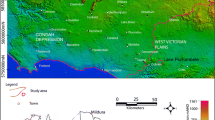
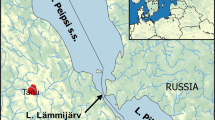
Abstract
Shallow lakes in the semi-arid climate zone of the Mediterranean are sensitive to drought due to the low annual precipitation and high evaporation. Changes in precipitation and temperature as projected by climate change scenarios will have an effect on the hydrology of these shallow lakes with secondary effects on nutrient dynamics and ecological state. In this study, we used a combined modelling approach that included the catchment model Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) and the lake model PCLake to study the possible effects of several climate scenarios on a shallow lake in semi-arid central Anatolia, Turkey. Our results show that lower precipitation and higher temperatures may reduce inflow rates and water levels drastically. Diffuse nutrient loading depended highly on precipitation and thus decreased as well. The lake model predicts an interaction between external nutrient loading and water levels. Low water levels benefited submerged macrophytes if nutrient concentrations were low, but low inflow rates and high evaporation during dry periods increased in-lake nutrient concentrations and chlorophyll-a. Cyanobacteria biomass was also higher in the drier and warmer scenarios. Overall, the results show that lower hydraulic loads and reduced flushing rates as a result of drier and warmer conditions lead to lower water levels and higher in-lake nutrient concentrations unless nutrient loading decreased as well. This implies that catchment-scale nutrient management is essential to maintain low nutrient concentrations in the lakes with increasing temperature and decreasing precipitation in a dry climate.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour KC (2012) Calibration and uncertainty programs – a user manual. Switzerland
Abbaspour KC, Yang J, Maximov I, Siber R, Bogner K, Mieleitner J, Zobrist J, Srinivasan R (2007) Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J Hydrol 333:413–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.09.014
Arnold JG, Srinivasan R, Muttiah RS, Williams JR (1998) Large area hydrologic modelling and assessment part I: model development. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 34:73–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05961.x
Beklioğlu M, Altinayar G, Tan CO (2006) Water level control over submerged macrophyte development in five shallow lakes of Mediterranean Turkey. Arch Hydrobiol 166:535–556. https://doi.org/10.1127/0003-9136/2006/0166-0535
Beklioğlu M, Cakiroğlu AI, Tavşanoğlu ÜN, Erdoğan Ş, Bucak T, Özkan K, Filiz N, Özen A, Levi EE, Bezirci G (2017) Restoration of eutrophic lakes with fluctuating water levels: a 20-year monitoring study of two inter-connected lakes. Water 9:127. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020127
Blenckner T, Adrian R, Livingston DM, Jennings E, Weyhenmeyer GA, George DG, Jankowski T, Järvinen M, Nic Aonghusa C, Noges T, Straile D, Teubner K (2007) Large-scale climatic signatures in lakes across Europe: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 13:1314–1326. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01364.x
Brucet S, Boix C, Nathansen LW, Quintana XD, Jensen E, Balayla D, Meerhoff M, Jeppesen E (2012) Effects of temperature, salinity and fish in structuring the macroinvertebrate community in shallow lakes: implications for effects of climate change. PLoS One 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030877
Bucak T, Saraoğlu E, ELevi EE, Tavşanoğlu ÜN, Çakıroğlu AI, Jeppesen E, Beklioğlu M (2012) The influence of water level on macrophyte growth and trophic interactions in eutrophic Mediterranean shallow lakes: a mesocosm experiment with and without fish. Freshw Biol 57:1631–1642. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2012.02825.x
Bucak T, Trolle D, Andersen HE, Thodsen H, Erdoğan Ş, Levi EE, Filiz N, Jeppesen E, Beklioğlu M (2017) Future water availability in the largest freshwater Mediterranean lake is at great risk as evidenced from simulations with the SWAT model. Sci Total Environ 581:413–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.149
Bucak T, Trolle D, Tavşanoğlu ÜN, Çakıroğlu AI, Özen A, Jeppesen E, Beklioğlu M (2018) Modeling the effects of climatic and land use changes on phytoplankton and water quality of the largest Turkish freshwater lake: Lake Beyşehir. Sci Total Environ 621:802–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.258
Chen W, Nielsen A, Kuhlmann T, Hu F, Chou Q, Søndergaard M, Jeppesen E, Trolle D (2020) Modelling the ecological response of a temporarily summer-stratified lake to extreme heatwaves. Water 12:94. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010094
Coops H, Beklioğlu M, Crisman TL (2003) The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems – workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 506–509:23–27. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008595.14393.77
Coppens J, Özen A, Tavşanoğlu ÜN, Erdoğan Ş, Levi EE, Yozgatligil C, Jeppesen E, Beklioğlu M (2016) Impact of alternating wet and dry periods on long-term seasonal phosphorus and nitrogen budgets of two shallow Mediterranean lakes. Sci Total Environ 563:456–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.028
