Abstract
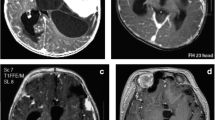
Desmoplastic gangliogliomas (DIG) are rare primary neoplasms that comprise 0.5–1.0% of all intracranial tumors. Clinically, there are two forms of DIG, the infantile and the non-infantile. These tumors invariably arise in the supratentorial region and commonly involve more than one lobe, preferentially the temporal and frontal. On neuroimaging are seen as large hypodense cystic masses with a solid isodense or slightly hyperdense superficial portion. The histologic diagnosis is characterized by the presence of three different cell lines: astrocytic, neuronal, and primitive neuroectodermal marker sites, which were demonstrable. The treatment of choice is radical surgical excision, and if this is done, achieved complete healing of the patient does not require additional treatment. A literature review of DIG was compiled through Medline/Ovid using the keywords “desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma”, “desmoplastic non-infantile ganglioglioma” covering the years 1984–2009. We present a review of a total of 113 cases of infantile (94) and non-infantile gangliogliomas (19) published to date, examining the clinical, radiologic, surgical, and pathological aspects, as well as the outcome. Desmoplastic gangliogliomas represent a rare tumor group with two well-defined age groups, the children and non-children. Desmoplastic infantile gangliogliomas are the most common and occur in children below 5 years of age, and the large majority of them present within the first year of life. Surgery is the treatment of choice and no complementary treatment is needed in cases of complete tumor resection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aida T, Abe H, Itoh T, Nagashima K, Inoue K (1993) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma—case report). Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 33:463–466
Alexiou GA, Stefanaki K, Sfakianos G, Prodromou N (2008) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: a report of 2 cases and a review of the literature. Pediatr Neurosurg 44:422–425
Antonelli M, Acerno S, Baldoli C, Terreni MR, Giangaspero F (2009) A case of melanotic desmoplastic ganglioglioma. Neuropathology 29:597–601
Avci E, Öztürk A, Baba F, Torun F, Karabağ H, Yücetaş S (2008) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: case report. Turk J Pediatr 50:495–499
Ávila de Espíndola A, Matushima H, Pimenta JM, da Silva AC, Rosemberg S, Reed UC (2007) Brain tumors in the first three years of life: a review of twenty cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 65:960–964
Bächli H, Avoledo P, Gratzl O, Tolnay M (2003) Therapeutic strategies and management of desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: two case reports and literature overview. Childs Nerv Syst 19:359–366
Balasubramanian D, Armes VG, Deiveegan K, Ghosh M, Mallikarjuna VS, Annapoorneswari TP, Chidambaranathan N, Ramani KV (2004) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Neurol India 52:384–386
Bhardwaj M, Sharma A, Pal HK (2006) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma with calcification. Neuropathology 26:318–322
Brat DJ, VandenBerg SR, Figarella-Branger D, Taratuto AL (2007) Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma and ganglioglioma. In: Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (eds) WHO classification of tumours of the Central Nervous System. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Lyon, pp 96–98
Craver RD, Nadell J, Nelson JS (1999) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Ped Dev Pathol 2:582–587
Darwish B, Arbuckle S, Kellie S, Besser M, Chaseling R (2007) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma/astrocytoma with cerebrospinal metastasis. J Clin Neurosci 14:498–501
De Chadarévian JP, Pattisapu JV, Faerber EN (1990) Desmoplastic cerebral astrocytoma of infancy. Light microscope, immunocytochemistry and ultrastructure. Cancer 66:173–179
De Munnynck K, Van Gool S, Van Calenbergh F, Demaerel P, Uyttebroeck A, Buyse G, Sciot R (2002) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: a potentially malignant tumor? Am J Surg Pathol 26:1515–1522
Duffner P, Burger P, Cohen M, Sanford R, Krischer J, El-Aronin P, Pullen J, Horowith M, Parent A, Martin P, Kun LEM (1994) Desmoplastic infantile gangliogliomas: an approach to therapy. Neurosurgery 34:583–589
Dunnick NR (2000) Image interpretation session: 1999. Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Radiographics 20:276–278
Fadare O, Mariappan MR, Hileeto D, Zieske AW, Kim JH, Ocal IT (2005) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: cytologic findings and differential diagnosis on aspiration material. CytoJournal 2:1–6
Fan X, Larson TC, Jennings MT, Tulipan NB, Toms SA, Johnson MD (2001) December 2000: 6 month old boy with 2 week history of progressive lethargy. Brain Pathol 11:265–266
Galatioto S, Gullota F (1996) Desmoplastic non-infantile ganglioglioma. J Neurosurg Sci 40:235–238
Ganesan K, Desai S, Udwadia-Hegde A (2006) Non-infantile variant of desmoplastic ganglioglioma: a report of 2 cases. Pediatr Radiol 36:541–545
