Abstract
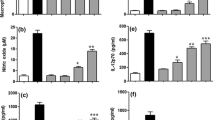
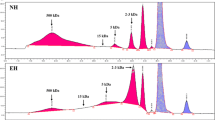
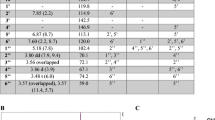
We investigated whether the brown seaweed Alariaceae Ecklonia cava (E. cava) has immunological effects on splenocytes in vitro. For that purpose, we prepared an enzymatic extract from E. cava (ECK) by using the protease, Kojizyme. Here, ECK administered to ICR mice dramatically enhanced the proliferation of their splenocytes and increased the number of their lymphocytes, monocytes and granulocytes. In flow cytometry assays performed to identify in detail the specific phenotypes of these proliferating cells after ECK treatment, the numbers of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and CD45R/B220+ B cells increased significantly compared to those in untreated controls. In addition, the mRNA expression and production level of Th1-type cytokines, i.e., TNF-α and IFN-γ, were down-regulated, whereas those of Th2-type cytokines, i.e., IL-4 and IL-10, were up-regulated by ECK. Overall, this dramatic increase in numbers of splenocytes indicated that ECK could induce these cells to proliferate and could regulate the production of Th1- as well as Th2-type cytokines in immune cells. These results suggest that ECK has the immunomodulatory ability to activate the anti-inflammatory response and/or suppress the proinflammatory response, thereby endorsing its usefulness as therapy for diseases of the immune system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn CB, Jeon YJ, Kang DS, Shin TS, Jung BM (2004a) Free radical scavenging activity of enzymatic extracts from a brown seaweed Scytosiphon lomentaria by electron spin resonance spectrometry. Food Res Intern 37, 253–258
Ahn MJ, Yoon KD, Min SY, Lee JS, Kim JH, Kim TG, Kim SH, Kim NG, Huh H, Kim J (2004b) Inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and protease by phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia cava. Biol Pharm Bull 27, 544–547
Athukorala Y, Jung WK, Vasanthan T, Jeon YJ (2006) An anticoagulative polysaccharide from an enzymatic hydrolysate of Ecklonia cava. Carbohydr Polym 66, 184–191
Choi EM, Kim AJ, Kim YO, Hwang JK (2005) Immunomodulating activity of arabinogalactan and fucoidan in vitro. J Med Food 8, 446–453
Chung F (2001) Anti-inflammatory cytokines in asthma and allergy: interleukin-10, interleukin-12, interferon-gamma. Mediators Inflamm 10, 51–59
Feili-Hariri M, Falkner DH, Morel PA (2005) Polarization of naive T cells into Th1 or Th2 by distinct cytokine-driven murine dendritic cell populations: implications for immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol 78, 656–664
Fukuyama Y, Kodama M, Miura I, Kinzyo Z, Kido M, Nakayama Y, Takahashi H (1989) Structure of an anti-plasmin inhibitor, eckol, isolated from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome Okamura and inhibitory activities of its derivatives on plasma plasmin inhibitors. Chem Pharm Bull 37, 349–353
Garcia D, Leiro J, Delgado R, Sanmartin ML, Ubeira FM (2003) Mangifera indica L. extract (Vimang) and mangiferin modulate mouse humoral immune responses. Phytother Res 17, 1182–1187
Guiry MD, Bulunden G (1991) Seaweed Resource in Europe: Uses and Potential. (Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons)
Heo SJ, Jeon YJ, Lee J, Kim HT, Lee KW (2003) Antioxidant effect of enzymatic hydrolyzate from a kelp, Ecklonia cava. Algae 18, 341–347
Heo SJ, Park EJ, Lee KW, Jeon YJ (2005a) Antioxidant activities of enzymatic extracts from brown seaweeds. Bioresour Technol 96, 1613–1623
Heo SJ, Park EJ, Lee KW, Jeon YJ (2005b) Antioxidative effect of proteolytic hydrolysates from Ecklonia cava on radical scavenging using ESR and H2O2-induced DNA damage. Food Sci 14, 614–620
Kang HS, Chung HY, Kim JY, Son BW, Jung HA, Choi JS (2004a) Inhibitory phlorotannins from the edible brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera on total reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Arch Pharm Res 27, 194–198
Kang HS, Kim HR, Byun DS, Son BW, Nam TJ, Choi JS (2004b) Tyrosinase inhibitors isolated from the edible brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera. Arch Pharm Res 27, 1226–1232
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae SW, Koh YS, Yoo BS, Kim JH, Ham YM, Baik JS, Lee NH, Hyun JW (2005a) Triphlorethol-A from Ecklonia cava protects V79-4 lung fibroblasts against hydrogen peroxide induced cell damage. Free Radic Res 39, 883–892
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae SW, Zhang R, Jung MS, Lee YG, Kim SY, Kim HS, Joo HG, Park JW, Ham YM, Lee NH, Hyun JW (2005b) Eckol isolated from Eclonia cava attenuates oxidative stress induced cell damage in lung fibroblast cells. FEBS Lett 579, 6295–6304
