Abstract
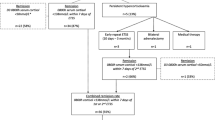
High levels of endogenous cortisol due to Cushing’s disease cause significant mortality and morbidity. Treatment of Cushing’s disease is challenging. For many years, transsphenoidal microsurgical resection of the adenoma has been the treatment of choice. However, recently, neuroendoscope has taken its place in the neurosurgeon’s armamentarium, and the endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of pituitary tumors has become a familiar approach. Our aim was to present the results of pure endoscopic surgery in the treatment of corticotropinomas for comparison with the results of previous endoscopic and microsurgical series. We present a retrospective analysis of 90 patients with diagnosis of Cushing’s disease who were operated between 2006 and 2012. Among 90 patients, a total of 81 (90.0 %) had a remission (28 out of 29 macroadenomas (96.6 %) and 53 out of 61 microadenoma patients (86.9 %)). Of note is that 66 out of 69 (95.7 %) primary patients (i.e., those who were operated in our center) and 15 out of 21 (71.4 %) patients previously operated in other centers reached a hypo/eucortisolemic state. A remission rate comparable with previous endoscopic series was achieved. In nine patients, it was not possible to achieve remission at all. On the other hand, only four of our cases (5.6 %) had a recurrence, and with reoperation, all of these patients entered a re-remission. To our knowledge, our series is the largest series studying endoscopically operated adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting adenomas. Our results suggest that the endoscopic approach has opened a new avenue in the treatment of Cushing’s disease, previously a therapeutic challenge for both the clinician and the neurosurgeon. Endoscopic approach in the treatment of Cushing’s disease is clearly better for patients because of its low morbidity rates and short duration of hospital stay. On the other hand, long-term follow-up of our patients will show whether these favorable observations will persist.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alwani RA, de Herder WW, van Aken MO, van den Berge JH, Delwel EJ, Dallenga AH, De Jong FH, Lamberts SW, van der Lely AJ, Feelders RA (2010) Biochemical predictors of outcome of pituitary surgery for Cushing’s disease. Neuroendocrinology 91(2):169–178. doi:10.1159/000258677
Andrioli M, Pecori Giraldi F, Losa M, Terreni M, Invitti C, Cavagnini F (2010) Cushing's disease due to double pituitary ACTH-secreting adenomas: the first case report. Endocr J 57(9):833–837
Arnaldi G, Angeli A, Atkinson AB, Bertagna X, Cavagnini F, Chrousos GP, Fava GA, Findling JW, Gaillard RC, Grossman AB, Kola B, Lacroix A, Mancini T, Mantero F, Newell-Price J, Nieman LK, Sonino N, Vance ML, Giustina A, Boscaro M (2003) Diagnosis and complications of Cushing’s syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(12):5593–5602
Berker D, Aydin Y, Işık S, Söylemezoğlu F, Tütüncü Y, Berker M, Delibaşı T, Guler S (2010) Cushing disease associated with Rathke’s cleft cyst. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 3:371–376
Berker M, Hazer DB, Yucel T, Gurlek A, Cila A, Aldur M, Onerci M (2012) Complications of endoscopic surgery of the pituitary adenomas: analysis of 570 patients and review of the literature. Pituitary 15(3):288–300. doi:10.1007/s11102-011-0368-2
Biller BM, Grossman AB, Stewart PM, Melmed S, Bertagna X, Bertherat J, Buchfelder M, Colao A, Hermus AR, Hofland LJ, Klibanski A, Lacroix A, Lindsay JR, Newell-Price J, Nieman LK, Petersenn S, Sonino N, Stalla GK, Swearingen B, Vance ML, Wass JA, Boscaro M (2008) Treatment of adrenocorticotropin-dependent Cushing’s syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(7):2454–2462. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-2734
Bochicchio D, Losa M, Buchfelder M (1995) Factors influencing the immediate and late outcome of Cushing’s disease treated by transsphenoidal surgery: a retrospective study by the European Cushing’s Disease Survey Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80(11):3114–3120
Cappabianca P, Alfieri A, Colao A, Ferone D, Lombardi G, de Divitiis E (1999) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach: an additional reason in support of surgery in the management of pituitary lesions. Skull Base Surg 9(2):109–117
Cappabianca P, Alfieri A, de Divitiis E (1998) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach to the sella: towards functional endoscopic pituitary surgery (FEPS). Minim Invasive Neurosurg 41(2):66–73. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1052019
Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, de Divitiis E (2004) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery 55(4):933–940, discussion 940–931
Chen JC, Amar AP, Choi S, Singer P, Couldwell WT, Weiss MH (2003) Transsphenoidal microsurgical treatment of Cushing disease: postoperative assessment of surgical efficacy by application of an overnight low-dose dexamethasone suppression test. J Neurosurg 98(5):967–973. doi:10.3171/jns.2003.98.5.0967
Ciric I, Ragin A, Baumgartner C, Pierce D (1997) Complications of transsphenoidal surgery: results of a national survey, review of the literature, and personal experience. Neurosurgery 40(2):225–236, discussion 236-227
