Abstract
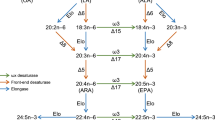
The marine copepod Calanus finmarchicus constitutes the substantial amount of biomass in the Arctic and Northern seas. It is unique in that this small crustacean accumulates a high level of wax esters as carbon storage which is mainly comprised of 20:1n−9 and 22:1n−11 alcohols (Alc) linked with various kinds of fatty acids, including n−3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. The absence of 20:1n−9 Alc and 22:1n−11 Alc in diatoms and dinoflagellates, the primary food sources of copepods, suggests the existence of de novo biosynthesis of fatty alcohols in C. finmarchinus. Here, we report identification of three genes, CfFAR1, CfFAR2, and CfFAR3, coding for fatty acyl-CoA reductases involved in the conversion of various fatty acyl-CoAs to their corresponding alcohols. Functional characterization of these genes in yeast indicated that CfFAR1 could use a wide range of saturated fatty acids from C18 to C26 as substrates, CfFAR2 had a narrow range of substrates with only very-long-chain saturated fatty acid 24:0 and 26:0, while CfFAR3 was active towards both saturated (16:0 and 18:0) and unsaturated (18:1 and 20:1) fatty acids producing corresponding alcohols. This finding suggested that these three fatty acyl-CoA reductases are likely responsible for de novo synthesis of a series of fatty alcohol moieties of wax esters in C. finmarchicus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts MG, Hodge R, Kalantidis K, Florack D, Wilson ZA, Mulligan BJ, Stiekema WJ, Scott R, Pereira A (1997) The Arabidopsis MALE STERILITY 2 protein shares similarity with reductases in elongation/condensation complexes. Plant J 12:615–623
Alaux C, Maisonnasse A, Le Conte Y, Gerald L (2010) Pheromones in a superorganism: from gene to social regulation. Vitam Horm 83:401–423
Antony B, Fujii T, Moto K, Matsumoto S, Fukuzawa M, Nakano R, Tatsuki S, Ishikawa Y (2009) Pheromone-gland-specific fatty-acyl reductase in the adzuki bean borer, Ostrinia scapulalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:90–95
Brown RGB, Gaskin DE (1988) The pelagic ecology of the grey and red-necked phalaropes Phalaropus fulicarius and P. lobatus in the Bay of Fundy, eastern Canada. Ibis 130:234–250
Cassier P, Lensky Y (1995) Ultrastructure of the wax gland complex and secretion of beeswax in the worker honey bee Apis mellifera L. Apidologie 26:17–26
Cheng JB, Russell DW (2004) Mammalian wax biosynthesis. I. Identification of two fatty acyl-coenzyme A reductases with different substrate specificities and tissue distributions. J Biol Chem 279:37789–37797
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG, Thompson JD (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3497–3500
Claros MG, von Heijne G (1994) TopPred II: an improved software for membrane protein structure predictions. Comput Appl Biosci 10:685–686
Doan TT, Carlsson AS, Hamberg M, Bulow L, Stymne S, Olsson P (2009) Functional expression of five Arabidopsis fatty acyl-CoA reductase genes in Escherichia coli. J Plant Physiol 166:787–796
Engelman DM, Steitz TA, Goldman A (1986) Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem 15:321–353
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package (version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Fixter LM, Nagi MN, McCormack JG, Fewson CA (1986) Structure, distribution and function of wax esters in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Gen Microbiol 132:3147–3157
Gatten RR, Sargent JR (1973) Wax ester biosynthesis in calanoid copepods in relation to vertical migration. Neth J Sea Res 7:150–158
Hargrove JL, Greenspan P, Hartle DK (2004) Nutritional significance and metabolism of very long chain fatty alcohols and acids from dietary waxes. Exp Biol Med 229:215–226
Hayashi K, Takagi T, Kitagawa M (1983) Compositions of ether-linked lipids in livers of two species of ratfish. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 49:777–782
Honsho M, Asaoku S, Fujiki Y (2010) Posttranslational regulation of fatty Acyl-CoA reductase 1, Far1, controls ether glycerophospholipid synthesis. J Biol Chem 285:8537–8542
Jetter R, Kunst L (2008) Plant surface lipid biosynthetic pathways and their utility for metabolic engineering of waxes and hydrocarbon biofuels. Plant J 54:670–683
Kattner G, Graeve M (1991) Wax ester composition of the dominant calanoid copepods of the Greenland Sea/Fram Strait region. Polar Res 10:479–485
Kattner G, Krause M (1987) Changes in lipids during the development of Calanus finmarchicus s.l. from copepodid I to adult. Mar Biol 96:511–518
Kolattukudy PE (1970) Reduction of fatty acids to alcohols by cell-free preparations of Euglena gracilis. Biochemistry 9:1095–1102
Lienard MA, Hagstrom AK, Lassance JM, Lofstedt C (2010) Evolution of multicomponent pheromone signals in small ermine moths involves a single fatty-acyl reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:10955–10960