Hasegawa Y, Hayabuchi Y, Namba I, Watanabe T, Kato K, Ijiri R, Tanaka Y, Sekido K, Kigasawa H, Hara M (2001) Cytologic features of desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: a report of two cases. Acta Cytol 45:1037–1042
Hoving EW, Kros JM, Groninger E, den Dunnen WF (2008) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma with a malignant course. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1:95–98
Iwami K (2007) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Childs Nerv Syst 23:619–620
Jay V, Edwards V, Rutka J, Mosskin M, Hwang P, Resch L (1998) Unique desmoplastic cerebral tumor in a patient with complex partial seizures. Pediatr Dev Pathol 1:234–242
Kesavadas Ch, Sonwalker H, Thomas B, Gupta AK, Radhakrishanan VV (2005) Atypical MRI appearance of desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Pediatr Radiol 35:1024–1026
Khaddage A, Chambonniere ML, Morrison AL, Allard D, Dumollard JM, Pasquier B, Péoch M (2004) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: A rare tumor with an unusual presentation. Ann Diagn Pathol 8:280–283
Khubchandani SR, Chitale AR, Doshi PK (2009) Desmoplastic non-infantile ganglioglioma: a low-grade tumor, report of two patients. Neurol India 57:796–799
Knapp J, Olson L, Tye S, Bethard JR, Welsh CA, Rumbolt Z, Takacs I, Maria BL (2005) Case of desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma secreting cerulopasmin. J Child Neurol 20:920–924
Komori T, Scheithauer BW, Parisi JE, Watterson J, Priest JR (2001) Mixed conventional and desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: an autopsied case with 6-year follow-up. Mod Pathol 14:720–726
Kros JM, Delwel EJ, de Jong TH, Tanghe HL, van Run PR, Vissers K, Alers JC (2002) Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma and ganglioglioma: a search for genomic characteristics. Acta Neuropathol 104:144–148
Kuchelmeister K, Bergman M, von Wild K, Hochreuther D, Busch G, Gullota F (1993) Desmoplastic ganglioglioma: report of two non-infantile cases. Acta Neuropathol 85:199–204
Lababede O, Bardo D, Goske MJ, Praysonn RA (2001) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma (DIG): craneal ultrasound findings. Pediatr Radiol 31:403–405
Lönnrot K, Terho M, Kähärä V, Haapasalo H, Helén P (2007) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: novel aspects in clinical presentation and genetics. Surg Neurol 68:304–308
Mallucci C, Lellouch-Tubiana A, Salazar C, Cinalli G, Renier D, Sainte-Rose C, Pierre-Khan A, Zerah M (2000) The management of desmoplastic neuroephitelial tumours in childhood. Childs Nerv Syst 16:8–14
Marti A, Almostarchid B, Maher M, Saidi A (2000) Desmoplastic non-infantile ganglioglioma. J Neurosurg Sci 44:150–154
Martin DS, Levy B, Awwad EE, Pittman T (1991) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: CT and MR features. AJNR 12:1195–1197
Milanaccio C, Nozza P, Ravegnani M, Rossi A, Raso A, Gambini C, Garré ML, Petsch T (2005) Cervico-medullary desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: an unusual case with diffuse leptomeningeal dissemination at diagnosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 45:986–990
Mhiri MS, Acour NA, Moulahi H, Bouraoui IH, Dali KM, Mokni M, Krifa H, Tlili-Graiess K (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging features of desmoplastic cerebral ganglioglioma of infancy: report of 1 case. Arch Pediatr 13:163–166
Mizuno M (2000) Desmoplastic infantile gangliogloma (DIG). Ryoikibetsu Shokogun Shirizu (Japanese) 28:75–76
Montes JL, Rosemblatt B, Farmer JP, O'Gorman AM, Andermann F, Watters GV, Meagher-Villemure K (1995) Lesionectomy of MRI detected lesions in children with epilepsy. Pediatr Neurosurg 22:167–173
Nanassis K, Tsitsopoulos PP, Marnopoulos D, Venizelos I, Tsitsopoulos PD (2010) Long-term follow-up of a non-infantile desmoplastic ganglioglioma. Cen Eur Neurosurg 71:50–53
Nikas I, Anagnostara A, Theophanopoulou M, Stefanaki K, Michail A, Hadjigeorgi Ch (2004) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: MRI and histological findings case report. Neuroradiology 46:1039–1043
Ng THK, Fung CF, Ma LT (1990) The pathological spectrum of desmoplastic infantile gangliogliomas. Histopathology 16:235–241
Onguru O, Celasun B, Gunhan O (2005) Desmoplastic non-infantile ganglioglioma. Neuropathology 25:150–152
Parisi JE, Scheithauer BW, Priest JR, Okazaki H, Komori T (1992) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma (DIG): a form of ganglio-gliomatosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 51:365
Park JP, Dossu JR, Rhodes CH (1996) Telomere associations in desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 92:4–7
Paulus W, Achlote W, Perentes E, Jacobis G, Warmuth-Metz M, Roggendorf W (1992) Desmoplastic supratentorial neuroepithelial tumours of infancy. Histopathology 21:43–49
Per H, Kontaş O, Kumandaş S, Kurtsoy A (2009) A report of a desmoplastic non-infantile ganglioglioma in a 6-year-old boy with review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev 32:369–374
