysm. J Neurosurg 101:82–87
Haukoos JS, Lewis RJ (2015) The propensity score. JAMA 314:1637–1638. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.13480
Horie N, Takahashi N, Furuichi S, Mori K, Onizuka M, Tsutsumi K, Shibata S (2003) Giant fusiform aneurysms in the middle cerebral artery presenting with hemorrhages of different origins: report of three cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 99:391–396. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.99.2.0391
Hu P, Zhang HQ, Li XY, Tong XZ (2019) Double-barrel superficial temporal artery to proximal middle cerebral artery bypass to treat complex intracranial aneurysms: a reliable high blood flow bypass. World Neurosurg 125:e884–e890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.203
Jolani S, Debray TPA, Koffijberg H, van Buuren S, Moons KGM (2015) Imputation of systematically missing predictors in an individual participant data meta-analysis: a generalized approach using MICE. Stat Med 34:1841–1863. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.6451
Joo SP, Kim TS, Choi JW, Lee JK, Kim YS, Moon KS, Kim JH, Kim SH (2007) Characteristics and management of ruptured distal middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Acta Neurochir 149:661–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1061-5
Kalani MYS, Zabramski JM, Nakaji P, Spetzler RF (2013) Bypass and flow reduction for complex basilar and vertebrobasilar junction aneurysms. Neurosurgery 72:763–775. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182870703
Kivipelto L, Niemelä M, Meling T, Lehecka M, Lehto H, Hernesniemi J (2014) Bypass surgery for complex middle cerebral artery aneurysms: impact of the exact location in the MCA tree. J Neurosurg 120:398–408. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.10.JNS13738
Krings T, Mandell DM, Kiehl T-R, Geibprasert S, Tymianski M, Alvarez H, TerBrugge KG, Hans F-J (2011) Intracranial aneurysms: from vessel wall pathology to therapeutic approach. Nat Rev Neurol 7:547–559. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2011.136
L.A. S, M. C, M. R, R.D. R, M. S, G. S (2015) Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data: the PRISMA-IPD statement. JAMA - J. Am. Med. Assoc.
Lanzino G, Kaptain G, Kallmes DF, Dix JE, Kassell NF (1997) Intracranial dissecting aneurysm causing subarachnoid hemorrhage: the role of computerized tomographic angiography and magnetic resonance angiography. Surg Neurol 48:477–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-3019(97)00178-X
Laukka D, Rautio R, Rahi M, Rinne J (2019) Acute treatment of ruptured fusiform posterior circulation posterior cerebral, superior cerebellar, and posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms with fred flow diverter: report of 5 cases. Oper Neurosurg 16:549–556. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opy194
Leibowitz R, Do HM, Marcellus ML, Chang SD, Steinberg GK, Marks MP (2003) Parent vessel occlusion for vertebrobasilar fusiform and dissecting aneurysms. Am J Neuroradiol 24:902–907
Lin N, Brouillard AM, Keigher KM, Lopes DK, Binning MJ, Liebman KM, Veznedaroglu E, Magarik JA, Mocco J, Duckworth EA, Arthur AS, Ringer AJ, Snyder KV, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH (2015) Utilization of pipeline embolization device for treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms: US multicenter experience. J Neurointerv Surg 7:808–815. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011320
Lin N, Lanzino G, Lopes DK, Arthur AS, Ogilvy CS, Ecker RD, Dumont TM, Turner RD, Gooch MR, Boulos AS, Kan P, Snyder KV, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH (2016) Treatment of distal anterior circulation aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device: a US multicenter experience. Neurosurgery 79:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001117
Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G, Pruvo JP, Bruneau M, De Witte O, Leclerc X (2010) Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke 41:2247–2253. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.589911
Meckel S, McAuliffe W, Fiorella D, Taschner CA, Phatouros C, Phillips TJ, Vasak P, Schumacher M, Klisch J (2013) Endovascular treatment of complex aneurysms at the vertebrobasilar junction with flow-diverting stents: initial experience. Neurosurgery 73:386–394. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000431472.71913.07
Mizutani T, Miki Y, Kojima H, Suzuki H (1999) Proposed classification of nonatherosclerotic cerebral fusiform and dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 45:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199908000-00010
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Monteith SJ, Tsimpas A, Dumont AS, Tjoumakaris S, Fernando Gonzalez L, Rosenwasser RH, Jabbour P (2014) Endovascular treatment of fusiform cerebral aneurysms with the Pipeline Embolization Device. J Neurosurg 120:945–954. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.12.JNS13945
Munich SA, Tan LA, Keigher KM, Chen M, Moftakhar R, Lopes DK (2014) The Pipeline Embolization Device for the treatment of posterior circulation fusiform aneurysms: lessons learned at a single institution. J Neurosurg 121:1077–1084. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.7.JNS132595
Murchison AG, Young V, Djurdjevic T, Cellerini M, Corkill R, Küker W (2018) Stent placement in patients with acute subarachnoid haemorrhage: when is it justified? Neuroradiology 60:735–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2020-6