Maes L, Van Nieuwerburgh FC, Zhang Y, Reed DW, Pollier J, Vande Casteele SR, Inze D, Covello PS, Deforce DL, Goossens A (2011) Dissection of the phytohormonal regulation of trichome formation and biosynthesis of the antimalarial compound artemisinin in Artemisia annua plants. New Phytol 189:176–189
McLaren IA, Head E, Sameoto DD (2001) Life cycles and seasonal distributions of Calanus finmarchicus on the central Scotian shelf. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:659–670
Metz JG, Pollard MR, Anderson L, Hayes TR, Lassner MW (2000) Purification of a jojoba embryo fatty acyl-coenzyme A reductase and expression of its cDNA in high erucic acid rapeseed. Plant Physiol 122:635–644
Michaud J, Taggart CT (2007) Lipid and gross energy content of North Atlantic right whale food, Calanus finmarchicus, in the Bay of Fundy. Endang Species Res 3:77–94
Morris RJ, Sargent JR (1973) Studies on the lipid metabolism of some oceanic crustaceans. Mar Biol 22:77–83
Moto K, Yoshiga T, Yamamoto M, Takahashi S, Okano K, Ando T, Nakata T, Matsumoto S (2003) Pheromone gland-specific fatty-acyl reductase of the silkmoth, Bombyx mori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9156–9161
Page RD (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Pollard MR, McKeon T, Gupta LM, Stumpf PK (1979) Studies on biosynthesis of waxes by developing jojoba seed. II. the demonstration of wax biosynthesis by cell-free homogenates. Lipids 14:651–662
Raymont JEG, Krishnaswamy S, Woodhouse MA, Griffin RL (1974) Studies on the fine structure of Copepoda observations on Calanus finmarchicus (Gunnerus). Proc Biol Sci 185:409–424
Ringuette M, Fortiera L, Fortiera M, Rungeb JA, Bélangerb S, Laroucheb P, Weslawskic JM, Kwasniewskic S (2002) Advanced recruitment and accelerated population development in Arctic calanoid copepods of the North Water. Deep-Sea Res II 49:5081–5099
Rossmann MG, Moras D, Olsen KW (1974) Chemical and biological evolution of nucleotide-binding protein. Nature 250:194–199
Rowland O, Zheng H, Hepworth SR, Lam P, Jetter R, Kunst L (2006) CER4 encodes an alcohol-forming fatty acyl-coenzyme A reductase involved in cuticular wax production in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 142:866–877
Samuels L, Kunst L, Jetter R (2008) Sealing plant surfaces: cuticular wax formation by epidermal cells. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:683–707
Sargent JR, Falk-Petersen S (1988) The lipid biochemistry of calanoid copepods. Hydrobiologia 167–168:101–114
Sargent JR, Gatten RR, McIntosh R (1974) Biosynthesis of wax esters in cell-free preparations of Euchaeta norvegica. Comp Biochem Physiol B 47:217–227
Snell TW, Morris PD (1993) Sexual communication in copepods and rotifers. Hydrobiologia 255–256:109–116
Soliday CL, Blomquist GJ, Jackson LL (1974) Cuticular lipids of insects. VI. Cuticular lipids of the grasshoppers Melanoplus sanguinipes and Melanoplus packardii. J Lipid Res 15:399–405
Teerawanichpan P, Qiu X (2010) Fatty acyl-CoA reductase and wax synthase from Euglena gracilis in the biosynthesis of medium-chain wax esters. Lipids 45:263–273
Teerawanichpan P, Robertson AJ, Qiu X (2010) A fatty acyl-CoA reductase highly expressed in the head of honey bee (Apis mellifera) involves biosynthesis of a wide range of aliphatic fatty alcohols. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 40:641–649
Tillman JA, Seybold SJ, Jurenka RA, Blomquist GJ (1999) Insect pheromones—an overview of biosynthesis and endocrine regulation. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 29:481–514
Toolson EC, Hadley NF (1977) Cuticular permeability and epicuticular lipid composition in two Arizona vejovid scorpions. Physiol Zool 50:323–330
Tucci S, Vacula R, Krajcovic J, Proksch P, Martin W (2010) Variability of wax ester fermentation in natural and bleached Euglena gracilis strains in response to oxygen and the elongase inhibitor flufenacet. J Eukaryot Microbiol 57:63–69
Vioque J, Kolattukudy PE (1997) Resolution and purification of an aldehyde-generating and an alcohol-generating fatty acyl-CoA reductase from pea leaves (Pisum sativum L.). Arch Biochem Biophys 340:64–72
Visser A, Jónasdóttir S (1999) Lipids, buoyancy and the seasonal vertical migration of Calanus finmarchicus. Fish Oceanogr 8:100–106
Wang A, Xia Q, Xie W, Dumonceaux T, Zou J, Datla R, Selvaraj G (2002) Male gametophyte development in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): molecular, cellular, and biochemical analyses of a sporophytic contribution to pollen wall ontogeny. Plant J 30:613–623
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Erica Head, Marc Ringuette, and Jeff Spry from the Department of Fisheries and Oceans, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Canada for providing the copepod materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teerawanichpan, P., Qiu, X. Molecular and Functional Analysis of Three Fatty Acyl-CoA Reductases with Distinct Substrate Specificities in Copepod Calanus finmarchicus . Mar Biotechnol 14, 227–236 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-011-9406-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-011-9406-3