Pommepuy I, Delage-Corre M, Moreau JJ, Labrouse F (2006) A report of desmoplastic ganglioglioma in a 12-year-old girl with review of the literature. J Neurooncol 76:271–275
Prayson RA (1996) Gliofibroma: a distinct entity or a subtype of desmoplastic astrocytoma? Hum Pathol 27:610–613
Qaddoumi I, Ceppa EP, Mansour A, Sughayer MA, Tihan T (2006) Desmoplastic noninfantile ganglioglioma: report of a case. Pediatr Dev Pathol 9:462–467
Rothman S, Sharon N, Shiffer J, Toren A, Pollak L, Mandel M, Kenet G, Neumann Y, Nass D (1997) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Acta Oncol 36:655–657
Rout P, Santosh V, Mahadevan A, Sastry-Kolluri VR, Yasha TC, Sahnkar SK (2002) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma-clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of four cases. Childs Nerv Syst 18:463–467
Sperner J, Gottschalk J, Neuman K, Schörner W, Lanksch WR, Scheffner D (1994) Clinical, radiological and histological findings in desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Childs Nerv Syst 10:458–462
Sugiyama K, Arita K, Shima T, Nakaoka M, Matsuoka T, Taniguchi E, Okamura T, Yamasaki H, Kajiwara Y, Kurisu K (2002) Good clinical course in infants with desmoplastic cerebral neuroepithelial tumor treated by surgery alone. J Neurol Oncol 59:63–69
Tadokoro M, Ozawa T, Abe M, Shinagawa T, Sakurai T, Taguchi Y (1994) A case of desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Noshuyo Byori (Japanese) 11:93–98
Taguchi Y, Sakurai T, Takamori I, Sekino H, Tadokoro M (1993) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma with extraparenchymatous cyst. Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 33:177–180
Takeshima H, Kawahara Y, Hirano H, Obara S, Niiro M, Kuratsu J (2003) Postoperative regression of desmoplastic infantile gangliogliomas: report of two cases. Neurosurgery 53:979–983
Tamburrini G, Colosimo C, Giangaspero F, Riccardi R, Di Rocco C (2003) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Childs Nerv Syst 19:292–297
Tantbirojn P, Sanpavat A, Bunyaratavej K, Desudchit T, Shuangshoti S (2005) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma with high proliferation index: report of a case. J Med Assoc Thai 88:1962–1965
Taranath A, Lam A, Wong CK (2005) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: a questionable bening tumour. Australas Radiol 49:433–437
Taratuto AL, Monges J, Lylyk P, Leiguarda R (1984) Superficial cerebral astrocytoma attached to dura. Report of six cases in infants. Cancer 54:2505–2512
Tekkök IH, Ventureyra ECG (1997) Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage of structural origin during the first year of life. Childs Nerv Syst 13:154–165
Tenreiro-Picon OR, Kamath SV, Knorr JR, Ragland RL, Smith TW, Lau KY (1995) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma: CT and MRI features. Pediatr Radiol 25:540–543
Torres LF, Reis Filho JS, Netto MR, de Noronha L, Aléssio AB, de Carvalho NA (1998) Infantile desmoplastic ganglioglioma: a clinical, histopathological and epidemiological study of five cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 56:443–448
Trehan G, Bruge H, Vinchon M, Khalil Ch, Ruchoux MM, Dhellemmes P, Ares GS (2004) MR imaging in the diagnosis of desmoplastic infantile tumor: retrospective study of six cases. AJNR 25:1028–1033
Tseng JH, Tseng MY, Kuo MF, Tseng CL, Chang YL (2002) Chronological changes on magnetic resonance images in a case of desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma. Pediatr Neurosurg 36:29–32
VandenBerg SR, May EE, Rubinstein LJ, Herman MM, Perentes E, Vinores SA, Collins VP, Park TS (1987) Desmoplastic supratentorial neuroepithelial tumors of infancy with divergent differentiation potential (“desmoplastic infantile gangliogliomas”). J Neurosurg 66:58–71
VandenBerg SR (1993) Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma and desmoplastic cerebral astrocytoma of infancy? Brain Pathol 3:275–281
Woesler B, Kuwert T, Kurlemann G, Morgenroth C, Probst-Cousin S, Lerch H, Gullota F, Wassmann H, Schober O (1998) High amino acid uptake in a low-grade desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma in a 14-year-old patient. Neurosurg Rev 21:31–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comments
Hamit Selim Karabekir, Afyon, Turkey
Gelabert-Gonzalez et al. defined desmoplastic gangliogliomas (infantile or non-infantile) clearly and summarized the literature for 29 years from 1980 to 2009. They looked at the age, gender, presenting symptoms, clinical findings, localization, size, diagnostic and surgical procedures, and survival of the cases. Also, they included the pathological findings and immunohistochemical assays. In the data of the literature, they commend that the end surgical treatment is the first and best choice if complete resection can be realized. This review is very useful for looking at desmoplastic gangliomas for the last 30 years and can show the way how to approach the cases to researchers. I congratulated the authors for catching the readers' interest in an actual way.
