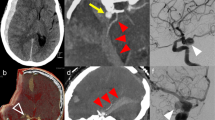
Abstract
Acute spontaneous subdural haematoma (SDH) is rarely associated with rupture of intracranial saccular aneurysm. We report our experience with four cases of non-traumatic SDHs secondary to rupture of an intracranial aneurysm and discuss the diagnosis and management of this condition. We retrospectively reviewed of four cases of acute SDH due to cerebral aneurysm rupture confirmed by cerebral angiography and surgery. Patients were evaluated using the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) and subarachnoid grade of the World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies (WFNS) and outcome with the Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS). Of the 232 patients with non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) treated between 1993 and 2002, only four patients (1.72%) presented SDH due to aneurysmal rupture. The SAH grade on admission was grade IV in one patient and V in the other three. In all cases the aneurysm was located in the posterior communicating artery. Spontaneous acute SDH secondary to aneurysm rupture has been rarely reported. We suggested that timely SDH removal and aneurysmal clipping surgery should be performed in such patients, including those in poor neurological condition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves OL, Gomes O (2000) Cocaine-related acute subdural haematoma: an emergent cause of cerebrovascular accident. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:819–821
Barton B, Tudor J (1982) Subdural hematoma in association with intracranial aneurysm. Neuroradiology 23:157–160
Gelabert-González M, Fernández-Villa JM, Iglesias-Pais M, González-García J, García-Allut A (2003) Acute spontaneous subdural haematoma of arterial origin. Neurocirugía (in press)
Hasse KE (1955) Die Krankheiten des Nervensystems. In: Virchow R (ed) Handbuch der speziellen Pathologie und Therapie, vol IV/1. Enke, Erlangen, Germany, p 404
Inamasu J, Saito R, Nakamura Y, Ichikizaki K, Suga S, Kawase T, Hori S, Aikawa N (2002) Acute subdural hematoma caused by ruptured cerebral aneurysms: diagnostic and therapeutic pitfalls. Resuscitation 52:71–76
Kondziolka D, Bernstein M, Brugge K, Schutz H (1988) Acute subdural hematoma from ruptured posterior communicating artery aneurysm. Neurosurgery 22:151–153
Meyer F, Sandvo BG (1977) Acute subdural hematoma associated with nontraumatic aneurysm rupture. Zentralbl Neurochir 58:66–70
Missori P, Fenga C, Maraglino C et al (2000) Spontaneous acute subdural hematomas. A clinical comparison with traumatic acute subdural haematomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:697–701
Nizzoli V, Brambilla P, Tonnarelli GP (1981) Acute subdural hematoma: spontaneous forms of arterial origin. Eur Neurol 20:4–8
Nonaka Y, Kusumoto M, Mori K, Maeda M (2000) Pure acute subdural haematoma without subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by rupture of internal carotid artery aneurysm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:941–944
Nowak G, Schwachenwald S, Kehler U, Muller H, Arnold H (1995) Acute subdural haematoma from ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 136:163–167
O’Sullivan MG, Whyman M, Steers JW, Whittle IR, Miller JD (1994) Acute subdural haematoma secondary to ruptured intracranial aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Br J Neurosurg 8:439–445
Ragland RL, Gelber ND, Wilkinson HA, Knorr JR, Tran AA (1993) Anterior communicating artery aneurysm rupture: an unusual cause of acute subdural hemorrhage. Surg Neurol 40:400–402
Reif J, Moringlane JR (1986) Acute aneurysmal haemorrhage presenting as space occupying subdural haematoma. Zentralbl Neurochir 47:226–243
Rengachary SS, Szymanski DC (1981) Subdural hematomas of arterial origin. Neurosurgery 8:166–172
Ricart C, Pujadas F, Royo M, Llovet J (1986) Acute spontaneous subdural hematoma of arterial origin. Neurología 1:227
Scott M (1949) Spontaneous nontraumatic subdural hematoma. J Am Med Assoc 141:596–602
Stephenson G, Gibson M (1989) Acute spontaneous subdural hematoma of arterial origin. Br J Neurosurg 3:225–228
Strang RR, Tovi D, Hugosson R (1961) Subdural haematomas resulting from the rupture of intracranial arterial aneurysms. Acta Chir Scand 121:345–350
Weir B, Myles T, Kahn M, Maroun F, Malloy D, Benoit B, McDermott M, Cochrane D, Mohr G, Ferguson D, Durity F (1984) Management of acute subdural hematomas from aneurysmal rupture. Can J Neurol Sci 11:371–376
Wright JR, Slavin RE, Wagner JA (1965) Intracranial aneurysm as a cause of subdural hematoma of the posterior fossa. J Neurosurg 22:86–89
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Mr Romen Das Gupta for his assistance in the preparation of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelabert-Gonzalez, M., Iglesias-Pais, M. & Fernández-Villa, J. Acute subdural haematoma due to ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev 27, 259–262 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-004-0333-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-004-0333-x