Erol A, Randhir TO (2012) Climatic change impacts on the ecohydrology of Mediterranean watersheds. Clim Chang 114:319–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-012-0406-8
Giorgi F, Lionello P (2008) Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Glob Planet Chang 63:90–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.09.005
Gyllström M, Hansson LA, Jeppesen E, Garcia Criado F, Gross E, Irvine K, Kairesalo T, Kornijow R, Miracle MR, Nykänen M, Noges T, Romo S, Stephen D, Van Donk E, Moss B (2005) The role of climate in shaping zooplankton communities of shallow lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 50:2008–2021. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2005.50.6.2008
Havens KE, Sharfstein B, Brady MA, East TL, Harwel MC, Maki RP, Rodusky AJ (2004) Recovery of submerged plants from high water stress in a large subtropical lake in Florida, USA. Aquat Bot 78:67–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2003.09.005
Hu F, Bolding K, Bruggeman J, Jeppesen E, Flindt MR, van Gerven L, Janse JH, Janssen ABG, Kuiper JJ, Mooij WM, Trolle D (2016) FABM-PCLake - linking aquatic ecology with hydrodynamics. Geosci Model Dev Discuss 9:2271–2278. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-9-2271-2016
Janse JH, Van Liere L (1995) PCLake: a modelling tool for the evaluation of lake restoration scenarios. Water Sci Technol 31:371–374. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1995.0332
Janssen ABG, Teurlincx S, Beusen AHW, Huijbregts MAJ, Rost J, Schipper AM, Seelen LMS, Mooij WM, Janse JH (2019) PCLake+: a process-based ecological model to assess the trophic state of stratified and non-stratified freshwater lakes worldwide. Ecol Model 396:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2019.01.006
Jeppesen E, Kronvang B, Meerhoff M, Søndergaard M, Hansen KM, Andersen HE, Lauridsen TL, Liboriussen L, Beklioğlu M, Özen A, Olesen JE (2009) Climate change effects on runoff, catchment phosphorus loading and lake ecological state, and potential adaptations. J Environ Qual 38:1930–1941. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2008.0113
Jeppesen E, Kronvang B, Olesen JE, Audet J, Søndergaard M, Hoffmann CC, Andersen HE, Lauridsen TL, Liboriussen L, Larsen SE, Beklioğlu M, Meerhoff M, Özen A, Özkan K (2011) Climate change effects on nitrogen loading from cultivated catchments in Europe: implications for nitrogen retention, ecological state of lakes and adaptation. Hydrobiologia 663:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0547-6
Jeppesen E, Brucet S, Naselli-Flores L, Papastergiadou E, Stefanidis K, Noges T, Noges P, Attayde JL, Zohary T, Coppens J, Bucak T, Menezes RF, Freitas FRS, Kernan M, Søndergaard M, Beklioğlu M (2015) Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 750:201–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2169-x
Meerhoff M, Clementes JM, Teixeira de Mello F, Iglesias C, Pedersen AR, Jeppesen E (2007a) Can warm climate-related structure of littoral predator assemblies weaken the clear water state in shallow lakes. Glob Chang Biol 13:1888–1897. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01408.x
Meerhoff M, Iglesias C, Teixeira de Mello F, Clemente JM, Jensen E, Lauridsen TL, Jeppesen E (2007b) Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton intemperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshw Biol 52:1009–1021. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01748.x
Molina-Navarro E, Trolle D, Martinez-Perez S, Sastre-Merlin A, Jeppesen E (2014) Hydrological and water quality impact assessment of a Mediterranean limno-reservoir under climate change and land use management scenarios. J Hydrol 509:354–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.053
Mooij WM, Brederveld RJ, de Klein JJM, DeAngelis DL, Downing AS, Faber M, Gerla DJ, Hipsey MR, ’t Hoen J, Janse JH, Janssen ABG, Jeuken M, Kooi BW, Lischke B, Petzoldt T, Postma L, Schep SA, Scholten H, Teurlincx S, Thiange C, Trolle D, van Dam AA, van Gerven L, van Nes EH, Kuiper JJ (2014) Serving many at once: how a database approach can create unity in dynamical ecosystem modelling. Environ Model Softw 61:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.04.004
Moran R, Harvey I, Moss B, Feuchtmayr H, Hatton K, Heyes T, Atkinson D (2010) Influence of simulated climate change and eutrophication on three-spined stickleback populations: a large scale mesocosm experiment. Freshw Biol 55:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02276.x
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE 50:885–900. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.23153
Moss B (2012) Cogs in the endless machine: lakes, climate change and nutrient cycles: a review. Sci Total Environ 434:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.069
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I - A discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290
Neitsch SL, Arnold JG, Kiniry JR, Wlliams JR (2011) Soil and Water Assessment Tool User’s Manual, Version (2009). Texas Water Resource Institute, Texas