Kaoru Kurisu, Hiroshima, Japan
Desmoplastic infantile and non-infantile ganglioglioma. Review of the literature submitted by Gelabert-Gonzales Miguel et al. is well discussed and precisely described in almost all aspects of the “special tumor” on etiology, histological character, image diagnosis, natural course, clinical presentation, treatment strategy, outcome, and prognosis, except only one issue. The authors emphasized the benign prognosis after a total or gross total removal of the tumor. But very less intraoperative findings during surgery we could find. Generally speaking, if the patient with some disease can be cured by surgery, the surgeons are eager to know how to remove the lesion without additional impairment. I think these kinds of tumor, DIG/DNIG, can be easily removed by the different “consistency” between tumor and surrounding brain tissue. The consistency of DIG/DNIG is relatively firm or of high consistency, so the operators can “relatively” easily remove the tumor in total or gross total fashion (Sugiyama et al, Good clinical course in infant with desmoplastic cerebral neuroepithelial tumor treated by surgery alone, J Neurooncol 59;63–69, 2002). This is just only one issue that I have to add to this wonderful review article.
Dattatraya Muzumdar, Mumbai, India
Gelabert-Gonzalez et al. have presented a comprehensive review of 119 cases of desmoplastic infantile and noninfantile ganglioglioma described in the literature. They have compiled the salient clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic features of these relatively benign tumors into various segments, which provide a quick overview.
Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma was first described in 1987. The term is self-explanatory. These tumors are usually seen in infancy, have prominent desmoplasia, and have neuronal differentiation. It is surprising to note that the most common presenting symptoms were macrocephaly in 40.7%, suggesting that it forms an entity to be included in the differential diagnosis of a large head in infancy. The electroencephalogram is normal in most cases inspite of seizures noted in 23 (23.7%) of patients, which is unusual. In addition, there is no higher incidence of developmental delay at presentation or at follow-up, which denotes that the integrity of brain substance is maintained in utero. CT and MR imaging features are not specific for DIG. They are heterogenous tumors, having solid–cystic components but show homogenous enhancement. Purely solid tumor is rare. Calcification is seen in few cases.There is no specific preference for hemispheric predominance, although it is most commonly found in the temporal lobe. The volume of the tumors or cysts ranged from 5 to 1000 cc, which suggests a differential growth pattern, which does not necessarily correlate with an oncologic progression. Although they can attain a voluminous size, they are relatively benign and long-term prognosis is usually good. Total excision is curative. Due to the large size seen at presentation, as well as diffuse vascularization of DIGs, blood loss during surgery poses increased risk for hemodynamic instability. Deep and inaccessible locations of the tumor preclude a radical excision. There is clear demarcation between the cortical surface and the tumor tends to fill the Virchow–Robin spaces. Adherence to the duramater is not seen in about 40% of the cases. The histological features are essentially benign, and proliferative index of these tumors is low. These characteristics suggest that the DIG have a low invasive potential and have a predictable behavior. Surgery is the mainstay of the treatment protocol. Residual or recurrent tumors can be considered for repeat surgery. There is a tendency for spontaneous regression in few cases due to induction of apoptosis. Radiation and chemotherapy is unlikely to be overwhelmingly responsive. Inspite of a benign nature of the DIGs, only seven reported cases survived beyond 10 years. The median survival is 36.7 months. There is a need for further research into the genetics of these tumors for better understanding of the biology and further evolution of therapeutics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelabert-Gonzalez, M., Serramito-García, R. & Arcos-Algaba, A. Desmoplastic infantile and non-infantile ganglioglioma. Review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev 34, 151–158 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-010-0303-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-010-0303-4