Kim KN, Lee KW, Song CB, Jeon YJ (2006a) Cytotoxic activity of green and brown seaweeds collected from Jeju Island against four tumor cell lines. J Food Sci Nutr 11, 17–24
Kim MM, Ta QV, Mendis E, Rajapakse N, Jung WK, Gyun HG, Jeon YJ, Kim SK (2006b) Phlorotannins in Ecklonia cava extract inhibit matrix metalloproteinase activity. Life Sci 79, 1436–1443
Lee JH, Kim ND, Choi JS, Kim YJ, Moon YH, Lim SY, Park KY (1998) Inhibitory effects of the methanolic extract of an edible brown alga, Ecklonia stolonifera and its component, phlorglucinol on aflatoxin B1 mutagenicity in vitro (Ames test) and on benzo(a)pyrene or N-methyl N-nitrosourea clastogenicity in vivo (mouse micronucleus test). Nat Prod Sci 4, 105–114
Liberman AC, Refojo D, Arzt E (2003) Cytokine signaling/transcription factor cross-talk in T cell activation and Th1-Th2 differentiation. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 51, 351–365
Maruyama M, Tamauchi H, Hasimoto M, Nakano T (2003) Antitumor activity and immune response of Mekabu fucoidan extracted from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida. In vivo (Athens, Greece) 17, 245–249
Meeran SM, Mantena SK, Katiyar SK (2006) Prevention of ultraviolet radiation-induced immunosuppression by (–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in mice is mediated through interleukin 12-dependent DNA repair. Clin Cancer Res 1, 2272–2280
Mosmann TR, Sad S (1996) The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol Today 17, 142–146
Nagayama K, Iwamura Y, Shibata T, Hirayama I, Nakamura T (2002) Bactericidal activity of phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome. J Antimicrob Chemother 50, 889–893
O’Garra A, Arai N (2000) The molecular basis of T helper 1 and T helper 2 cell differentiation. Trends Cell Biol 10, 542–550
Park PJ, Heo SJ, Park EJ, Kim SK, Byun HG, Heon BT, Jeon YJ (2005) Reactive oxygen scavenging effect of enzymatic extracts from Sargassum thunbergii. J Agric Food Chem 53, 6666–6672
Patwardhan B, Gautam M (2005) Botanical immunodrugs: scope and opportunities. Drug Discov Today 10, 495–502
Rao A, Avni O (2000) Molecular aspects of T-cell differentiation. Br Med Bull 56, 969–984
Ruperez P, Saura-Calixto F (2001) Dietary fibers and physiochemical properties of edible seaweeds. Eur Food Res Technol 212, 349–354
Saito H, Yamagata T, Suzuki S (1968) Enzymatic methods for the determination of small quantities of isomeric chondroitin sulfates. J Biol Chem 243, 1536–1542
Saker KE, Fike JH, Veit H, Ward DL (2004) Brown seaweed-(Tasco) treated conserved forage enhances antioxidant status and immune function in heat-stressed wether lambs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 88, 122–130
Schepetkin IA, Faulkner CL, Nelson-Overton LK, Wiley JA, Quinn MT (2005) Macrophage immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides isolated from Juniperus scopolorum. Int Immunopharmacol 5, 1783–1799
Schifitto G, McDermott MP, Evans T, Fitzgerald T, Schwimmer J, Demeter L, Kieburtz K (2000) Autonomic performance and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate levels in HIV-1-infected individuals: relationship to TH1 and TH2 cytokine profile. Arch Neurol 57, 1027–1032
Siriwardhana N, Jeon YJ, Kim SH, Ha JH, Heo SJ, Lee KW (2004) Enzymatic hydrolysis for effective extraction of antioxidative compounds from Hizikia fusiformis. Algae 19, 59–68
Skapenko A, Niedobitek GU, Kalden JR, Lipsky PE, Schulze-Koops H (2004) IL-4 exerts a much more profound suppression of Th1 immunity in humans than in mice. J Immunol 172, 6427–6434
Waterman PG, Mole S (1994) Analysis of Phenolic Plant Metabolites. (Oxford: Blackwell)
Yeh ST, Lee CS, Chen JC (2006) Administration of hot-water extract of brown seaweed Sargassum duplicatum via immersion and injection enhances the immune resistance of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol 20, 332–345
Acknowledgment
This research was performed under a program of the Basic Atomic Energy Research Institute (BAERI), which is a part of the Nuclear R&D Programs funded by the Ministry of Science & Technology (MOST) of Korea. The authors thank P. Minick for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y-J. Jeon and Y. Jee contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, G., Hwang, I., Park, E. et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of an Enzymatic Extract from Ecklonia cava on Murine Splenocytes. Mar Biotechnol 10, 278–289 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-9062-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-9062-9