Dehdashti AR, Gentili F (2007) Current state of the art in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of Cushing disease: early experience with a purely endoscopic endonasal technique. Neurosurg Focus 23(3):E9. doi:10.3171/foc.2007.23.3.11
Frank G, Pasquini E, Farneti G, Mazzatenta D, Sciarretta V, Grasso V, Faustini Fustini M (2006) The endoscopic versus the traditional approach in pituitary surgery. Neuroendocrinology 83(3–4):240–248. doi:10.1159/000095534
Hammer GD, Tyrrell JB, Lamborn KR, Applebury CB, Hannegan ET, Bell S, Rahl R, Lu A, Wilson CB (2004) Transsphenoidal microsurgery for Cushing’s disease: initial outcome and long-term results. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(12):6348–6357. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-032180
Hofmann BM, Fahlbusch R (2006) Treatment of Cushing’s disease: a retrospective clinical study of the latest 100 cases. Front Horm Res 34:158–184. doi:10.1159/000091580
Jagannathan J, Smith R, DeVroom HL, Vortmeyer AO, Stratakis CA, Nieman LK, Oldfield EH (2009) Outcome of using the histological pseudocapsule as a surgical capsule in Cushing disease. J Neurosurg 111(3):531–539. doi:10.3171/2008.8.JNS08339
Jankowski R, Auque J, Simon C, Marchal JC, Hepner H, Wayoff M (1992) Endoscopic pituitary tumor surgery. Laryngoscope 102(2):198–202. doi:10.1288/00005537-199202000-00016
Jho HD (2001) Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery. J Neurooncol 54(2):187–195
Jho HD, Alfieri A (2001) Endoscopic endonasal pituitary surgery: evolution of surgical technique and equipment in 150 operations. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 44(1):1–12. doi:10.1055/s-2001-13590
Jho HD, Carrau RL (1997) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: experience with 50 patients. J Neurosurg 87(1):44–51. doi:10.3171/jns.1997.87.1.0044
Lindholm J, Juul S, Jorgensen JO, Astrup J, Bjerre P, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Hagen C, Jorgensen J, Kosteljanetz M, Kristensen L, Laurberg P, Schmidt K, Weeke J (2001) Incidence and late prognosis of Cushing’s syndrome: a population-based study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(1):117–123
Lindsay JR, Oldfield EH, Stratakis CA, Nieman LK (2011) The postoperative basal cortisol and CRH tests for prediction of long-term remission from Cushing’s disease after transsphenoidal surgery. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(7):2057–2064. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0456
Ludecke DK, Niedworok G (1985) Results of microsurgery in Cushing’s disease and effect on hypertension. Cardiology 72(Suppl 1):91–94
Netea-Maier RT, van Lindert EJ, den Heijer M, van der Eerden A, Pieters GF, Sweep CG, Grotenhuis JA, Hermus AR (2006) Transsphenoidal pituitary surgery via the endoscopic technique: results in 35 consecutive patients with Cushing’s disease. Eur J Endocrinol 154(5):675–684. doi:10.1530/eje.1.02133
Oldfield EH, Vortmeyer AO (2006) Development of a histological pseudocapsule and its use as a surgical capsule in the excision of pituitary tumors. J Neurosurg 104(1):7–19. doi:10.3171/jns.2006.104.1.7
Oruckaptan HH, Senmevsim O, Ozcan OE, Ozgen T (2000) Pituitary adenomas: results of 684 surgically treated patients and review of the literature. Surg Neurol 53(3):211–219
Prevedello DM, Pouratian N, Sherman J, Jane JA Jr, Vance ML, Lopes MB, Laws ER Jr (2008) Management of Cushing’s disease: outcome in patients with microadenoma detected on pituitary magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 109(4):751–759. doi:10.3171/JNS/2008/109/10/0751
Ram Z, Nieman LK, Cutler GB Jr, Chrousos GP, Doppman JL, Oldfield EH (1994) Early repeat surgery for persistent Cushing’s disease. J Neurosurg 80(1):37–45. doi:10.3171/jns.1994.80.1.0037
Rees DA, Hanna FW, Davies JS, Mills RG, Vafidis J, Scanlon MF (2002) Long-term follow-up results of transsphenoidal surgery for Cushing’s disease in a single centre using strict criteria for remission. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 56(4):541–551
Rollin G, Ferreira NP, Czepielewski MA (2007) Prospective evaluation of transsphenoidal pituitary surgery in 108 patients with Cushing’s disease. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 51(8):1355–1361
Schrell U, Fahlbusch R, Buchfelder M, Riedl S, Stalla GK, Muller OA (1987) Corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulation test before and after transsphenoidal selective microadenomectomy in 30 patients with Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 64(6):1150–1159
Shimon I, Ram Z, Cohen ZR, Hadani M (2002) Transsphenoidal surgery for Cushing’s disease: endocrinological follow-up monitoring of 82 patients. Neurosurgery 51(1):57–61, discussion 61–52
Storr HL, Afshar F, Matson M, Sabin I, Davies KM, Evanson J, Plowman PN, Besser GM, Monson JP, Grossman AB, Savage MO (2005) Factors influencing cure by transsphenoidal selective adenomectomy in paediatric Cushing’s disease. Eur J Endocrinol 152(6):825–833. doi:10.1530/eje.1.01921
Trainer PJ, Lawrie HS, Verhelst J, Howlett TA, Lowe DG, Grossman AB, Savage MO, Afshar F, Besser GM (1993) Transsphenoidal resection in Cushing’s disease: undetectable serum cortisol as the definition of successful treatment. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 38(1):73–78
