Abstract
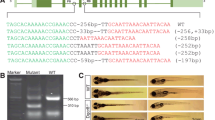
Zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) can generate targeted gene disruption (GD) directly in developing embryos of zebrafish, mouse and human. In the fish medaka, ZFNs have been attempted on a transgene. Here, we developed procedures and parameters for ZFN-mediated direct GD on the gonad-specifically expressed gsdf locus in medaka. A pair of ZFNs was designed to target the first exon of gsdf and their synthetic mRNAs were microinjected into 1-cell stage embryos. We reveal dose-dependent survival rate and GD efficiency. In fry, ZFN mRNA injection at 10 ng/μl led to a GD efficiency of 30 %. This value increased up to nearly 100 % when the dose was enhanced to 40 ng/μl. In a typical series of experiments of ZFN mRNA injection at 10 ng/μl, 420 injected embryos developed into 94 adults, 4 of which had altered gsdf alleles. This leads to a GD efficacy of ∼4 % in the adulthood. Sequencing revealed a wide variety of subtle allelic alterations including additions and deletions of 1∼18 bp in length in ZFN-injected samples. Most importantly, one of the 4 adults examined was capable of germline transmission to 15.2 % of its F1 progeny. Interestingly, ontogenic analyses of the allelic profile revealed that GD commenced early in development, continued during subsequent stages of development and in primordia for different adult organs of the three germ layers. These results demonstrate the feasibility and—for the first time to our knowledge—the efficacy of ZFN-mediated direct GD on a chromosomal gene in medaka embryos.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GD:
-
Gene disruption
- gsdf:
-
Gonadal soma derived factor
- Hm:
-
Homoduplex
- Ht:
-
Heteroduplex
- WT:
-
Wild-type
- ZFN:
-
Zinc finger nuclease
References
Ansai S, Ochiai H, Kanie Y, Kamei Y, Gou Y, Kitano T, Yamamoto T, Kinoshita M (2012) Targeted disruption of exogenous EGFP gene in medaka using zinc-finger nucleases. Develop Growth Differ 54:546–556
Ansai S, Sakuma T, Yamamoto T, Ariga H, Uemura N, Takahashi R, Kinoshita M (2013) Efficient targeted mutagenesis in medaka using custom-designed transcription activator-like effector nucleases. Genetics 193:739–749
Baker M (2012) Gene-editing nucleases. Nat Meth 9:23–26
Capecchi MR (2005) Gene targeting in mice: functional analysis of the mammalian genome for the twenty-first century. Nat Rev Genet 6:507–512
Carroll D (2011) Genome engineering with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 188:773–782
Chen J, Zhang X, Wang T, Li Z, Guan G, Hong Y (2012) Efficient detection, quantification and enrichment of subtle allelic alterations. DNA Res 19:423–433
Collins FS, Rossant J, Wurst W (2007) A mouse for all reasons. Cell 128:9–13
Cui X, Ji D, Fisher DA, Wu Y, Briner DM, Weinstein EJ (2011) Targeted integration in rat and mouse embryos with zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 29:64–67
Doyon Y, Mccammon JM, Miller JC, Faraji F, Ngo C, Katibah GE, Amora R, Hocking TD, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Amacher SL (2008) Heritable targeted gene disruption in zebrafish using designed zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotech 26:702–708
Gautier A, Le Gac F, Lareyre JJ (2011) The gsdf gene locus harbors evolutionary conserved and clustered genes preferentially expressed in fish previtellogenic oocytes. Gene 472:7–17
Hong Y, Winkler C, Schartl M (1996) Pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cell lines from the medakafish (Oryzias latipes). Mech Dev 60:33–44
Hong Y, Winkler C, Schartl M (1998) Production of medakafish chimeras from a stable embryonic stem cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3679–3684
Hong Y, Liu T, Zhao H, Xu H, Wang W, Liu R, Chen T, Deng J, Gui J (2004) Establishment of a normal medakafish spermatogonial cell line capable of sperm production in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:8011–8016
Hong N, Li M, Zeng Z, Yi M, Deng J, Gui J, Winkler C, Schartl M, Hong Y (2010) Accessibility of host cell lineages to medaka stem cells depends on genetic background and irradiation of recipient embryos. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:1189–1202
Iwamatsu T (2004) Stages of normal development in the medaka Oryzias latipes. Mech Dev 121:605–618
