Abstract
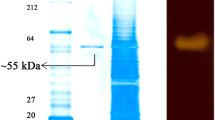
An actinomycete strain 7326 producing cold-adapted α-amylase was isolated from the deep sea sediment of Prydz Bay, Antarctic. It was identified as Nocardiopsis based on morphology, 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, and physiological and biochemical characteristics. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and zymogram activity staining of purified amylase showed a single band equal to a molecular mass of about 55 kDa. The optimal activity temperature of Nocardiopsis sp. 7326 amylase was 35°C, and the activity decreased dramatically at temperatures above 45°C. The enzyme was stable between pH 5 and 10, and exhibited a maximal activity at pH 8.0. Ca2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, and Co2+ stimulated the activity of the enzyme significantly, and Rb2+, Hg2+, and EDTA inhibited the activity. The hydrolysates of soluble starch by the enzyme were mainly glucose, maltose, and maltotriose. This is the first report on the isolation and characterization of cold-adapted amylase from Nocardiopsis sp.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Zarban SS, Abbas I, Al-Musallam AA, Steiner U, Stackebrandt E, Kroppenstedt RM (2002) Nocardiopsis halotolerans sp. nov., isolated from salt marsh soil in Kuwait. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52, 525–529
Ballschmiter M, Futterer O, Liebl W (2006) Identification and characterization of a novel intracellular alkaline alpha-amylase from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima MSB8. Appl Environ Microbiol 72, 2206–2211
Cavicchioli R, Siddiqui KS, Andrews D, Sowers KR (2002) Low-temperature extremophiles and their applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13, 253–261
Chessa JP, Feller G, Gerday C (1999) Purification and characterization of the heat-labile alpha-amylase secreted by the psychrophilic bacterium TAC 240B. Can J Microbiol 45, 452–457
Chun J, Bae KS, Moon EY, Jung SO, Lee HK, Kim SJ (2000) Nocardiopsis kunsanensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic actinomycete isolated from a saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50(Pt 5), 1909–1913
Cordeiro CAM, Martins MLL, Luciano AB (2002) Production and properties of α-amylase from thermophilic Bacillus sp. Braz J Microbiol 33, 57–61
D’Amico S, Gerday C, Feller G (2003) Temperature adaptation of proteins, engineering mesophilic-like activity and stability in a cold-adapted alpha-amylase. J Mol Biol 332, 981–988
D’Amico S, Sohier JS, Feller G (2006) Kinetics and energetics of ligand binding determined by microcalorimetry: insights into active site mobility in a psychrophilic alpha-amylase. J Mol Biol 358, 1296–1304
Declerck N, Machius M, Joyet P, Wiegand G, Huber R, Gaillardin C (2003) Hyperthermostabilization of Bacillus licheniformis alpha-amylase and modulation of its stability over a 50 degrees C temperature range. Protein Eng 16, 287–293
DeLong EF (1992) Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89, 5685–5689
Deming JW (1998) Deep ocean environmental biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 9, 283–287
Elif S, Velittin G (2000) Increase of the α-amylase yield by some Bacillus strains. Turk J Biol 24, 299–308
Evtushenko LI, Taran VV, Akimov VN, Kroppenstedt RM, Tiedje JM, Stackebrandt E (2000) Nocardiopsis tropica sp. nov., Nocardiopsis trehalosi sp. nov., nom. rev. and Nocardiopsis dassonvillei subsp. albirubida subsp. nov., comb. Nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50(Pt 1), 73–81
Feller G (2003) Molecular adaptations to cold in psychrophilic enzymes. Cell Mol Life Sci 60, 648–662
Feller G, Gerday C (2003) Psychrophilic enzymes, hot topics in cold adaptation. Nat Rev Microbiol 1, 200–208
Feller G, D’Amico D, Gerday C (1999) Thermodynamic stability of a cold-active alpha-amylase from the Antarctic bacterium Alteromonas haloplanctis. Biochemistry 38, 4613–4619
Gerday C, Aittaleb M, Bentahir M, Chessa JP, Claverie P, Collins T, D’Amico S, Dumont J, Garsoux G, Georlette D, Hoyoux A, Lonhienne T, Meuwis MA, Feller G (2000) Cold-adapted enzymes, from fundamentals to biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 18, 103–107
Groudieva T, Kambourova M, Yusef H, Royter M, Grote R, Trinks H, Antranikian G (2004) Diversity and cold-active hydrolytic enzymes of culturable bacteria associated with Arctic sea ice, Spitzbergen. Extremophiles 8, 475–488