Nielsen A, Trolle D, Bjerring R, Søndergaard M, Olesen JE, Janse JH, Mooij WM, Jeppesen E (2014) Effects of climate and nutrient load on the water quality of shallow lakes assessed through ensemble runs by PCLake. Ecol Appl 24:1926–1944. https://doi.org/10.1890/13-0790.1
Nunes JP, Seixas J, Pacheco NR (2008) Vulnerability of water resources, vegetation productivity and soil erosion to climate change in Mediterranean watersheds. Hydrol Process 22:3115–3134. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6897
Önol B, Unal YS (2014) Assessment of climate change simulations over climate zones of Turkey. Reg Environ Chang 14:1921–1935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-012-0335-0
Özen A, Karapinar B, Küçük I, Jeppesen E, Beklioğlu M (2010) Drought-induced changes in nutrient concentrations and retention in two shallow Mediterranean lakes subjected to different degrees of management. Hydrobiologia 646:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0179-x
Özkan K, Jeppesen E, Johansson LS, Beklioğlu M (2010) The response of periphyton and submerged macrophytes to nitrogen and phosphorus loading in shallow warm lakes: a mesocosm experiment. Freshw Biol 55:463–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02297.x
Paerl HW, Huisman J (2008) Blooms like it hot. Science 320:57–58. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1155398
Panagopoulos Y, Makropoulos C, Mimikou M (2011) Diffuse surface water pollution: driving factors for different geoclimatic regions. Water Resour Manag 25:3635–3660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9874-2
Peel MC, Finlayson BL, McMahon TA (2007) Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 11:1633–1644. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007
Penman HL (1948) Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proc R Soc London Series A Math Physical Sci 193:120–145. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1948.0037
Scheffer M, Hosper SH, Meijer M-L, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol Evol 8:257–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5347(93)90254-M
Schmidt M, Köster O (2016) Excess warming of a Central European lake driven by solar brightening. Water Resour Res 52:8103–8116. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR018651
Shrestha MK, Recknagel F, Frizenschaf J, Meyer W (2017) Future climate and land uses effects on flow and nutrient loads of a Mediterranean catchment in South Australia. Sci Total Environ 590-591:186–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.197
Strecker AL, Cobb TP, Vinebrooke RD (2004) Effects of experimental greenhouse warming on phytoplankton and zooplankton communities in fishless alpine ponds. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1182–1190. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2004.49.4.1182
Tavşanoǧlu ÜN, Çakiroǧlu AI, Erdoǧan Ş, Meerhoff M, Jeppesen E, Beklioğlu M (2012) Sediments, not plants, offer the preferred refuge for Daphnia against fish predation in Mediterranean shallow lakes: an experimental demonstration. Freshw Biol 57:795–802. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2012.02745.x
Wagner C, Adrian R (2009) Cyanobacteria dominance: quantifying the effects of climate change. Limnol Oceanogr 54:2460–2468. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2009.54.6_part_2.2460
Woolway RI, Merchant CJ, Van Den Hoek J, Azorin-Molina C, Nõges P, Laas A, Mackay AB, Jones ID (2019) Northern Hemisphere atmospheric stilling accelerates lake thermal responses to a warming world. Geophys Res Lett 46:11983–11992. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL082752
Yvon-Durocher G, Montoya JM, Trimmer M, Woodward G (2011) Warming alters the size spectrum and shifts the distribution of biomass in freshwater ecosystems. Glob Chang Biol 17:1684–1694. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02321.x
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Anne Mette Poulsen for proofreading the manuscript. We are thankful to all past and current members of the METU Limnology laboratory who have contributed to the sampling of the lakes and analyses of the samples in the past 18 years (www.limnology.bio.metu.edu.tr/en/).
Funding
This study was supported by the MARS project (Managing Aquatic ecosystems and water Resources under multiple Stress) funded under the 7th EU Framework Programme, Theme 6 (Environment including Climate Change), Contract No.: 603378 (http://www.mars-project.eu); by METU-BAP programme and the Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBITAK) ÇAYDAĞ, project no: 110Y125. JC was supported by TÜBİTAK 2215 Scholarship Programme. EJ and MB were also supported by the TÜBİTAK programme 2232 to Outstanding Researchers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Wolfgang Cramer
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 127 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coppens, J., Trolle, D., Jeppesen, E. et al. The impact of climate change on a Mediterranean shallow lake: insights based on catchment and lake modelling. Reg Environ Change 20, 62 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-020-01641-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-020-01641-6