Katogi R, Nakatani Y, Shin-I T, Kohara Y, Inohaya K, Kudo A (2004) Large-scale analysis of the genes involved in fin regeneration and blastema formation in the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Mech Dev 121:861–872
Li M, Hong N, Xu H, Yi M, Li C, Gui J, Hong Y (2009) Medaka vasa is required for migration but not survival of primordial germ cells. Mech Dev 126:366–381
Liu T, Liu L, Wei Q, Hong Y (2011) Sperm nuclear transfer and transgenic production in the fish medaka. Int J Biol Sci 7:469–475
Meng X, Noyes MB, Zhu LJ, Lawson ND, Wolfe SA (2008) Targeted gene inactivation in zebrafish using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 26:695–701
Myosho T, Otake H, Masuyama H, Matsuda M, Kuroki Y, Fujiyama A, Naruse K, Hamaguchi S, Sakaizumi M (2012) Tracing the emergence of a novel sex-determining gene in medaka, Oryzias luzonensis. Genetics 191:163–170
Nasevicius A, Ekker SC (2000) Effective targeted gene ‘knockdown’ in zebrafish. Nat Genet 26:216–220
Sawatari E, Shikina S, Takeuchi T, Yoshizaki G (2007) A novel transforming growth factor-beta superfamily member expressed in gonadal somatic cells enhances primordial germ cell and spermatogonial proliferation in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Dev Biol 301:266–275
Shibata Y, Paul-Prasanth B, Suzuki A, Usami T, Nakamoto M, Matsuda M, Nagahama Y (2010) Expression of gonadal soma derived factor (GSDF) is spatially and temporally correlated with early testicular differentiation in medaka. Gene Expr Patterns 10:283–289
Tong C, Li P, Wu NL, Yan Y, Ying Q-L (2010) Production of p53 gene knockout rats by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature 467:211–213
Urnov FD, Rebar EJ, Holmes MC, Zhang HS, Gregory PD (2010) Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nat Rev Genet 11:636–646
Wang R-H, Sengupta K, Li C, Kim H-S, Cao L, Xiao C, Kim S, Xu X, Zheng Y, Chilton B, Jia R, Zheng Z-M, Appella E, Wang XW, Ried T, Deng C-X (2008) Impaired DNA damage response, genome instability, and tumorigenesis in SIRT1 mutant mice. Cancer Cell 14:312–323
Watanabe T, Asaka S, Kitagawa D, Saito K, Kurashige R, Sasado T, Morinaga C, Suwa H, Niwa K, Henrich T, Hirose Y, Yasuoka A, Yoda H, Deguchi T, Iwanami N, Kunimatsu S, Osakada M, Loosli F, Quiring R, Carl M, Grabher C, Winkler S, Del Bene F, Wittbrodt J, Abe K, Takahama Y, Takahashi K, Katada T, Nishina H, Kondoh H, Furutani-Seiki M (2004) Mutations affecting liver development and function in Medaka, Oryzias latipes, screened by multiple criteria. Mech Dev 121:791–802
Xu X, Wagner KU, Larson D, Weaver Z, Li C, Ried T, Hennighausen L, Wynshaw-Boris A, Deng CX (1999) Conditional mutation of Brca1 in mammary epithelial cells results in blunted ductal morphogenesis and tumour formation. Nat Genet 22:37–43
Yan Y, Hong N, Chen T, Li M, Wang T, Guan G, Qiao Y, Chen S, Schartl M, Li CM, Hong Y (2013) p53 gene targeting by homologous recombination in fish ES cells. PLoS One 8:e59400
Yano A, Guyomard R, Nicol B, Jouanno E, Quillet E, Klopp C, Cabau C, Bouchez O, Fostier A, Guiguen Y (2012) An immune-related gene evolved into the master sex-determining gene in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Curr Biol 22:1423–1428
Yi M, Hong N, Hong Y (2009) Generation of medaka fish haploid embryonic stem cells. Science 326:430–433
Zhao H, Hong N, Lu W, Zeng H, Song J, Hong Y (2011) Fusion gene vectors allowing for simultaneous drug selection, cell labeling, and reporter assay in vitro and in vivo. Anal Chem 84:987–993
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Deng for fish breeding. This work was supported by the National Research Foundation Singapore (NRF-CRP7-2010-03) and the Japan Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST). We acknowledge the NUS for scholarship to X. Zhang and J. B. Chen.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
Additional information noted in text includes supplementary figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xi Zhang and Guijun Guan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Guan, G., Chen, J. et al. Parameters and Efficiency of Direct Gene Disruption by Zinc Finger Nucleases in Medaka Embryos. Mar Biotechnol 16, 125–134 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-013-9556-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-013-9556-6