Hagihara H, Igarashi K, Hayashi Y, Endo K, Ikawa-Kitayama K, Ozaki K, Kawai S, Ito S (2001) Novel alpha-amylase that is highly resistant to chelating reagents and chemical oxidants from the alkaliphilic Bacillus isolate KSM-K38. Appl Environ Microbiol 67, 1744–1750
Igarashi K, Hatada Y, Hagihara H, Saeki K, Takaiwa M, Uemura T, Ara K, Ozaki K, Kawai S, Kobayashi T, Ito S (1998) Enzymatic properties of a novel liquefying alpha-amylase from an alkaliphilic Bacillus isolate and entire nucleotide and amino acid sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 64, 3282–3289
Kroppenstedt RM, Evtushenko LI (2002) The Family Nocardiopsaceae. In Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E (eds), The Prokaryotes. An Evolving Electronic Resource for the Microbiological Community. http://141.150.157.117,8080/prokPUB/index.htm
Lealem F, Gashe BA (1994) Amylase production by a Gram-positive bacterium isolated from fermenting tef (Eraglostis tef). J Appl Bacteriol 77, 348–352
Lee SP, Morikawa M, Takagi M, Imanaka T (1994) Cloning of the aapT gene and characterization of its product, alpha-amylase-pullulanase (AapT), from thermophilic and alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. strain XAL601. Appl Environ Microbiol 60, 3764–3773
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193, 265–275
Pridham TG, Anderson P, Foley C, Lindenfelser LA, Hesseltine CW, Benedict RG (1956) A selection of media for maintenance and taxonomic study of Streptomyces. Antibiot Annu 1, 947–953
Rainey FA, Ward-Rainey N, Kroppenstedt RM, Stackebrandt E (1996) The genus Nocardiopsis represents a phylogenetically coherent taxon and a distinct actinomycete lineage, proposal of Nocardiopsaceae fam. Nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46, 1088–1092
Russell NJ (1998) Molecular adaptations in psychrophilic bacteria, potential for biotechnological applications. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 61, 1–21
Schipper A, Bosecker K, Willscher S, Sproer C, Schumann P, Kroppenstedt RM (2002) Nocardiopsis metallicus sp. nov., a metal-leaching actinomycete isolated from an alkaline slag dump. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52, 2291–2295
Sengupta S, Jana ML, Sengupta D, Naskar AK (2000) A note on the estimation of microbial glycosidase activities by dinitrosalicylic acid reagent. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53, 732–735
Shen G, Saha B, Lee Y, Bhatnagar L, Zeikus J (1998) Purification and properties of an extracellular α-amylase from Thermus sp. Bot Bull Acad Sci 36, 195–200
Siddiqui KS, Poljak A, Guilhaus M, De Francisci D, Curmi PM, Feller G, D’Amico S, Gerday C, Uversky VN, Cavicchioli R (2006) Role of lysine versus arginine in enzyme cold-adaptation: modifying lysine to homo-arginine stabilizes the cold-adapted alpha-amylase from Pseudoalteramonas haloplanktis. Proteins 64, 486–501
Stamford TL, Stamford NP, Coelho LC, Araujo JM (2001) Production and characterization of a thermostable alpha-amylase from Nocardiopsis sp. endophyte of yam bean. Bioresour Technol 76, 137–141
Takami H, Inoue A, Fuji F, Horikoshi K (1997) Microbial flora in the deepest sea mud of the Mariana Trench. FEMS Microbiol Lett 152, 279–285
Yang SJ, Lee HS, Park CS, Kim YR, Moon TW, Park KH (2004) Enzymatic analysis of an amylolytic enzyme from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus reveals its novel catalytic properties as both an alpha-amylase and a cyclodextrin-hydrolyzing enzyme. Appl Environ Microbiol 70, 5988–5995
Zeng R, Zhang R, Zhao J, Lin N (2003) Cold-active serine alkaline protease from the psychrophilic bacterium Pseudomonas strain DY-A: enzyme purification and characterization. Extremophiles, 7, 335–337
Zeng R, Xiong P, Wen J (2006) Characterization and gene cloning of a cold-active cellulase from a deep sea psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. DY3. Extremophiles 10, 79–82
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Funds of China (No. 40406029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, JW., Zeng, RY. Purification and Characterization of a Cold-Adapted α-Amylase Produced by Nocardiopsis sp. 7326 Isolated from Prydz Bay, Antarctic. Mar Biotechnol 10, 75–82 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-9035-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-9035-z