Abstract
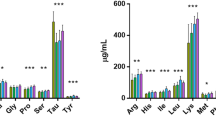
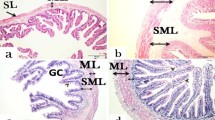
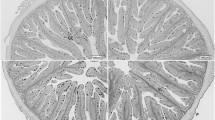
The replacement of fish oil with a dried product made from thraustochytrid culture, a marine microorganism, in canola-oil-based diets for Atlantic salmon was investigated. Salmon (37 g) were fed for 51 days on diets containing only canola oil, canola oil and fish oil, or canola oil and the thraustochytrid. There were no significant differences in final weight (106.1 ± 1.1 g), weight gain (69.6 ± 1.1 g), feed consumption (16.5 ± 0.2 mg dry matter g-1 d-1), feed efficiency ratio (1.15 ± 0.03 g g-1), or productive protein value (51.2% ± 1.7%) between the diets. Nor were there any significant differences in whole-body chemical composition, organ somatic indices, or measures of immune function. However, following transfer to seawater and 2 challenges with Vibrio anguillarum, cumulative mortality was significantly lower in fish fed some fish oil than in those fed the 2 diets containing no fish oil. In conclusion, the thraustochytrid had no detrimental effects on the performance of salmon but, at the current inclusion of 10%, failed to confer the same effect as fish oil under challenging conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, C., Bransden, M., Lewis, T. et al. Potential of Thraustochytrids to Partially Replace Fish Oil in Atlantic Salmon Feeds. Mar. Biotechnol. 5, 480–492 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-002-0096-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-002-0096-8