Wagenmakers MA, Netea-Maier RT, van Lindert EJ, Timmers HJ, Grotenhuis JA, Hermus AR (2009) Repeated transsphenoidal pituitary surgery (TS) via the endoscopic technique: a good therapeutic option for recurrent or persistent Cushing’s disease (CD). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 70(2):274–280. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03334.x
Yap LB, Turner HE, Adams CB, Wass JA (2002) Undetectable postoperative cortisol does not always predict long-term remission in Cushing’s disease: a single centre audit. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 56(1):25–31
Disclosure
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comments
Paolo Cappabianca, Naples, Italy
It can be claimed as real progress of a surgical procedure both the improvement of the outcomes and the reduction of complications. The article from Dr. Berker confirms that the growing experience in endoscopic endonasal technique leads to results at least similar to those achieved by means of the microsurgical transsphenoidal approach [2, 4–11]. Up to now, it has not been possible to compare the large microsurgical series with smaller endoscopic ones, but the outcomes are promising. Prospective studies should be performed to give conclusive remarks.
On the other hand, the complication rate of the endoscopic endonasal technique appeared immediately lower as compared to the conventional microsurgical transsphenoidal technique [1, 3].
At the beginning of the 2000s, a foreign neurosurgeon who came to Naples for our workshop on endoscopic endonasal pituitary surgery told us that not that far away from his hospital there was a neurosurgeon who was still approaching the sellar area via a lateral rhinotomy and who did not intend to change his mind. We understand that it can be quite difficult to adopt a new surgical technique when the previous well-established one has been proven to be effective, according to the personal neurosurgical armamentarium and know-how. Nevertheless, it can be useful to adopt new strategies and techniques for the sake of our patients rather than being anchored to one’s own already good experience and attitude. In the case of the endoscopic endonasal technique for pituitary adenomas, many authors have shown the safety and the effectiveness of such method, and the present contribution adds another brick to this new building.
References
1. Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Colao A, de Divitiis E (2002) Surgical complications associated with the endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas. J Neurosurg 97(2):293–298
2. Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Colao A, Del Basso De Caro M, Esposito F, Cirillo S, Lombardi G, de Divitiis E (2002) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach: outcome analysis of 100 consecutive procedures. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 45(4):193–200
3. Ciric I, Ragin A, Baumgartner C, Pierce D (1997) Complications of transsphenoidal surgery: results of a national survey, review of the literature, and personal experience. Neurosurgery 40(2):225–236; discussion 236–227
4. Dehdashti AR, Ganna A, Karabatsou K, Gentili F (2008) Pure endoscopic endonasal approach for pituitary adenomas: early surgical results in 200 patients and comparison with previous microsurgical series. Neurosurgery 62(5):1006–1015; discussion 1015–1007
5. Frank G, Pasquini E, Farneti G, Mazzatenta D, Sciarretta V, Grasso V, Faustini Fustini M (2006) The endoscopic versus the traditional approach in pituitary surgery. Neuroendocrinology 83(3-4):240–248
6. Gondim JA, Schops M, de Almeida JP, de Albuquerque LA, Gomes E, Ferraz T, Barroso FA (2010) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: surgical results of 228 pituitary adenomas treated in a pituitary center. Pituitary 13(1):68–77
7. Jho HD, Carrau RL (1997) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: experience with 50 patients. J Neurosurg 87(1):44–51
8. Kassam AB, Prevedello DM, Carrau RL, Snyderman CH, Thomas A, Gardner P, Zanation A, Duz B, Stefko ST, Byers K, Horowitz MB (2011) Endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery: analysis of complications in the authors' initial 800 patients. J Neurosurg 114(6):1544–1568
9. Koc K, Anik I, Ozdamar D, Cabuk B, Keskin G, Ceylan S (2006) The learning curve in endoscopic pituitary surgery and our experience. Neurosurg Rev 29(4):298–305; discussion 305
10. McLaughlin N, Eisenberg AA, Cohan P, Chaloner CB, Kelly DF (2013) Value of endoscopy for maximizing tumor removal in endonasal transsphenoidal pituitary adenoma surgery. J Neurosurg 118(3):613–620
11. Tabaee A, Anand VK, Barron Y, Hiltzik DH, Brown SM, Kacker A, Mazumdar M, Schwartz TH (2009) Endoscopic pituitary surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg 111(3):545–554
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berker, M., Işikay, I., Berker, D. et al. Early promising results for the endoscopic surgical treatment of Cushing’s disease. Neurosurg Rev 37, 105–114 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-013-0506-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-013-0506-6