Nakatomi H, Segawa H, Kurata A, Shiokawa Y, Nagata K, Kamiyama H, Ueki K, Kirino T (2000) Clinicopathological study of intracranial fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms: insight on the mechanism of growth. Stroke. 31:896–900. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.31.4.896
Nasr DM, Brinjikji W, Rouchaud A, Kadirvel R, Flemming KD, Kallmes DF (2016) Imaging characteristics of growing and ruptured vertebrobasilar non-saccular and dolichoectatic aneurysms. Stroke. 47:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.011671
Nasr DM, Flemming KD, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF, Murad MH, Brinjikji W (2018) Natural history of vertebrobasilar dolichoectatic and fusiform aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis 45:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1159/000486866
Natarajan SK, Lin N, Sonig A, Rai AT, Carpenter JS, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH (2016) The safety of pipeline flow diversion in fusiform vertebrobasilar aneurysms: a consecutive case series with longer-term follow-up from a single US center. J Neurosurg 125:111–119. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.6.JNS1565
Niikawa S, Yamada J, Sumi Y, Yamakawa H (2002) Dissecting aneurysm of the middle cerebral artery manifesting as subarachnoid hemorrhage and hemorrhagic infarctions - case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 42:62–66. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.42.62
Park S-H, Yim M-B, Lee C-Y, Kim E, Son E-I (2008) Intracranial fusiform aneurysms: It’s pathogenesis, clinical characteristics and managements. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 44:116–123. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2008.44.3.116
Park W, Kwon DH, Ahn JS, Lee SH, Park JC, Kwun BD (2015) Treatment strategies for dissecting aneurysms of the posterior cerebral artery. Acta Neurochir 157:1633–1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2526-1
Pumar JM, Arias-Rivas S, Rodríguez-Yáñez M, Blanco M, Ageitos M, Vazquez-Herrero F, Castiñeira-Mourenza JA, Masso A (2013) Using Leo Plus stent as flow diverter and endoluminal remodeling in endovascular treatment of intracranial fusiform aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg 5:iii22–iii27. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010661
Qu S, Lv X, Wu Z (2009) Clinical outcomes of basilar artery aneurysms. Neuroradiol J 22:228–238. https://doi.org/10.1177/197140090902200215
Resche-Rigon M, White IR, Bartlett JW, Peters SAE, Thompson SG (2013) Multiple imputation for handling systematically missing confounders in meta-analysis of individual participant data. Stat Med 32:4890–4905. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.5894
Rho MH, Park HJ, Chung EC, Choi YJ, Lee SY, Won YS, Kim BM (2013) Various techniques of stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-necked or fusiform artherosclerotic and dissecting unruptured vertebrobasilar artery aneurysms for reducing recanalization: mid-term results. Acta Neurochir 155:2009–2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1866-y
Roh HG, Kim SS, Han H, Kang HS, Moon WJ, Byun HS (2008) Endovascular treatment of posterior cerebral artery aneurysms using detachable coils. Neuroradiology 50:237–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0321-2
Safavi-Abbasi S, Kalani MYS, Frock B, Sun H, Yagmurlu K, Moron F, Snyder LA, Hlubek RJ, Zabramski JM, Nakaji P, Spetzler RF (2017) Techniques and outcomes of microsurgical management of ruptured and unruptured fusiform cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 127:1353–1360. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.JNS161165
Seo BR, Kim TS, Joo SP, Lee JM, Jang JW, Lee JK, Kim JH, Kim SH (2009) Surgical strategies using cerebral revascularization in complex middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 111:670–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2009.06.002
Stroke T, Gates MF, Carolina N (2012) S 1258. 116:1258–1266
Suh SH, Kim BM, Chung TS, Kim DI, Kim DJ, Hong CK, Kim CH, Ahn JY, Kim SS (2010) Reconstructive endovascular treatment of intracranial fusiform aneurysms: a 1-stage procedure with stent and balloon. Am J Neuroradiol 31:155–160. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1784
Wang Q, Leng B, Song D, Chen G (2010) Fusiform aneurysms of the vertebrobasilar arterial trunk: choice of endovascular methods and therapeutic efficacy. Acta Neurochir 152:1467–1476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0691-9
Xu F, Xu B, Huang L, Xiong J, Gu Y, Lawton MT (2018) Surgical treatment of large or giant fusiform middle cerebral artery aneurysms: a case series. World Neurosurg 115:e252–e262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.031
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the local Ethics Committee (ID: 12089), and patient consent was waived because of the retrospective design.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 3616 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Telles, J.P.M., Solla, D.J.F., Yamaki, V.N. et al. Comparison of surgical and endovascular treatments for fusiform intracranial aneurysms: systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 44, 2405–2414 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01440-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01440-x